* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7.1 Study Guide
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
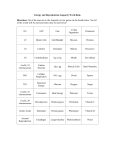
Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ Section 1: Chromosomes and Phenotype Study Guide A KEY CONCEPT The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. VOCABULARY carrier sex-linked gene X chromosome inactivation MAIN IDEA: Two copies of each autosomal gene affect phenotype. Fill in the blank or circle the word or phrase that best completes the sentence. 1. Sex chromosomes determine an organism’s _______________. All other chromosomes, which do not directly affect an organism’s sex, are called _______________. 2. A person who is a carrier differs from a person who has a genetic disorder. A carrier does / does not show symptoms of a disorder but can / cannot pass the disorder to offspring. 3. Complete the two Punnett squares below to compare autosomal recessive disorders with autosomal dominant disorders. Fill in the possible genotypes for offspring, and write in the phenotype (no disorder, carrier, or disorder) for each. Autosomal Recessive D Autosomal Dominant d D D D d d d © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Holt McDougal Biology Study Guide A 0 Extending Mendelian Genetics Section 1: Chromosomes and Phenotype Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ Study Guide A continued MAIN IDEA: Males and females can differ in sex-linked traits. 4. Sex-linked genes are located on the _____________________. 5. Fill in the Punnett square below to show the pattern of inheritance for sex chromosomes. Write in the phenotype (male or female) for each. Sex Chromosome Inheritance X X X Y Circle the word or phrase that best completes the statement. 6. In humans, a gamete from a male determines the sex of the offspring, because a male can pass on only X / only Y / either X or Y chromosomes. In contrast, a female passes on only X / only Y / either X or Y chromosomes. 7. The genes on the Y chromosome are responsible for male / female characteristics. 8. Place a check mark in the appropriate boxes to show how sex-linked genes are expressed in the phenotypes of males and females. Males Females Show phenotypes from all sex-linked genes. Show phenotypes similarly to autosomal gene expression. Vocabulary Check Circle the word or phrase that best completes the statement. 9. The verb carry means “to transport.” This meaning is related to the term carrier in genetics, because a carrier is a person who “transports” a disease-causing allele to offspring / parents. 10. With X chromosome inactivation, which occurs in males / females, one of the two X chromosomes in every cell is randomly “turned off” / “turned up.” © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Holt McDougal Biology Study Guide A 1 Extending Mendelian Genetics Section 1: Chromosomes and Phenotype Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Holt McDougal Biology Study Guide A 2 Extending Mendelian Genetics Section 3: Gene Linkage and Mapping Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Holt McDougal Biology Study Guide A 3 Extending Mendelian Genetics Section 4: Human Genetics and Pedigrees