* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry Study Guide
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Livermorium wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear transmutation wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
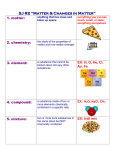
Chemistry Study Guide Atoms and Subatomic Particles Atom. Al matter is made up of unique particles called atoms. An atom contains: o Protons- Positively charged; have atomic mass of one; Located in the nucleus of the atom. o Neutrons- Neutral in charge; the same mass as the proton; also located in the nucleus of the atom. o Electrons- Negatively charged; they move around the nucleus at high speeds on electron rings; same number as protons. Atomic Notation Atomic Symbol- Scientists use a symbol of one or two letters to identify elements. The first letter is always capitalized, but not the second. Examples: H, O, He, Fe Atomic Number- The number of protons an atom has; also equals the number of electrons of the uncharged atom. Atomic Mass- The number of protons and neutron in an atom. Elements and Compounds Elements- Any form of matter made up of identical atoms. Examples: carbon, oxygen. Compounds- A substance made up of atoms of different elements joined chemically together. These elements are always combined in fixed proportions. Examples: water, salt, sugar Molecule- A group of atoms that share one or more pairs of electrons; the smallest part of a compound with its properties. Chemical Reactions Chemical Reactions- These are combinations of divisions of substances that result in one or more new substances with new physical and chemical properties. Chemical Equations- There should be the same number of atoms on each side of the equation. Multiply the atoms in each molecule by the number of molecules to see that they balance: 2H2 + O2 2H2O Conservation of Mass- Mass cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Physical and Chemical Properties Physical Properties- every type of matter has its own physical properties. These include its color, odor, density (mass/volume), hardness, melting and boiling point, and how well it conducts heat and electricity. A physical property can change wiout changing a substance’s chemical make-up (arrangement of atoms). Chemical Properties- Chemical properties refer to the ability of a substance to react with other forms of matter. For example, some substances are flammable. If they are heated with oxygen, they will react and burst into flames. The ability of a substance to combine with oxygen is an example of chemical property. Periodic Table of the Elements Table of elements arranged by their atomic number – the number of protons. An elements position on the table will show many of its general properties Periods- The table is arranged in horizontal rows called periods. The period tells you how many electron energy levels the atom has. Groups- Vertical columns whose members of the same group have similar chemical and physical properties. o Have the same number of outer electrons. o Often share other characteristics like the ability to conduct electricity or heat Compound, Mixtures and Solutions Compound- Made of two or more elements chemically combined. The elements in a compound are always in the same proportion. The properties of the compound differ from the elements that make it up. Mixture- Two or more substances mixed together without chemically combining. The substances can be separated without a chemical reaction. Solution- A mixture in which one substance is dissolved uniformly in another substance. Elements Metals- Hard, shiny elements appearing on the left side of the Periodic Table. They are good conductors of heat and electricity. Examples include; iron (Fe), aluminum (Al), and sodium (Na). Metalloids- Appear alon the bolded line on the Periodic Table. They conduct electricity under some conditions. Examples include; boron (B) and silicon (Si). They are important to the semiconductor industry. Nonmetals- These appear to the right of the Periodic Table. They are poor conductors of heat, and do not conduct electricity. Many are gases, or brittle solids. Examples include: carbon (C) oxygen (O), and sulfur (S). Nobel Gases- Appear to the far right of the Periodic Table. (Group 18). They do not usually combine with other substances. Examples include: argon (Ar) and neon (Ne).