* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NATURAL SELECTION This is
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
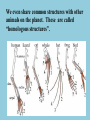
EVOLUTION EVOLUTION is “change over time”. It is how all living things on this planet became what they are today. But where did the idea of how things change come from? There was a scientist named Lamarck who believed that animals were able to change to fit their environment, and they could then pass these changes on to their offspring. Lamarck was wrong. Charles Darwin came up with the idea of Natural Selection, and it has been proven to be the way individuals change to best survive in their environment. Charles Darwin (1809 – 1882) was an English scientist who had an interest in all living things. He took a trip to the Galapagos Islands, and after spending some time there observing the wildlife, came up with the theory of Natural Selection while observing the local finches. Darwin noticed that there were several species of finch that had beaks that seemed to be perfectly designed for the food they ate. How is this possible? Darwin thought that the beaks changed over time to become the perfect shape. But how? NATURAL SELECTION This is “survival of the fittest”, except being “fit” doesn’t mean being in shape. Being “fit” means having the traits you need to survive in your environment, and to have healthy children capable of having children of their own. Nature “selects” these traits almost like a process of elimination, and they get passed on to future generations in the population. Here’s how it works……the ones with the best traits get to pass them on. The ones that don’t, tend to die off, or there are nowhere near as many of them. Some animals have adaptations that help them survive, like colors or claws or fur. These adaptations developed over time due to natural selection “choosing” them. Some of these changes are from slight mutations! All life on Earth evolved from a single common ancestor. A singlecelled organism that lived in the water. As time went forward, that organism changed and evolved and became different things, depending on the environment. Groups formed. One group stayed the same, the other groups changed and became different organisms. This happened over millions and millions of years, and that’s how we got all the different forms of life on Earth. Fossils provide proof of this. Fossils are preserved in date-order, and give us an accurate timeline of what happened, and in the order it happened. We even share common structures with other animals on the planet. These are called “homologous structures”. TYPES OF NATURAL SELECTION STABILIZING SELECTION In this type of natural selection, the EXTREME phenotypes are eliminated, and the population resembles a “middle of the road” blend between the two extremes. DIRECTIONAL SELECTION In this type of natural selection, one of the extremes of the phenotypes is favored, and the population moves towards those set of traits. DISRUPTIVE SELECTION In this type of natural selection, the extreme phenotypes both become dominant, and the common phenotype is eliminated. This usually occurs as the result of a natural disaster. SPECIATION There’s so much differentiation in life on this planet. How do we get new species? Where do they come from? There are 2 mechanisms we are going to look at that help explain this a little better. SPECIATION First, let’s define what makes something a species. Two organisms are considered to be the same species when: 1. They are able to successfully produce a healthy offspring 2. The offspring they produce are fertile, and able to have offspring of their own. ALLOPATRIC SPECIATION ALLOPATRIC SPECIATION occurs when you have a natural separation of a single species. Over time, they develop different traits, and can no longer produce fertile offspring, making them each a new species! SYMPATRIC SPECIATION Couldn’t find a good pic. Gotta draw one. Ugh. Do the tree/bush thing, that works. SYMPATRIC SPECIATION occurs when you have NO separation. Over time, two new species develop SIDE BY SIDE due to a difference in environment that does not physically separate them.