* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download plant final
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
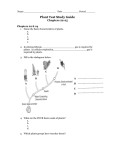
PLANT FINAL CH 22, 23, 24 DO NOT WRITE ON THE TEST CLASSIFICATION Bryophyta, Hepaticophyta Anthcerophyta Lycophyta Arthrophyta Pterophyta Anthophyta Coniferophyta 1. Which of these are not vascular plants. a. Bryophyta b. Anthophyta c. Coniferophyta d. Arthrophyta 2. Which of these produce fruit as a reproductive structure? a. Pterophyta, b. Hepaticophyta c. Anthophyta, d. Lycophyta 3. Which of these produce a seed to help reproduce? a. Bryophyta, b. Coniferophyta, c. Arthrophyta d. Lycophyta 4. Some general charecteristics of the Kingdom Plantae are: a. cellulose cell wall, multicellular b. chiton cell wall, multicellular c. photosynthesis, multicellular and single cellular d. vascular, heterotrophic 5. An example of vascular tissue is: a. xylem, b. epidermis, c. bark, d. cortex 6. Spores are used by some plants to: a. reproduce, b. digest food, c. pollination, d. asexual reproduction 7. Ferns belong to which group? a. Bryophyta, b. Coniferophyta c. Arthrophyta, d. Pterophyta 8. Which group produces cones and a naked seed? a. Coniferophyta, b. Anthcerophyta, c. Anthophyta. d. none of these ROOTS AND STEMS 9. Which of these is a function of roots. a. storage, b. transport nutrients, c. absorption d. anchorage, e. all of these 10. Which root system is best to plant on the side of a hill to control erosion? a. fibrous, b. adventicious, c. tap root system, d. aerial system 11. Which root system is best to plant where it may become dry? a. fibrous, b. adventicious, c. tap root system, d. aerial system 12. Which root system doesn’t have root hairs? a. fibrous, b. aquatic, c. adventicious, d. primary 13. What part of the root system’s function is to absorb the majority of nutrients? a. tap root, b. secondary root c. root cap, d. root hairs, f. meristematic 14-15. Label the parts of the root longitudinal section. Longitudinal picture here . a. root cap, b. meristematic region c. elongation region, d. maturatin region 16-17. Label the parts of the crossection of a root. a. epidermis b. xylem, c. phloem, d. endodermis, e. vascular cambium crossection of dicot root picture here 18. What part of the vascular system brings sugar down to the roots? a. xylem, b. phloem, c. vascular cambium, d. endodermis 19-20. Label the parts of the stem. a. node, b. lenticel, c. leaf scar, d. bud scale scar, e. terminal bud stem picture here 21. How old is the twig in the above picture? (years old) a. 1 b. 2, c. 3 d. 4, e. 5 22-23. Label the parts of the crossection of a stem below. a. phloem, b. xylem, c. cambium, d. cortex, e. cork dicot stem crossection picture here LEAVES 24. The leaf arrangement in the picture is: leaf picture here a. opposite, b. alternate, c. whorled, d. palmate, e. pinnate 25. Which of the pictures below is a pinnately compound leaf? Leaves pictures here 26-27. Label the parts of a crossection of a leaf. a. phloem, b. xylem, c. palisasde mesophyll, d. spongy mesophyll, e. cuticle leaf crossection picture here 28. What is the pigment in a leaf called that absorbs the light for photosynthesis? a. green, b. chloroplast, c. chlorophyll, d. photoptics, e. none of these 29. Which is an example of a palmately veined leaf? Leaves pictures here 30. Which of these are charecteristics of Monocots? a. parallel veined, two cotyledons b. parallel veined, one cotyledon c. vascular bundles in a ring d. contains a cortex and a pith 31-32. Label the parts of the lower epidermis of a leaf. a. stomata b. epidermis c. guard cells d. parenchyma cells epidermis picture here 33. Two plants are connected by an underground stem. This stem is called: a. stolen, b. tuber, c. rhizome, d. corm 34. Name the structure in the picture below. a. epidermis, b. thorn, c. tuber, d. corm, e. tendril picture here SEEDS 35-36. Label the parts of the seed. a. seed coat, b. hilum, c. micropyle, d. cotyledon e. epicotyl seed picture here 37. What part of the seed supplies food for the growing baby plant? a. epicotyl, b. radical, c. hypocotyl, d. cotyledon NUTRIENTS and FOOD TYPES 38. On a fertilizer bag is says: 30:20:15. This represents the percentage of: a. nitrogen, potassium, carbon b. phosphorous, potash, iron c. nitrogen, phosphorous, potash d. carbon, hydrogen, oxygen 39. What is the most common nutrient farmers and home owners add to the soil? a. nitrogen, b. phosphorous, c. carbon, d. potash, e. oxygen 44-43. Use these answers for the following questions a. petiole b. leaf c. root d. stem e. fruit 40. celery and rhubarb 41. potato 42. carrot 43. beans GENERAL QUESTIONS FROM THE TEXT BOOK Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 44. