* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download “DEVLOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF SPECTROSCOPIC AND
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Effects of long-term benzodiazepine use wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of pharmaceuticals and personal care products wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical marketing wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
“DEVLOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF SPECTROSCOPIC
AND CHROMATOGRAPHIC METHODS FOR
SIMULTANEOUS ESTIMATION OF ANTI ANXIETY DRUGS ALPRAZOLAM AND MELATONIN”
SYNOPSIS FOR
M. PHARM DISSERTATION
SUBMITTED TO
RAJIV GANDHI UNIVERSITY OF HEALTH SCIENCES
BENGALURU, KARNATAKA
BY
M. THOMSON
I M. PHARM
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACEUTICAL ANALYSIS
PES COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
BENGALURU-560050
UNDER THE GUIDENCE OF
DR. NAGARAJ
PROF & HEAD
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACEUTICAL ANALYSIS
(2013-14)
RAJIV GANDHI UNIVERSITY OF HEALTH SCIENCES
BENGALURU, KARNATAKA.
ANNEXURE-II
PROFORMA FOR REGISTRATION OF SUBJECTS FOR DISSERTATION
1.
Name of the candidate
M.THOMSON
and address:
Department of Pharmaceutical Analysis,
PES College of Pharmacy,
50 Feet Road, Hanumanthanagar,
BSK I-Stage,
Bengaluru-560050.
Permanent Address
S/O M.Thomas Jaya Kumar,
Flat no.401, Hanuman Residency,
Srinivas Nagar Colony,
Hanamakoda,
Dist: Warangal, Andhra Pradesh.
500037.
2.
Name of the institution:
PES College of Pharmacy
50 Feet Road, Hanumanthanagar,
BSK I- Stage,
Bengaluru -560050
3.
4.
Course of study and
MASTER OF PHARMACY IN
subject:
PHARMACEUTICAL ANALYSIS
Date of the admission:
20/11/2012
5. Title of the topic:
“DEVLOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF SPECTROSCOPIC AND
CHROMATOGRAPHIC METHODS FOR SIMULTANEOUS ESTIMATION
OF ANTI ANXIETY DRUGS - ALPRAZOLAM AND MELATONIN”
2
6. BRIEF RESUME OF THE INTENDED WORK:
6.1 Need for the study:
General Discussion :
The neurocircuitry of anxiety has been postulated to arise from the amygdala, the brain area that
registers the emotional significance of environmental stimuli and stores emotional memories. The
efferent pathways from the central nucleus of the amygdala travel to a multiplicity of critical brain
structures, including the parabrachial nucleus (resulting in dyspnea and hyperventilation), the
dorsomedial nucleus of the vagus nerve and nucleus ambiguous (activating the parasympathetic nervous
system), and the lateral hypothalamus (resulting in SNS activation). Anxiety is a normal reaction to
stress and can actually be beneficial in some situations. For some people, however, anxiety can become
excessive. While the person suffering may realize their anxiety is too much, they may also have
difficulty controlling it and it may negatively affect their day-to-day living. There are many types of
anxiety disorders that include panic disorder, obsessive compulsive disorder, post-traumatic stress
disorder, social anxiety disorder, specific phobias, and generalized anxiety disorder.(1)
Causes of Anxiety Disorders:-(2)
The exact cause of anxiety disorders is unknown; but anxiety disorders -- like other forms of mental
illness are not the result of personal weakness, a character flaw, or poor upbringing. As scientists
continue their research on mental illness, it is becoming clear that many of these disorders are caused by
a combination of factors, including changes in the brain and environmental stress.
Like certain illnesses, such as diabetes, anxiety disorders may be caused by chemical imbalances in the
body. Studies have shown that severe or long-lasting stress can change the balance of chemicals in the
brain that control mood. Other studies have shown that people with certain anxiety disorders have
changes in certain brain structures that control memory or mood. In addition, studies have shown that
anxiety disorders run in families, which means that they can be inherited from one or both parents, like
hair or eye color. Moreover, certain environmental factors -- such as a trauma or significant event -- may
trigger an anxiety disorder in people who have an inherited susceptibility.
Alprazolam is a short-acting anxiolytic of the benzodiazepine class of psychoactive drugs. Alprazolam is
commonly used and FDA approved for the medical treatment of panic disorder, and anxiety disorders,
such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) or social anxiety disorder (SAD). Alprazolam is available
for oral administration in compressed tablet (CT) and extended-release capsule (XR) formulations.
