* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cross section of the Earth
Chicxulub crater wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Clastic rock wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Baltic Shield wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
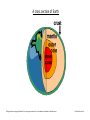
A cross section of Earth © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. Y3 Sc Rocks Session B The Structure of the Earth Further Information The Earth is a sphere with a diameter of 12,700m. As we go deeper and deeper into the Earth the temperature & pressure rises. Considering the size of the planet, the Crust is very thin. We live on this outer layer. It is made of hard rocks that have been wrinkled & bent to make mountains and valleys. The thinnest parts of the crust are under the oceans; the thickest parts are in mountainous regions on the continents. The Mantle is the layer under the crust. It is a very thick layer of red-hot solid rocks; some of these rocks are so soft that they ooze about and can blast out of cracks in the crust, as lava. The layer under the mantle is called the Outer Core. It is made of liquid iron and nickel. Special movement in this section is responsible for the Earth’s magnetic field Finally, the bit in the middle is called the Inner Core. The weight of all the rocks above it squash the core into a solid ball of iron and nickel. It is thought to be between 5000-6000°C – unbelievably hot – 60 times hotter than boiling water!! © Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. Y3 Sc Rocks Session B