* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Export To Word
Algebraic variety wikipedia , lookup
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Mirror symmetry (string theory) wikipedia , lookup
Cartan connection wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Algebraic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
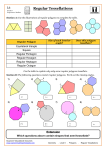
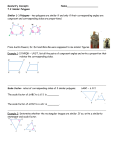
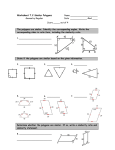
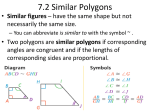
Access Point #: MA.912.G.2.In.c (Archived Access Point) This document was generated on CPALMS - www.cpalms.org Identify triangles and rectangles that are the same shape and size (congruent) and same shape, but not same size (similar) using physical and visual models. Number: MA.912.G.2.In.c Category: Independent Date Adopted or Revised: 09/07 Standard: Polygons : Identify and describe polygons (triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, hexagons, etc.), using terms such as regular, convex, and concave. Find measures of angles, sides, perimeters, and areas of polygons, justifying the methods used. Apply transformations to polygons. Relate geometry to algebra by using coordinate geometry to determine transformations. Use algebraic reasoning to determine congruence, similarity, and symmetry. Create and verify tessellations of the plane using polygons. Related Benchmarks Name MA.912.G.2.3: Description Use properties of congruent and similar polygons to solve mathematical or real-world problems. Remarks/Examples: Example: Suppose a building is in the shape of a regular hexagon. The architect wants to put walkways as indicated. Show that the triangles formed are equal in size and shape. Use coordinate geometry to prove properties of congruent, regular and similar polygons, and to perform transformations in the plane. Remarks/Examples: MA.912.G.2.6: Example: Draw the polygon defined by the following vertices ( 1, 3), ( -1, 3), (3, 1), (-3, 1), (1, -3), (-1, -3), (-3, -1), (3, -1). Is this polygon regular? Justify your answer. Example: Is the polygon formed by connecting the points (2, 1), ( 6, 2), (5, 6), and (1, 5) a square? Justify your answer. Related Resources Image/Photograph Name Clipart: Geometric Shapes: Description In this lesson, you will find clip art and various illustrations of polygons, circles, ellipses, star polygons, and inscribed shapes. Video/Audio/Animation Name Description This video is meant to be a fun, hands-on session that gets students to think hard about how machines work. It teaches them MIT BLOSSOMS - Using Geometry to Design Simple Machines: the connection between the geometry that they study and the kinematics that engineers use -explaining that kinematics is simply geometry in motion. Parent Resources Name Clipart: Geometric Shapes: Description In this lesson, you will find clip art and various illustrations of polygons, circles, ellipses, star polygons, and inscribed shapes.