3
Alprazolam possesses anxiolytic, sedative, hypnotic, skeletal muscle relaxant, anticonvulsant, and
amnestic properties.
Alprazolam is mostly used to treat anxiety disorders, panic disorders, and nausea due to chemotherapy.
The FDA label advises that the physician should periodically reassess the usefulness of the drug.
Drug profile:
ALPRAZOLAM:Alprazolam is a short-acting anxiolytic of the benzodiazepine class of psychoactive drugs. Alprazolam is
commonly used and FDA approved for the medical treatment of panic disorder, and anxiety disorders,
such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) or social anxiety disorder (SAD).
Chemical profile:
N
N
N
N
Cl
ALPRAZOLAM
IUPAC name: 8-chloro-1-methyl-6-phenyl-4H-[1, 2, 4] triazolo [4, 3-a][1,4] benzodiazepine
Empirical Formula: - C17H13Cl N4
Molecular Weight: - 308.77
Solubility in water: - 0.11 g/L (250C)
Nature: Alprazolam is a white to almost white powder.
Solubility: water solubility at 40 mg/L at pH 7; 12 mg/ml at pH 1.2
Availability: Each alprazolam tablet for oral administration contains 0.25,0.5 or 1mg of alprazolam
4
Pharmacodynamics: - (3)
Alprazolam, a benzodiazepine, is used to treat panic disorder and anxiety disorder. Unlike
chlordiazepoxide, clorazepate, and prazepam, alprazolam has a shorter half-life and metabolites with
minimal activity. Like other triazolo benzodiazepines such as triazolam, alprazolam may have
significant drug interactions involving the hepatic cytochrome P-450 3A4 isoenzyme. Clinically, all
benzodiazepines cause a dose-related central nervous system depressant activity varying from mild
impairment of task performance to hypnosis. Unlike other benzodiazepines, alprazolam may also have
some antidepressant activity, although clinical evidence of this is lacking.
In treatment of Anxiety disorders: - (4)
Alprazolam is mostly used to treat anxiety disorders, panic disorders, and nausea due to chemotherapy.
The FDA label advises that the physician should periodically reassess the usefulness of the drug. In the
US alprazolam is FDA-approved for the management of anxiety disorders or the short-term relief of
symptoms of anxiety. Anxiety associated with depression is responsive to alprazolam. Demonstrations
of the effectiveness by systematic clinical study are limited to 4 months duration for anxiety disorder. In
one study, some long term, high-dosage users of alprazolam developed reversible depression. In the UK,
alprazolam is recommended for the short-term treatment (2–4 weeks) of severe acute anxiety.
Alprazolam may be used in combination with other medications for chemotherapy-induced nausea and
vomiting.
Pharmacology:- (5 & 12)
There is preclinical and clinical evidence suggesting that one neural mechanism responsible for antipanic
efficacy is a reduction in brain noradrenergic function. Alprazolam, a triazolobenzodiazepine, has been
demonstrated to have antipanic properties; however, to our knowledge, its effects on noradrenergic
function have not been established. To assess whether alprazolam alters noradrenergic function, the
effects of alprazolam on baseline plasma free 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylethyleneglycol (MHPG), and
yohimbine-induced increases in plasma MHPG level, anxiety-nervousness, blood pressure, and somatic
symptoms were studied in 14 patients with agoraphobia and panic disorder. Long-term alprazolam
treatment significantly reduced plasma MHPG baseline and blunted the yohimbine-induced increases in
plasma MHPG, anxiety-nervousness, and sitting systolic blood pressure. These observations suggest that
5
the antipanic mechanism of action of alprazolam may be due in part to an interaction between
benzodiazepine-sensitive and noradrenergic neural systems.(1)
Adverse effects:- (6)
depressed mood, thoughts of suicide or hurting yourself, unusual risk-taking behavior, decreased
inhibitions, no fear of danger;
confusion, hyperactivity, agitation, hostility, hallucinations;
feeling like you might pass out;
urinating less than usual or not at all;
chest pain, pounding heartbeats or fluttering in your chest;
uncontrolled muscle movements, tremor, seizure (convulsions); or
Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes).
MELATONIN:- (7)
Melatonin is a hormone found naturally in the body. Melatonin used as medicine is usually made
synthetically in a laboratory. It is most commonly available in pill form, but melatonin is also available
in forms that can be placed in the cheek or under the tongue. This allows the melatonin to be absorbed
directly into the body. The hormone melatonin is the primary controller of circadian (day/night) biorhythms.
