* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geog 101: Chapter 3 Quiz
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Provenance (geology) wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
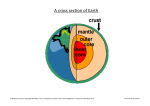
Geog 1001: Quiz 2 study guide J. Naumann 1. Know the difference between endogenic processes and exogenic processes of land formation. 2. Of what is the lithosphere composed? 3. Where are earthquakes most likely to occur? 4. What is the place where the earth’s crust actually moves in an earthquake called? 5. What factors influence the amount of ground shaking caused by earthquakes? 6. What is the nature and behavior of magma? 7. In what kind of plate boundary is material from the crust very slowly forced downward, back into the mantle? 8. What kind of rocks are formed when molten crustal material cools and solidifies? 9. What kind of rocks result when rocks eroded from higher elevations (mountains, hills, plains) accumulate at lower elevations (such as swamps and ocean bottoms)? 10. Where are shields located? 11. Near a convergent plate boundary, rocks fracture because they are compressed: such fractures are what kind of faults? 12. During dry periods, most of the water flowing into streams is supplied from where or by what? 13. The Appalachians, the European Alps, and the Himalayas are examples of mountain ranges formed by what process? 14. What are some of the effects of meandering streams? 15. What are Alpine glaciers like and where do they form? 16. What is a ridge of material dumped at the end of a glacier called? 17. What is the term for thick layers of wind-blown silt? 18. What landform features have resulted from the melting back of glaciers? 19. What is an extremely long ocean wave created by an underwater earthquake that may travel hundreds of kilometers per hour and cause much damage called? 20. What were the Hawaiian islands actually built from and what was the nature of their formation?