* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download General Ecology
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive evolution in the human genome wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
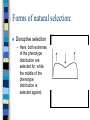
General Ecology Basic Principles Basic Principles Definition of principle / law: – Hypothesis – Theory – Law How do we test hypotheses? – Support or falsification? – Consequences of a wrong decision Scientific Method Science is a process of conjecture and refutation. – Each time we make a decision about a conjecture, we might be wrong. – Consider the definitions of the following words: Truth, Fact, Reality, Belief, and Proof. – Now, as an example, consider how a bat views the world. What are the basic principles of Ecology? Laws of physics and chemistry. – Laws of thermodynamics Evolution via natural selection. – Definition of evolution: – Organic evolution is defined as a change in allele frequencies over time. Some examples of evolution The peppered moth in England. Kangaroo rats in California domestic dogs People – Diabetes – Skin color – Height??? How does evolution work? Darwin’s observations: – There is variation amongst organisms. – That variation is heritable. – Some forms of variation are better than others. – Those organisms with the better forms of variation survive longer, and produce more offspring. How does evolution work? What is the consequence of these observations? – Changes in allele frequencies over time. Important point! Notice, we did not use the idea “survival of the fittest.” – This idea was used to justify ‘social darwinism’ earlier this century. – What we as ecologists mean by ‘fittest’ is not the same as what the general public thinks. – Fitness refers to production and survival of progeny. Another important point! Evolution is not theory, it is law (principle). This does not mean it is true, it means that the hypothesis has been tested extensively, and never falsified. The veracity of evolution says nothing about the existence of a supreme being. Forms of natural selection Stabilising selection. – Here, the extremes of the phenotyps distribution are selected against, while the center of the phenotype distribution is selected for. Forms of natural selection Directional selection – Here, one end of the phenotype distribution is selected for, while the other end is selected against. The result is a shift in the phenotype distribution. Forms of natural selection: Disruptive selection – Here, both extremes of the phenotype distribution are selected for, while the middle of the phenotype distribution is selected against. Forms of natural selection Sexual selection – Here, members of one sex select specific characteristics in the opposite sex. – Consider the secondary sexual characteristics in humans, colors in birds, sexual size dimorphism in mammals, dewlaps in Anoles, reverse sexual size dimorphism, etc. – Sexual selection is important because the resource is limiting. Forms of natural selection Kin selection – We often observe behaviors that are difficult to interpret. For example, green woodhoopoes remain at the natal nest and help their parents rather than establish their own nests. – Prairie dogs give alarm calls to warn of coyotes. Forms of natural selection Kin selection cont. – These patterns make sense only in the context of inclusive fitness. – There are examples from humans: • who is most likely to rush into a burning house to save a child? • Does altruism exist, or can it be explained as a selfish act? Forms of natural selection Group selection – This idea is derived from a book by V. C. Wynn-Edwards back in the early 60’s. Wynn-Edwards was trying to explain the fact that few organisms overpopulate their habitats (except humans apparently). He suggested that lemmings committed suicide by going over the cliffs of Dover, for the good of the species. Forms of natural selection Group selection cont. – Walt Disney picked up on this, and produced a film for his weekly ‘Wonderful World of Disney’ back in the 60’s. It has become an urban legend that lemmings commit suicide. They do not. How did Disney film the mass suicide? Forms of natural selection At what level does natural selection operate? – Allele? – Chromosome? – Cell? – Organism? – Population? – Species? How does speciation occur? Natural selection is only the mechanism by which most evolution occurs. In order to understand the history of life on earth, we must understand how speciation works. We need: some form of reproductive isolation. Reproductive isolation Behavioral Temporal Morphological Social Geographic Speciation Once there is reproductive isolation, there must be selection which produced different phenotypes/genotypes in the 2 groups. Thus, if the groups again become sympatric, there will not be gene flow. A species is a group of individuals that is reproductively isolated from other such groups. Obviously, there are problems with this definition. Consider some examples: Rasenkreise of salamanders and pocket mice. K-rats in California Domestic dogs. Humans? Even though we rarely (note, I did not use never) observe speciation, it clearly happens. More examples Convergence in design – hedge hogs, porcupines, and echidnas. – Whales & dolphins, penguins, and tuna (note: the writers of the Bible did not realize whales were mammals - neither do most people). Pilot whale (porpoise) Killer Whales False killer whales Emperor Penguins If speciation occurs, what can we say about the history of life? Consider the homologies between organisms. For example: limb structure in vertebrates; circulation in fish, amphibians, reptiles, mammals, and birds; distribution of sebaceous glands in vertebrates; heterochrony in humans and chimps. What is the ultimate homology? The genetic code. Now, are we biased in any way? Of course. – Gradualism: the idea that all evolutionary change is slow and stately. – Progressivism: the idea that evolution leads to some pinacle or perfect form (presumably us). – Determinism: the idea that our fates are predetermined. Evolutionary biases – Adaptationism: the idea that we are perfectly adapted to our environment. – Consider the panda, consider your pinky or your baby toe, or consider your ear lobes.