* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Newton`s Laws Assignment
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Roche limit wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's law of universal gravitation wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
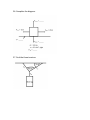
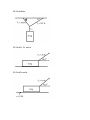
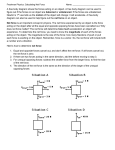
Dynamics Practice Questions 1. There is a formula that can be used to find acceleration and also shows how it is produced. What is this formula? 2. State Newton’s 1st Law. 3. How much weight does a 5.0 kg object have on Earth? 4. Two identical books are resting on a table. One is lying flat while the other is positioned on its end. If both books are exerting the same force, why does the book positioned on its end exert more pressure? Explain. 5. State Newton’s 2nd Law. 6. When two objects collide, there is a pair of forces. What are the names, in general, that we give to these two forces? 7. State Newton’s 3rd Law. 8. You can hit a punching bag with a force of 250 N. If for every action there is an opposite and equal reaction, why can you not hit a piece of paper with 250 N? Explain. 9. Compare a litre of water with a litre of air. Answer yes or no for each question below: a) Do they have the same volume? b) Do they have the same mass? c) Do they have the same inertia? 10. An object weighs 60.0 N. What would its mass be on Earth? 11. An object with a mass of 30.0 kg has a weight of 150.0 N on a distant planet. What must be the force of gravity on this planet? 12. In general, what does an unbalanced force, or net force, on an object cause? 13. A van weighs 2.6 x 104 N. What force would be required to accelerate the van at 5.7 m/s2 if the van is driving on Earth? 14. An object on a table has a normal force of 25 N. The coefficient of friction for the table is 0.55. What frictional force must be overcome to get the object to move? 15. Fill in the missing values: 16. An object has a mass of 50.0 kg. What would it's weight be on Earth? 17. Let's say you wanted to accelerate an object on Earth at 3.0 m/s2, and the object weighs 2.7 x 103 N. How hard would you have to push it? 18. On the moon an object that has a mass of 40.0 kg has a weight of about 66.6 N. What is the force of gravity on the moon? 19. A surface has a frictional coefficient of 0.20. If an object on this surface experiences a normal force of 85 N, how much force is needed to make the book move? 20. A 6.0 x 103 kg truck pushes itself forward with a force of 1.0 x 103 N. What is the truck's acceleration? 21. On a certain planet, a local resident notices that he must use a force of 3.00 x 103 N to make an object accelerate at a rate of 5.00 m/s2. If the object weighs 3.4 x 102 N, what is the planet's force of gravity? 22. A sign is hanging on a wall and has a mass of 100.0 kg. If two vertical cords are used to hang the sign, how much tension is in each of the cords? 23. Find the missing forces given the following situations. Make sure you give an answer for every letter. (Don't worry about sig. digs.) a) b) c) 24. Complete the diagram 25. Complete the diagram. 26. Complete the diagram. 27. Find the three tensions. 28. Find theta. 29. Find FN, Fax, and a. 30. Find FN and a. 31. Find FN and a. 32. Find FN and a. Solutions 1. a = Fnet/m 2. Objects in motion or rest tend to stay in motion or at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. 3. How much weight does a 5.0 kg object have on Earth? Fw = mg Fw = (5.0 kg)(10 N/kg) Fw = 50 N or 5.0 x 101 N 4. Because the book positioned on its end has a greater force per unit area. As a formula: P = F/A 5. Three main parts to this law: -Acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it. -Acceleration of an object is inversely proportional to the mass of the object. -Acceleration of an object is in the same direction as the net force. Thus aptly called the law of acceleration. 