HN
O
O
N
H
MELATONIN
Chemical profile:IUPAC Name: N-[2-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl) ethyl] acetamide
Empirical Formula: C13H16N2O2
Molecular Weight: 232.27834
6
Nature: Melatonin is a white amorphous powder.
Solubility: H2O: soluble0.1 mg/ml; ethanol: soluble8 mg/ml.
Availability: Melatonin is available as melatonin powder or as 1mg, 3mg, and 5mg tablets.
Pharmacodynamics: -(8)
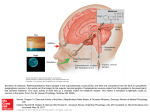
Melatonin is a hormone normally produced in the pineal gland and released into the blood. The essential
amino acid L-tryptophan is a precursor in the synthesis of melatonin. It helps regulate sleep-wake cycles
or the circadian rhythm. Production of melatonin is stimulated by darkness and inhibited by light. High
levels of melatonin induce sleep and so consumption of the drug can be used to combat insomnia and jet
lag. MT1 and MT2 receptors may be a target for the treatment of circadian and non circadian sleep
disorders because of their differences in pharmacology and function within the SCN. SCN is responsible
for maintaining the 24 hour cycle which regulates many different body functions ranging from sleep to
immune functions.
In treatment of anxiety disorders:- (9)
Melatonin is used in treating anxiety disorders .Melatonin is also used for the inability to fall asleep
(insomnia); delayed sleep phase syndrome (DSPS); insomnia associated with attention deficithyperactivity disorder (ADHD); insomnia due to certain pressure medications called beta-blockers; and
sleep problems in children with developmental disorders including autism, cerebral palsy,
and retardation. It is also used as a sleep aid after discontinuing the use of benzodiazepine drugs and to
reduce the side effects of stopping smoking.
Pharmacology:- (10)
Melatonin exerts its effects through activation of at least two high-affinity G-protein-coupled receptors,
MT1 and MT2. These are unique receptors as they show distinct molecular structures, pharmacological
characteristics and chromosomal localization. The MT1 and MT2receptors are 350 and 362 amino acids
long respectively, with calculated molecular weights of 39–40 kDa. MT1 and MT2melatonin receptors
signal by coupling to heterotrimeric G proteins formed by α, β and γ subunits. Activation of these
receptors promotes dissociation of G proteins into α and β, γ dimers, which interact with various effector
molecules involved in the transmission of cell signaling. Effector systems involved in MT1 and
MT2 melatonin receptor signaling through G-protein coupling include adenylyl cyclase, phospholipase
C, phospholipase A2, potassium channels and potentially guanylyl cyclase and calcium channels.
7
Tissues endowed with fully characterized functional MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptors include the
retina, brain, suprachiasmatic nucleus, pars tuberalis, ovaries, cerebral and peripheral arteries, kidney,
pancreas, adiposities and immune cells.
ADVERSE EFFECTS:- (11)
The most common melatonin side effects include:
Daytime sleepiness
Dizziness
Headaches
Other, less common melatonin side effects might include abdominal discomfort, mild anxiety,
irritability, confusion and short-lasting feelings of depression.
ALPRAZOLAM IN COMBINATION WITH MELATONIN:Melatonin is a hormone produced by the body that regulates your sleeping and waking patterns. It is also
available as a supplement and works as an antioxidant. Melatonin supplements are used to treat
insomnia, a common symptom of anxiety. Anxiety can interfere with your ability to fall asleep or cause
you to toss and turn throughout the night. According to a study published in the January 2011 issue of
"Clinical Medical Research and Opinion," sleep latency, sleep quality and quality of life improved
among participants aged 18 to 80 who took prolonged-release melatonin over a three-week period.
Alprazolam is an anti-anxiety medication that is used to treat anxiety disorders as well as panic disorder,
and may be prescribed for some cases of depression. It is a strong, habit-forming medication and is not
prescribed to alleviate day-to-day anxiety or stress. The starting dosage is typically 0.25 mg or 0.5 mg
per day and may be gradually increased up to 4 mg daily.
So, this combination of alprazolam along with melatonin can be preferred for the treatment of the
anxiety disorders. This drug combination of alprazolam and melatonin is readily available in the market.
