* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download January 29, 2002 - wvhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
Survey
Document related concepts
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
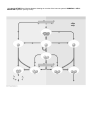
WLHS / AP Bio / Monson Name Date Per CH 43 STUDY QUESTIONS, part 2 – Immunity; Immune Disruptions (43.3-43.4) 1) In general, what is the difference between humoral immunity and cell mediated immunity? Which cells are involved in each? 2) What are “antigen presenting cells” (APCs)? What is their function in the immune response? 3) a) What are CYTOKINES? b) From which cells are cytokines secreted? (see fig. 43.16) c) What stimulates the release of cytokines? (see fig. 43.16) 4) How does an activated cytotoxic T cell kill its target cell? (see fig. 43.17) 5) Label the following diagram showing the activation of a B cell and the subsequent humoral response. (see fig. 43.18) 6) Describe the various mechanisms of antigen disposal: ● neutralization: ● opsonization: ● complement activation & pore formation: 7) a) Distinguish between active and passive immunity. (How is each type acquired? Which type is lasts longer?) b) Distinguish between naturally acquired and artificially acquired immunity. c) Describe how one might develop artificially acquired passive immunity. 8) How are MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES being used in recent medical diagnoses & treatments? 9) REVIEW: A woman of blood type B-negative is pregnant with a fetus whose blood type is A-positive. a) Explain (genetically) how this occurred. (i.e. what blood type could the father be?)…think GENOTYPES! b) Is there any risk to mother or child with respect to the different ABO blood groups? Why or why not? c) Is there any risk to the mother, child, or subsequent children with respect to the Rh factor? Explain. 10) a) What are two measures taken to reduce the chances of rejection of a transplanted organ or transplanted tissue? 1) 2) b) What is unique about bone marrow transplants? What is done to minimize the risks that accompany a bone marrow transplant? 11) a) Describe the major events that occur in an ALLERGIC REACTION. What are some common ALLERGENS? b) Why is an acute allergic response (i.e. anaphylactic shock) so dangerous? What substances are known to provoke such extreme reactions in some people? 12) a) What is meant by AUTOIMMUNITY? b) What conditions / events might result in autoimmunity? c) Complete the chart of autoimmune diseases below: Disease Symptoms Targets of autoimmune response Lupus erythematosus Rheumatoid arthritis Insulin-dependent diabetes (type 1) Multiple sclerosis 13) What does HIV stand for? 14) List four ways in which HIV is transmitted. 15) List two ways that HIV is NOT transmitted. 16) What is the role of CD4 in HIV infection? Why are T H cells highly susceptible to HIV infection? 17) Why has a vaccine for HIV been so elusive? See back of this page for one more diagram! 18) Label (& STUDY!) the following diagram showing an overview of the immune system’s HUMORAL & CELLMEDIATED responses. (see fig. 43.20)