* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Calculating Net Force - Rider Freshman Physics
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
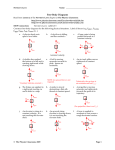
Freshman Physics: Calculating Net Force Name: ____________________________ A free body diagram shows the forces acting on an object. A free body diagram can be used to figure out if the forces on an object are balanced or unbalanced. If the forces are unbalanced, Newton’s 1st Law tells us the motion of the object will change: it will accelerate. A free-body diagram can also be used to help figure out the net force on an object. Net force is an important concept in physics. The net force experienced by an object is the force acting on the object after all the equal and opposite opposing forces have been cancelled out. Why does net force matter? The net force will determine how much acceleration an object will experience. To determine the net force, you need to know the magnitude of each of the forces acting on the object. The magnitude is the size of the force: how many Newtons of push or pull each force is exerting on the object. Remember, force is a vector. So, the net force will include both a number and a direction. Here’s how to determine net force: 1. Equal and opposite forces cancel out, and don’t affect the net force. If all forces cancel out, the net force is zero. 2. If there are two forces acting in the same direction, add the before moving to step 3. 3. For unequal opposing forces: subtract the smaller force from the larger force, to find the size of the net force. 4. The direction of the net force is the same as the direction of the larger of the unequal opposing forces Freshman Physics: Calculating Net Force Name: ____________________________ 1. The free-body diagram below shows the forces acting on a lamp hanging from the ceiling. a. Are the forces acting on the lamp balanced or unbalanced? Ften = 10 N b. What is the net force on the lamp? (Remember: the net force is a number and a direction) Fgrav = 10 N a. Describe the motion of the lamp. Is it at rest (not moving at all), moving at a constant velocity, or is it accelerating? If it is moving, in what direction? How do you know? 2. The free-body diagram below shows the forces acting on an apple that is falling from a tree, toward Isaac Newton’s head. Fair = 3 N b. Are the forces acting on the apple balanced or unbalanced? c. What is the net force on the apple? (Remember: the net force is a number and a direction) Fgrav = 10 N d. Describe the motion of the apple. Is it at rest (not moving at all), moving at a constant velocity, or is it accelerating? If it is moving, in what direction? How do you know? Freshman Physics: Calculating Net Force Name: ____________________________ 3. The free body diagram below shows the forces acting on a remote control toy car. a. Are the forces acting on the car balanced or unbalanced? b. What is the net force on the car? (Remember: the net force is a number and a direction) Fnorm = 10 N Ffrict = 20 N Fapp = 120 N Fgrav = 10 N c. Describe the motion of the car. Is it at rest (not moving at all), moving at a constant velocity, or is it accelerating? If it is moving, in what direction? How do you know? 4. The free body diagram below shows the forces acting on Q, Ms. Crock’s cat, as he slides on an icy Portland sidewalk during the last ice storm. a. Are the forces acting on Q balanced or unbalanced? b. What is the net force on the Q? (Remember: the net force is a number and a direction) Fnorm = 10 N Ffrict = 3 N Fgrav = 10 N c. Describe the motion of Q. Is he at rest (not moving at all), moving at a constant velocity, or is he accelerating? If he is moving, in what direction? How do you know? . Freshman Physics: Calculating Net Force Name: ____________________________ 5. The free body diagram below shows Mr. Ziady as he flies in the air, using his jet pack. a. Are the forces acting on Mr. Ziady balanced or unbalanced? b. What is the net force on the box? (Remember: the net force is a number and a direction) c. Describe Mr. Ziady’s motion. Is he at rest (not moving at all), moving at a constant velocity, or accelerating? If he is moving, in what direction? How do you know? Fapp = 300 N Fgrav = 100 N Fair = 10 N 6. The free body diagram below shows the forces on a skater as she skates down Central St toward Ida into a strong headwind. a. Are the forces acting on the box balanced or unbalanced? Fnorm = 65 N Fair = 30 N b. What is the net force on the box? (Remember: the net force is a number and a direction) Fapp = 50 N Ffrict = 25 N Fgrav = 65 N c. Describe the object’s motion. Will it stay at rest, continue moving at a constant velocity, or will it accelerate? Freshman Physics: Calculating Net Force Name: ____________________________ 7. Draw a free body diagram that shows a ball bearing rolling across a frictionless surface at a constant velocity. The net force on the ball is zero. Gravity pulls on the ball with a force of 1 N. 8. Draw a free body diagram that shows the forces acting a car moving to the right and slowing down as a result of friction from the brakes and the tires on the road. The net force on the car is 5000 N. The force of gravity on the car is 11,000 N. 9. Draw a free body diagram that shows the forces acting on a woman jumping off a high dive. The net force experienced by the woman is 700 N. As she falls, she experiences a 50 N push from air resistance. Freshman Physics: Calculating Net Force Name: ____________________________ Extension: 1. 2. 3. 4. Get a Chromebook Go here: goo.gl/RiyCHo Read the page, through “The Pythagorean Theorem” Use the instructions given to find the net force on the object represented in the free body diagrams shown below. Fnorm = 30 N Ffrict = 20 N Fgrav = 10 N Fnorm = 50 N Ffrict = 20 N Fapp = 120 N Fgrav = 10 N Fnorm = 5 N Fapp = 15 N Fapp = 5 N Fgrav = 10 N