* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download • - Hatboro
Cyclic nucleotide–gated ion channel wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
P-type ATPase wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Mechanosensitive channels wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
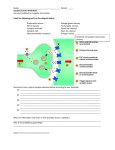
Name _______________________ Per ____ Muscle Physiology Project OBJECTIVES: Learn the biochemistry behind muscle cell contraction and relaxation Relate the structures of a nerve cell and muscle cell to their functions You may create a stand-alone poster, animated PPT (animations or stop-action), stop-action photography, videotaped skit, illustrated book or any other medium that will effectively complete the objectives in a visual manner. All steps must be shown in order. You must show the following structures/events: motor neuron synaptic knob muscle fiber (cell) synaptic cleft transverse tubules sarcoplasmic reticulum movement of ions (charged molecules) movement of ACh and AChE all mentioned channels all mentioned pumps myosin heads cocked-back myosin heads forming cross-bridges with actin sarcomere relaxed sarcomere contracted 40 steps x 2 pts apiece = 80 + 10pts for creativity/neatness = 90 pts total Step Score _____/40 493722328 Step Score x 2 ______ + Creativity Score ______ = Total Score ______/90 6/28/2017 1 To start things off (9): _____synaptic vesicles containing Acetylcholine (ACh) are in motor neuron _____sodium (Na+) is concentrated in the synaptic cleft _____potassium (K+) is concentrated within the muscle fiber _____Ca2+ has been sequestered within the sarcoplasmic reticulum in the muscle fiber. _____Ca2+ is also highly concentrated outside the synaptic knob _____The myosin heads are cocked back, with ADP and Pi present _____Tropomyosin covers the actin binding sites _____The interior of the muscle fiber is negatively charged _____the muscle fiber is relaxed Contraction (17): _____within neuron, electrical impulse travels down axon to synaptic knob _____voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in synaptic knob open in response to impulse _____ Ca2+ diffuses into synaptic knob _____ synaptic vesicles containing acetylcholine (ACh) fuse with neuron membrane in synaptic knob _____ACh released into synaptic cleft through exocytosis, diffuses across cleft _____ACh binds with ligand-gated Na+ channels in motor end plate of muscle fiber (and transverse tubules) _____Sodium (Na+) channels open in sarcolemma (and transverse tubules) _____Na+ diffuses into muscle fiber 493722328 6/28/2017 2 _____interior of muscle fiber becomes positively charged (due to Na+) _____voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in sarcoplasmic reticulum open _____Ca2+ diffuses from sarcoplasmic reticulum into sarcoplasm _____Ca2+ binds to troponin (the “lock”), causing a conformational change (change in shape) _____Tropomyosin (the dead-bolt) fibers are pushed out of the way, exposing actin binding sites _____The myosin heads of the thick fibers bind with the actin, forming crossbridges _____myosin heads flex (causing the release of ADP and Pi, from the myosin head) and pull on actin, causing sarcomeres to shorten. _____potassium (K+) channels open SLOWLY in sarcolemma (and transverse tubules) _____K+ diffuses out of muscle fiber (although more slowly than Na+ diffuses in) Relaxation (14): _____voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in the motor neuron close _____Ca2+ pumps in the motor neuron cell membrane pump Ca2+ out of motor neuron and out of synaptic knob using ATP _____ACh is broken-down into acetyl (A) and choline (Ch) by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in the synaptic cleft. Both are recycled back into the neuron where acetyl and choline are combined back into ACh and stored once again in synaptic vesicles (endocytosis) 493722328 6/28/2017 3 _____chemically-gated Na+ channels in the sarcolemma close _____K+ channels in sarcolemma close _____the Na+/K+ ATP pump in the sarcolemma pumps 3 sodium back out into the synaptic cleft along with 2 potassium pumped into the muscle fiber using ATP _____This makes the interior of the muscle fiber negatively charged once again _____ voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in the SR close because the muscle fiber is now negatively charged _____Ca2+ pumps in the SR membrane actively (using ATP) pump Ca2+ back into the SR _____ Ca2+ releases from the actin binding sites _____ATP binds to the myosin head, causing it to release from actin binding site _____ ATP is hydrolyzed into ADP and Pi, causing a conformational (shape) change in the myosin head and “cocking” it back to the origin position (like a mouse trap) _____tropomyosin slides back over to cover the actin binding sites _____Sarcomeres slide apart, thereby allowing the muscle to relax 493722328 6/28/2017 4