* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download exam1
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
History of subatomic physics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Chien-Shiung Wu wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
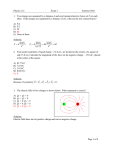
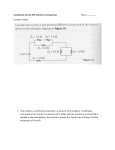
Physics 112 Exam I Spring 2006 Name_________________ Physics 112 Spring 2006 Exam 1 Wednesday, Feb 8 Directions: This 50-minute exam consists of twenty multiple-choice questions. This test is worth 20% of your final grade. (One point is equal to 1% of the final grade.) The questions on this test are not in order of difficulty. You must mark all of your answers on both your test and the answer sheet. In marking the multiple choice bubble sheet use a number 2 pencil. Do not use ink. If you did not bring a pencil, ask for one. Fill in the appropriate circles completely. If you need to change any entry, you must completely erase your previous entry. Carefully read each question and its five possible answers. Select one and only one answer for each question. Choose the answer that is closest to the correct one. Be sure to write you name on every sheet. You have a sheet in the back of the test that you may use for any extra rough work. When you are finished with the exam, place all exam materials, including the bubble sheet, the exam itself, and scratch paper that you used for the exam, in your folder and return the folder. Good luck! Page 1 of 9 Physics 112 Exam I Spring 2006 1. A downward force is exerted on a negative charge. What is the direction of the electric field at the point where the charge is located? A. B. C. D. E. Left Right Upward Downward Not enough information to answer the question 2. Two particles of equal charge, Q = 1.0 μC are located at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side d = 10.0 cm. What is the magnitude of the electric field at the third corner of the triangle? A. B. C. D. E. 0.9 x106 N/C 1.6 x106 N/C 3.2 x106 N/C 4.8 x106 N/C 0 3. Four particles of equal charge, Q = 1.0 μC are located at the corners of a square of side d = 10.0 cm. What is the electric field at the center of the square? A. B. C. D. E. 0.9 x106 N/C 1.6 x106 N/C 3.2 x106 N/C 4.8 x106 N/C 0 4. The electric field lines in a certain region of space are as shown below. Compare the magnitude of the electric field at points 1, 2 and 3. 1 A. B. C. D. E. 2 3 E1 = E2 = E3 E1 = E2 > E3 E1 > E2 > E3 E1 = E2 < E3 E1 = E2; E3=0 Page 2 of 9 Physics 112 Exam I Spring 2006 5. A solid metal sphere of radius 2.0 cm carries a total charge of -0.1 μC. What is the magnitude of the electric field at a distance from the sphere center of 1.0cm? A. B. C. D. E. 0.9 x106 N/C 9.0 x106 N/C -0.9 x106 N/C -9.0 x106 N/C 0 6. An unknown electric charge is placed in the center of a cubic box. What will happen with the flux from the box if each side of the box will be doubled, but the charge will remain unchanged? A. B. C. D. E. The flax will remain the same The flax will be doubled The flax will increase four times The flax will decrease two times The flax will decrease four times 7. An electron (charge q = 1.60x10-19 C, and mass m = 9.11x10-31 kg) is accelerated in a uniform field between two parallel charged plates. Potential difference between the plates is V = 1000 V. The electron is accelerated from rest near the negative plate. What is the speed of the electron as it reaches the positive plate? A. B. C. D. E. 1.2 x107 1.9 x107 2.5 x107 3.2 x107 4.1 x107 m/s m/s m/s m/s m/s 8. Five identical capacitors, 50 μF each, are connected in series, and are then connected to a battery of 3 V. What charge is stored in each capacitor? A. B. C. D. E. 30 μC 60 μC 83 μC 150 μC 750 μC Page 3 of 9 Physics 112 Exam I Spring 2006 9. How does the energy stored in the capacitor change if the potential difference between the plates of the capacitor is doubled? A. B. C. D. E. Increased twice Decreased twice Increased four times Decreased four times Remains the same 10. Ten resistors 50 each are connected in parallel. What is the effective resistance? A. B. C. D. E. 5 10 50 100 500 11. Two cylindrical resistors, R1 and R2, are made of identical material. R2 has twice the length of R1 but half the radius of R1. They are connected to a battery as shown. The internal resistance of the battery can be neglected. The ratio of currents I1 /I2 flowing through R1 and R2 is equal to I1 A. B. C. D. E. I2 0.5 1 2 4 8 Page 4 of 9 Physics 112 Exam I Spring 2006 12. Two resistors R1 = 5 and R2 = 10 are connected in series and are then connected to a battery with emf, ε = 12 V. The internal resistance of the battery can be neglected. Find the electric power delivered by the battery. A. B. C. D. E. 1.6 W 3.2 W 6.4 W 9.6 W 12.8 W 13. A battery with emf of 12 V and internal resistance 2 Ω is connected to the resistance of 22 Ω. What is the terminal voltage of the battery? A. 12 V B. 11 V C. 10 V D. 9 V E. 3 V 14. What is the resistance of an electric light bulb that consumes 100 W when connected to a 120 V outlet? A. B. C. D. E. 1.2 Ω 100 Ω 120 Ω 144 Ω 12 k Ω 15. What is the peak (amplitude) value of voltage in the standard 120 V line used in US? A. B. C. D. E. 110 V 120 V 170 V 240 V 360 V Page 5 of 9 Physics 112 Exam I Spring 2006 16. Two batteries with ε1 = 9.0 V and ε2 = 6.0 V, and two resistors R1 = 30 Ω and R2 = 30 Ω are connected as shown below. What is the current in resistance R1? 1 R1 R2 2 A. B. C. D. E. 0 0.1 A 0.2 A 0.3 A 0.5 A 17. What statement is wrong? A. At any junction point in an electric circuit, the sum of all currents entering the junction must equal to the sum of all currents leaving the junction. B. The sum of the changes in potential around any closed path of a circuit must be zero. C. The ammeter should be inserted in series with the resistance, to measure the current in this resistance. D. The voltmeter should be connected in series with the resistance, to measure potential across the resistor. E. Resistance of an ideal ammeter is zero. 18. The relaxation time of the RC circuit is 10.0 s. The initial current (during the discharging process) is 10.0 mA. What current will be after 20.0 s? A. B. C. D. E. 0 1.35 mA 3.68 mA 5.00 mA 10.0 mA Page 6 of 9 Physics 112 Exam I Spring 2006 19. Positive charge q is moving with velocity v in the magnetic field B as shown below (with vectors v and B on the surface of the page). What is the direction of the magnetic force? v q A. B. C. D. E. B Parallel to v Parallel to B Exactly between v and B Into the page Out of the page 20. A positively charged particle is moving in a magnetic field. What is the angle between the velocity of the charge and the direction of the magnetic field if the magnetic force on the particle is zero? A. B. C. D. E. 90° 45° 30° 0 Magnetic force can not be zero if the speed of the particle and the magnetic field are not zero. Page 7 of 9 Physics 112 Exam I Spring 2006 Scratch Paper (intentionally left blank) Page 8 of 9 Physics 112 Exam I Spring 2006 Record Sheet You may fill in this sheet with your choices, detach it and take it with you after the exam for comparison with the posted answers 1 11 2 12 3 13 4 14 5 15 6 16 7 17 8 18 9 19 10 20 Page 9 of 9