6. Action force and reaction force. 7. For every reaction there is an equal and opposite reaction. 8. The paper does not have enough mass (inertia) to exert back an equal and opposite reaction force. 9. a) Do they have the same volume? yes b) Do they have the same mass? no c) Do they have the same inertia? no 10. Fw = mg 60.0 N = m(10 N/kg) m = 60.0 N/ 10 N/kg m = 6.00 kg 11. Fw = mg 150.0 N = (30.0 kg)g g = 150.0 N/30.0 kg g = 5.00 N/kg 12. An acceleration 13. F = Fwa g F = (2.6 x 104 N)( 5.7 m/s2) 10 m/s2 F = 14 820 N, or 1.5 x 104 N 14. Ffrict = uFnorm Ffrict = (0.55)(25 N) Ffrict = 13.75 N or 1.4 x 101 N 15. Fnet = 10 N, Fgrav = 50 N, Fnorm = 50 N, Ffrict = 5 N, Fapp = 15 N. 16. Fw = mg Fw = (50.0 kg)(10 N/Kg) Fw = 500 N or 5.00 x 102 N 17. F = Fwa/g F = (2.7 x 103 N)( 3.0 m/s2)/10 m/s2) F = 810 N or 8.1 x 102 N 18. Fw = mg 66.6 N = (40.0 kg)(g) g = 1.67 N/kg 19. A surface has a frictional coefficient of 0.20. If an object on this surface experiences a normal force of 85 N, how much force is needed to make the book move? Ffrict = uFnorm Ffrict = (0.2)(85 N) Ffrict = 17 N 20. A 6.0 x 103 kg truck pushes itself forward with a force of 1.0 x 103 N. What is the truck's acceleration? Fnet = ma 1.0 x 103 N = (6.0 x 103 kg)(a) a = 0.16 N/kg or 1.6 x 10-1 N/kg 21. On a certain planet, a local resident notices that he must use a force of 3.00 x 103 N to make an object accelerate at a rate of 5.00 m/s2. If the object weighs 3.4 x 102 N, what is the planet's force of gravity? F = Fwa/g 3.00 x 103 N = (3.4 x 102 N)(5.00 m/s2)/g g = 1.76 m/s2 or 1.8 m/s2 22. A sign is hanging on a wall and has a mass of 100.0 kg. If two vertical cords are used to hang the sign, how much tension is in each of the cords? 2T - mg = 0 2T - (100.0 kg)(10 N/kg) = 0 2T - 1000 = 0 2T = 1000 T = 500 N or 500.0 N 23. a) C = 1100 N b) D = 20 N, E = 300 N c) F = H = any numbers, as long as they are equal, G = 50 N 24. Fnet = 0 N; Fgrav = 60 N; Fnorm = 60 N; Fapp = 15 N 25. Fnet = 0 N; Fgrav = 100 N; Fnorm = 100 N; Ffrict = 20 N, Fapp = 20 N 26. Fnet = 10 N, right; Fgrav = 50 N; Fnorm = 50 N; Ffrict = 5 N, Fapp = 15 N. 27. 180o - 100.0o - 33.0o = 47.0o for the missing angle. -T1cos47.0o + T2cos33.0o = 0 T2cos33.0o = T1cos47.0o T2 = T1cos47.0o cos33.0o T2 = T1(0.813) T1sin47.0o + T2sin33.0o - mg = 0 T1sin47.0o + T1(0.813)sin33.0o -(60.0 kg)(10 N/kg) = 0 T1(0.731) + T1(0.442) - 600 = 0 T1(1.173) = 600 T1 = 511 N T2 = T1(0.813) T2 = (511)(0.813) T2 = 415 N T3 = 600 N or 6.00 x 102 N 28. sinƟ = opposite/hypotenuse sin27o = T2y/257 N T2y = 116.67 T1y + T2y - T3 = 0 T1y + 116.67 - 350 N = 0 T1y = 233.33 N sinƟ = opposite/hypotenuse sinƟ = 233.33 N/345 N sinƟ = 0.676 Ɵ = 43o 29. FN + Fasinθ - Fg = 0 FN + (55 N)(sin35.0o) - 150 N = 0 FN + 31.54 = 150 N FN = 118.46 or 1.2 x 102 N Fax = Facosθ Fax = (55 N)(cos35.0o) Fax = 45 N a = Fnet/m a = 45 N/15 kg a = 3.0 N/kg 30. FN + Fasinθ - Fg = 0 FN + (64 N)(sin42.0o) - 130 N = 0 FN + 42.82 = 130 N FN = 87.18 or 8.7 x 101 N Facosθ - μFN = ma (64 N)(cos42.0o) - (0.35)(87.18N) = (13 kg)a 47.56 N- 30.51 N= (13 kg)a 17.05 N = (13 kg)a a = 17.05 N/13 kg a = 1.3 N/kg or m/s2 31. FN = mgcosθ FN = (45 kg)(10 N/kg)(cos30.0o) FN = 389.71 N or 3.9 x 102 N a = gsinθ a = (10 m/s2)(sin30.0o) a = 5.00 m/s2 32. 180o - 90.0o - 66.0o = 24.0o for the missing angle FN = mgcosθ FN = (52 kg)(10 N/kg)(cos24.0o) FN = 475.04 N or 4.8 x 102 N a = gsinθ - μgcosθ a = (10 N/kg)(sin24.0o) - (0.36)(10 N/kg)(cos24.0o) a = 4.067 - 3.288 a = 0.779 N/kg or 7.8 x 10-1 N/kg