* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download genetics test study guide
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
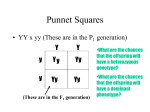
GENETICS TEST STUDY GUIDE NAME:__________________________ DATE:_____________ BLOCK:______ 1. Tongue rolling (R) is dominant over non-tongue rolling (r). If a person cannot roll their tongue, what would be his/her genotype? _____ 2. Genetic disorders like Down syndrome are caused by __________________. 3. What is the process of cloning? ________________________________________________________ 4. The failure of one or more pairs of chromosomes to separate is called _____________________. Round seed pods are dominant over wrinkled seed pods. The Punnett square below shows a cross between parents with round and wrinkled seed pods. Use the following diagram to answer the next three questions. 5. What is the phenotype of the offspring in block A? ________________ 6. What is the genotype of the offspring in blocks B and D? _____________ 7. What is the phenotype of the offspring in block C? ________________ 8. In 1910, Thomas Morgan discovered traits linked to sex chromosomes in fruit fly. The Punnett square below shows the cross between red-eyed females and white-eyed males. Fruit flies usually have red eyes. If a female and male offspring from the cross shown below are allowed to mate, list what the offspring would probably look like? (see figure) __________________________________________________________________________________ 9. Which genotype illustrates codominance of alleles that control blood type in humans?_________ 10. What conclusion about the F1 genotype can be drawn from the genetic information above?____________________________________________ 11. In pea plants, purple flowers are dominant to white flowers. If two heterozygous purple plants are crossed, what percent of the offspring will probably be white? ________ 12. Examination of the diagram indicates that these are the chromosomes of a __________ with ________ ______________. 13. In cats, gene E produces yellow fur and gene B produces black fur. A cat that inherits both of these genes has patches of yellow and black fur and is known as a calico. The alleles for black or yellow are located on the X-chromosome. Calico coat color is most likely due to ________________ _______________ genes. 14. Complete the Punnett square below for a cross of cats. 15. What is the phenotype of the male cat? _______________ 16. What is the phenotype of the female cat? _______________ 17. List what the offspring look like. ________________________________________________________ 18. One way to increase the number of organisms in an endangered species is to let the few remaining individuals of that species breed. However, this breeding may also lead to species extinction because inbreeding over a short period of time may reduce ___________ _______________. 19. In cows, long hair is dominant to short hair. In a cow that is heterozygous for long hair, what percentage of the cells undergoing meiosis will carry the dominant allele? ___________. 20. Forms of the same gene with different phenotypic expressions are called ____________. 21. In corn plants, green (G) is dominant to albino (g). What is the chance of a heterozygous cross producing albino corn plants? ____________ 22. What do eye color, skin color, and blood group have in common?______________________________ 23. When using Punnett squares to show inherited probability, a capital letter stands for the ________________ allele. 24. In humans, a disease inherited by a single pair codominant genes is _______________ ___________. Using the genetic pedigree above, answer the following questions. 25. Person #4 represents _______________________________________. 26. Person #3 represents a _____________________________________. 27. Person #1 had to be _______________________. 28. In turkeys, the dominant gene B results in black pigment throughout the feathers. Most of the feathers of homozygous recessive individuals have light edges. Heterozygous individuals have a few feathers with light edges. If two turkeys with mostly light-edged feathers are crossed, how many chicks would probably have only the black-pigmented feathers? _______________________ 29. In a Mendelian Cross of purebred dominant and purebred recessive, the ratio of dominant to recessive in the F1 generation is __________. 30. A color-blind woman marries a man who has normal color vision. What are their chances of having a color-blind daughter? ____________ 31. A genetic pedigree showing that only males are affected by a certain disorder is evidence of what type of inheritance? _____________ 32. In mice, the gray fur gene (G) is dominant and the gene for black fur (g) is recessive. If 50% of a mouse litter is black, what parental cross probably produced this result? _____X_____ 33. If a man has type O blood, his red blood cells would have what type of antigen? ___________ 34. If “S” stands for a dominant form of the “smooth” gene in a plant (producing smooth leaves), and “s” stands for a recessive form of the “smooth” gene (producing wrinkled leaves), what gene structure would a hybrid plant have? ______ 35. Two hybrid fruit flies each have one dominant gene for brown eyes (B) and one recessive gene for red eyes (b). They are mated. What percent of the offspring have brown eyes? ________ 36. Mendel’s early work with pea plants demonstrated a significant genetic discovery. The crossing of homozygous tall pea plants with homozygous short pea plants always resulted in tall plants and demonstrated that tallness in pea plants is a trait that is _______________. 37. In parrots, a sharp beak (A) is dominant to a dull beak (a), and shiny feathers (L) are dominant to dull feathers (l). According to this Punnett square, how many of the baby parrots from this cross could have a dull beak and dull feathers? ___________________ Circle the appropriate boxes. 38. What is the chance that the child of two individuals, one heterozygous with Type A blood, and the other heterozygous with Type B blood, will have Type O blood? _______________ 39. An allele that expresses itself in a hybrid is a(n) ________________. 40. An organism in which two alleles for a trait are different is _________________. 41. Each of the seven pea traits that Mendel studied occurred in ___ ___________, _____________ forms. 42. When purebred tall plants are crossed with hybrid tall plants, the offspring would be _______________________________________________________________________________ 43. Another name for clones could be _______________ __________. (HINT: natural clones) 44. Crossing a pure-bred green pod plant with a purebred yellow pod plant is symbolized by ____ X ____ 45. Traits that are found on the X chromosome are said to be _____-___________. 46. A person has been diagnosed with AIDS. Did this is this the result of a genetic mutation? ______ 47. The actual genetic makeup of an organism is called its _________________. 48. What an organism looks like is referred to as its _______________. 49. In a Mendel’s experiment, the monohybrid cross of the short and tall plants in the Pl generation resulted in 100 % heterozygous plants in the Fl generation. What was the phenotypic ratio of the F2 generation?_________________________ 50. In the figure, what disorder does the person have with chromosome pattern number 4? ___________________________ 51. Complete the Punnett Squares below and answer the following questions. In Hobbits, hairy feet are dominant over hairless feet. F1 generation: cross 1 homozygous dominant with a homozygous recessive F2 generation: cross 2 of the offspring of the F1 generation 52. In the first generation, what portion of the Hobbits has hairless feet? ___________ 53. In the first generation, what portion of the Hobbits has hairy feet? ___________ 54. In the second generation, what portion of the Hobbits is purebred? ____________ 55. In the second generation, what portion of the Hobbits has hairless feet? ____________ 56. What are the genotypes that you would have to cross to get Hobbit offspring with 50% hairy feet and 50% hairless feet? _______ X ______