Interactions:
Melatonin can have negative side effects as a result of interaction with a number of other types of
medication. For example, caution should be taken when taking melatonin along with psychotropic
medications such as antidepressants, antipsychotics or benzodiazepines, such as alprazolam. It can be
dangerous when taken in combination with blood pressure medications or blood thinners. Alprazolam
can interact with other psychotropic drugs, anticonvulsants and antihistamines that also depress the
central nervous system. So, these drugs must be used only as directed by the physician. (13)
Literature survey reveals that, Alprazolam and Melatonin are both official in of the pharmacopoeias
8
like IP, BP, USP and European pharmacopoeia and it was found that above mentioned anti- anxiety drug
was estimated alone or in combination with other drugs by various analytical methods like UV visible
spectrophotometer (14, 15 & 16), HPLC (17, 18, 19 & 20), HPTLC–UV (21), and spectrofluorimetric
(22) methods were reported. In view of need for a suitable method for routine analysis in formulation, an
attempt has been made to develop simple, efficient spectroscopic and chromatographic methods for the
simultaneous estimation of both Alprazolam and Melatonin in pharmaceutical dosage form.
.Analytical validation is the corner stone of process validation. Without a proven measurement
system it is impossible to confirm whether the manufacturing process has done what it purport to do.
Hence, there is a need to validate the new methods developed.
6.2 REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE:
Gupta M, et al. have published a review article on a reverse phase high performance liquid
chromatography method for simultaneous estimation of melatonin, carbamazepine epoxide and
carbamazepine simultaneously in serum.
Makwana DH, Patel PB have published review article on development and validation of
spectroscopic methods for simultaneous estimation of alprazolam and mebeverine hydrochloride
in bulk drug and pharmaceutical dosage form.
Ayesha SS, et al. have published a review article on method development &validation for the
simultaneous estimation of zolpidem and melatonin in pharmaceutical dosage form by using rphplc.
Priscilla K, et al have published a review article on validated liquid chromatographic method for
simultaneous estimation of melatonin and zolpidem tartarate in tablet dosage form.
Darwish HW, et al. have published a review article on New spectrofluorimetric methods for
determination of melatonin in the presence of N-{2-[1-({3-[2-(acetylamino)ethyl]-5-methoxy1H-indol-2-yl}methyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl]-
ethyl}acetamide:
a
contaminant
in
commercial melatonin preparations.
Kuchekar BS, et al. have published a review article on spectrophotometric estimation of
melatonin and pyridoxine hydrochloride in combined dosage forms.
Guo NC, et al have published a review article on Chemiluminescence determination of melatonin
and some of its derivatives using potassium permanganate and formaldehyde system.
9
Kiran K, et al. have published a review article on UV spectrophotometric method for the
estimation of alprazolam in tablet dosage form.
Magdalena WK, et.al have published a review article on Quantitative determination of melatonin
in Lamium album flos.
Sharma S, et.al have published a review article on Method development and validation of UV
spectrophotometric method for alprazolam in pharmaceutical dosage forms using ferric chloride
and indigo carmine.
Madhur G, et.al have published a review article on reverse phase high performance liquid
chromatography method for simultaneous estimation of melatonin, carbamazepine epoxide and
carbamazepine simultaneously in serum.
Venkateshwarulu, et.al have published a review article on Development of HPTLC–UV
absorption densitometry method for the analysis of alprazolam and sertraline in combination and
its application in the evaluation of marketed preparations.
Sagar B, et.al have published a review article on A novel HPTLC method for simultaneous
determination of alprazolam and methyl paraben in tablet dosage form.
6.2 OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY:
In the proposed work attempts shall be made to:
Develop new analytical methods and validation for the simultaneous estimation of
Alprazolam and Melatonin.
Validate the proposed method in accordance with ICH and Pharmacopoeial guidelines for
the intended analytical application.
Apply the proposed methods for analysis of Alprazolam and Melatonin as API and in
dosage form.
10
7. MATERIALS AND METHODS:
7.1 Source of data:
Literature survey was done at P.E.S. College of Pharmacy using Internet facilities
(RGUHS HELINET) and at Library.
Reference from library at RGUHS, Bangalore.
Indian Institute of Sciences, Bangalore.
Department of Drug testing Laboratories, Bangalore.
7.2Method of collection of data:
Simultaneous estimation and analytical method development on Alprazolam and Melatonin drug shall be
carried out in PES COLLEGE OF PHARMACY. The analytical methods will be developed by using
instruments like UV visible spectrophotometer, HPLC, HPTLC instrument. The data so obtained is
treated statistically to determine the compliance of the experimental result as per ICH and
Pharmacopoeial guidelines and for the routine use of the developed analytical methods in industry.
JOURNALS:
1. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences.
2. Journal of Chromatography A
3. Journal of Chromatography B.
4. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research.