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of all plants? a. are eukaryotic c. produce seeds b. have cell walls d. are multicellular 45. Which of the following statements is true about bryophytes? a. They have specialized tissues that conduct water. b. They draw up water by osmosis. c. They are not highly dependent on water. d. They are a group of plants made up of algae and mosses. 46. Bryophytes need standing water to a. reproduce. c. undergo photosynthesis. b. draw up water by osmosis. d. grow tall. 47. Which of the following includes all the others? a. xylem c. phloem b. vascular tissue d. tracheids 49. Xylem tissue is important to ferns because it a. can conduct water over long distances. b. allows water to diffuse into the roots. c. carries carbohydrates to all parts of the plant. d. allows ferns to reproduce in dry environments. 50. Club mosses are a. nonvascular plants. c. seedless vascular plants. b. seed plants. d. none of the above 51 Horsetails do NOT a. have xylem tissue. c. have roots. b. produce seeds. d. have phloem tissue. 52. Which of the following includes a plant embryo, a food supply, and a protective covering? a. pollen grain c. seed b. spore d. gametophyte 53. The gametophytes of gymnosperms are found inside reproductive structures called a. flowers. c. embryos. b. cones. d. angiosperms. 54. The four groups of gymnosperms are conifers, cycads, ginkgoes, and a. bryophytes. c. liverworts. b. horsetails. d. gnetophytes. 55. Angiosperms produce seeds inside protective structures called a. pollen grains. c. ovaries. b. cones. d. petals. 56. Which type of plant lives the longest? a. annual c. perennial b. biennial d. none of the above 57. If some of the xylem of a young oak tree were destroyed, it would most likely interfere with the tree’s ability to a. conduct sugars to the roots. c. absorb water from the soil. b. absorb sunlight. d. conduct water to the leaves. 58. Which of the following is the only tissue that produces new plant cells? a. meristematic tissue c. ground tissue b. phloem d. xylem 59. A carrot is a(an) a. taproot. c. monocot. b. fibrous root. d. extensive root system. 60. Starting from the root cap, which of the following is the correct sequence of cell activity in a root? a. elongation division differentiation b. division elongation differentiation c. differentiation elongation division d. division differentiation elongation 61. The primary growth of a stem a. is produced by cell division in the cambium. b. is produced by cell division in the xylem and phloem. c. increases the length of the stem. d. increases the width of the stem. 62. What might a thin tree ring indicate? a. increased production of xylem c. decreased production of phloem b. xylem production in winter d. a year of drought 63. Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse in and out of a leaf through the a. palisade mesophyll. c. phloem. b. guard cells. d. stomata. 64. Most of the photosynthetic activity in plants takes place in the a. mesophyll. c. stomata. b. guard cells. d. xylem. 65. Which of the following does NOT directly enable photosynthesis to take place in a leaf? a. guard cells c. phloem b. stoma d. xylem 66. The stomata of leaves are usually open in a. light if a plant has enough water. c. darkness if a plant has enough water. b. light if a plant has too little water. d. darkness if a plant has too little water. 67. Pollen grains are produced by a. male reproductive structures. c. ovules. b. female reproductive structures. d. flowers. 68. In angiosperms, reproduction takes place in a. leaves. c. cones. b. flowers. d. pollen. 69. The tough outer layer of a seed is called the a. seed coat. c. nut. b. fruit. d. embryo wall. 70 A ripened ovary that contains angiosperm seeds is called a(an) a. embryo. c. fruit. b. seed. d. vegetable. 71 The early growth stage of a plant embryo is called a. fertilization. c. germination. b. dormancy. d. pollination. 72. When a plant reproduces vegetatively, its offspring a. are genetically different. c. remain dormant until the spring. b. are genetically identical. d. grow from seeds. Figure 24–2 73. The horizontal stems of the strawberry plant shown in Figure 24–2 are called a. scions. c. buds. b. stolons. d. plantlets. 74. For a graft to be successful, what part of the two plants must be firmly connected? a. bark c. vascular cambiums b. roots d. stolons