* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
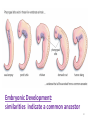
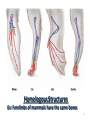
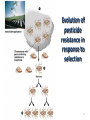
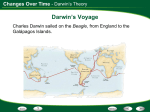
Evolution Genetic change in a species over time Charles Darwin 1831- Ship’s doctor, HMS Beagle Travelled around the world observing species and collecting specimens Darwin Left England in 1831 Darwin returned 5 years later in 1836 3 Darwin was influenced by: 1. James Hutton – geologist The same geologic processes have occurred throughout Earth’s history 2. Charles Lyell – geologist Earth’s surface has changed over time, Earth is millions, not thousands of years old 3. Thomas Malthus – economist if unchecked, human population will double every 25 years (the struggle for survival prevents this) 1859 Book: Origin of Species Theory: Natural Selection 1. Overproduction occurs in all species 2. Variations occur in all species 3. Struggle for survival- resources are limited, not all born will survive 4. Survival of the fittest- those best adapted to their environment will survive and reproduce. Fitness: ability of an individual to survive and reproduce - central to the process of Evolution - individuals with low fitness either die or produce few offspring Adaptation: Inherited characteristic that increases an organisms chance for survival Adaptations Can Be: Physical - Speed, Camouflage, Claws, Quills, etc. Behavioral - Solitary, Herds, Packs, Activity, etc. Evidence of Evolution 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Fossils Comparative Embryology Homologous structures Vestigial Organs Biogeography Biochemistry Fossil Record • Earth is Billions of Years Old • Fossils in different layers of sedimentary rock show evidence of gradual change over time 9 Evidence for Evolution - Comparative Embryology Embryonic Development: similarities indicate a common ancestor 10 Homologous Structures Ex: Forelimbs of mammals have the same bones 11 Vestigial Organs not used by us, used by related species Ex: appendix (koalas need theirs) Ex: Human coccyx (tailbone) Ex: hip bones in snakes Geographic Distribution of Living Species Unrelated animals on different continents have similar adaptations to similar environments. Ex: deer, kangaroo – eat the same food, have same skull and jaw 13 Biochemistry – similar DNA and amino acid sequences indicate a common ancestor Evolution of pesticide resistance in response to selection 15 Key Concept Over time, Natural Selection results In changes in the inherited characteristics of a population. These changes increase a species fitness in its environment 16