5. Eurasian Journal of Pharma Chemistry.
6. International Journal of Pharma Research and Development.
7. Journal of Medical Microbiology.
8. Journal of Young Pharmacist.
9. World Journal of Pharmaceutical research.
10. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical sciences.
11. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology.
11
7.3. DOES THE STUDY REQUIRE ANY INVESTIGATION OR INTERVENTIONS TO BE
CONDUCTED ON PATIENTS OR OTHER HUMANS OR ANIMALS?
NOT APPLICABLE
7.4.
HAS
ETHICAL
CLEARENCE
BEEN
OBTAINED
FROM
YOUR
INSTITUTION
IN CASE OF 7.3?
NOT APPLICABLE.
8. REFERENCES:
1. http://www.health.am/psy/more/pathophysiology_of_anxiety/
2. http://www.webmd.com/anxiety-panic/guide/mental-health-anxiety-disorders?page=2
3. http://neurolex.org/wiki/Category:Alprazolam
4. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alprazolam
5. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2859008
6. http://www.drugs.com/sfx/xanax-side-effects.html
7. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/natural/940.html
8. http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01065
9. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/natural/940.html
10. http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/780687_11
11. http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/sleep-aids/SL00016/NSECTIONGROUP=2
12. Charney D. Noradrenergic function and the mechanism of action of antianxiety treatment.
I. The effect of long-term alprazolam treatment. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1985;42(5):45867.
13. Scientific discussions.
14. Sharma M. Method development and validation of UV spectrophotometric method for
alprazolam in pharmaceutical dosage forms using ferric chloride and indigo carmine.
European journal of applied sciences. 2011; 3(3):81-5.
15. Kuchekar B, Thakkar S, Hiremath M, Cothe P, Shinde D. spectrophotometric estimation
12
of melatonin and pyridoxine hydrochloride in combined dosage forms. Indian journal of
pharmaceutical sciences. 2002;64(2):158-60.
16. Kiran KA, Mohan KA, Sudheer M, Sai RK, Ramalingam P. UV spectrophotometric
method for the estimation of alprazolam in tablet dosage form. International journal of
chemtech research. 2011;3(1):161-4.
17. Magdale N. Quantitative determination of melatonin in Lamium album flos
Herbapolonica. 2008; 54(7).
18. Gupta M. A reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography method for
simultaneous estimation of melatonin, carbamazepine epoxide and carbamazepine
simultaneously in serum. Indian J Physiol Pharmacology. 2006;50(4):427-30.
19. Ayesha SS, Rajkumar B, Bharadwaja B, Priyanka S, Ramachandrudu B, Bhagyawati M,
et al. Method development and validation for simultaneous estimation of zolpidolem and
melatonin in pharmaceutical dosage form by using RP-HPLC. IJPWR. 2012; 3(1).
20. Guo N. Chemiluminescence determination of melatonin and some of its derivatives using
potassium permanganate and formaldehyde system. Analytical & Bioanalytical
Chemistry. 2003; 376(6):873.
21. Venkateshwarulu. Development of HPTLC–UV absorption densitometry method for the
analysis of alprazolam and sertraline in combination and its application in the evaluation
of marketed preparations Journal of Chromatographic Science. 2007; 45:537-9
22. Darwish H. New spectrofluorimetric methods for determination of melatonin in the
presence of N-{2-[1-({3-[2-(acetyl amino) ethyl]-5-methoxy-1H-indol-2-yl} methyl)-5methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl] - ethyl} acetamide: a contaminant in commercial melatonin
preparations. Chem Cent J. 2012;6(1):36.
13
9. Websites:
http://www.sciencedirect.com
http://www.ingentaconnect.com
http://www.rguhs.ac.in
http://www.pubmed.com
http://www.medline.com
http://www.chemindustry.com
http://www.google.com
14
10. Signature of the candidate
(M. Thomson)
Forwarded for Approval
11. Remarks of the guide
12. Name and Designation of
Dr. Nagaraj
Professor & Head
12.1 Guide
Department of Pharmaceutical Analysis,
PES College of Pharmacy,
Hanumanthanagar, Bengaluru-560050
12.2 Signature
Dr. Nagaraj
Professor & Head
Department of Pharmaceutical Analysis,
12.3 Head of the department
PES College of Pharmacy,
Hanumanthanagar, Bengaluru-560050
12.4 Signature
13.
Remarks of the Chairman and
Forwarded for Approval
Principal
Prof. Dr. S. Mohan
Principal & Director,
13.1 Signature
PES College of Pharmacy,
Hanumanthanagar, Bengaluru-560050
15
16