* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIO101 Unit 4
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
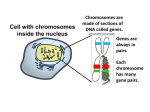
BIO101 Unit 13 Meiosis, Organismic Reproduction & Genetics Glossary alleles one member of a pair of genes that occupy a specific position on a specific chromosome that affect the same trait. asexual reproduction Type of reproduction that usually requires only one parent and only one sex cell. binary fission a type of asexual reproduction which occurs when a unicellular organism divides into two unicellular organisms by mitosis. blastocyst early stage of human embryonic development that consists of a hollow fluid-filled ball of cells that implants in the uterus wall of the female. blastula hollow ball of cells occurring during the first stages of animal embryonic development prior to the gastrula stage; 23 to 32 cells big. budding A type of asexual reproduction which occurs when a new organism grows directly off an adult. cleavage rapid cellular divisions that occur during the first stages of animal development; usually occurs without cytoplasmic increases or cellular enlargement. conjugation The type of sexual reproduction when there is a temporary union between two individuals in which genetic material is exchanged; usually this occurs between two unicellular organisms. dominant allele A gene which is always expressed when present. diploid the normal number of chromosomes; (2n) twice the number of chromosomes found in a gamete. egg female sex cell; also referred to as ovum. ectoderm the outer germ layer of the gastrula stage that gives rise to the nervous system, epidermis layer of the skin, and lining of the oral cavity and the rectum. endoderm the inner layer of the gastrula stage that gives rise to the lining of the digestive, urinary and respiratory systems. fertilization union of the sperm nucleus and the egg nucleus which creates the zygote with a diploid number of chromosomes. gamete a haploid sex cell; the egg or sperm which contain one-half the normal number of chromosomes; the egg unites with a sperm to form the zygote during fertilization. gastrula an early cleavage stage of embryonic development between 32 and 64 cells big which results in the formation of the three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. gene locus the position that a given gene occupies on a chromosome. genetics The branch of biology that deals with heredity, especially the mechanisms of hereditary transmission and the variation of inherited characteristics among similar or related organisms genotype the combination of alleles (genes) located on homologous chromosomes that determines a specific characteristic or trait. gonads an organ that produced gametes; testes produce sperm, and the ovary produces eggs. haploid one-half the normal number of chromosomes; (n) sex cells are haploid cells. heredity the biological process whereby genetic factors are transmitted from one generation to the next; the total of inherited attributes; the transmission of traits from ancestor to descendant. Inheritance the process of genetic transmission of characteristics from parents to offspring; the sum of characteristics genetically transmitted from parents to offspring. meiosis the cellular division process that results in the production of sex cells; this process is a reduction division because the number of chromosomes in the sex cells is reduced by one-half. mesoderm the middle layer of the gastrula stage that gives rise to the muscles, skeleton and urinary, circulatory and reproductive systems. monohybrid cross a one-trait genetic cross; a genetic cross involving only one characteristic such as hairline. morula ball like cleavage stage of embryonic development resembling a mulberry 8 to 16 cells big. oogenesis production of eggs in females by the process of meiosis. phenotype The observable physical characteristics of an organism, as determined by the organisms genetic makeup; the expression of a specific trait, such as hair color or blood type, based on genetic makeup of an organism. recessive allele A gene or allele which is only expressed in the absence of a dominant gene (allele). regeneration a type of asexual reproduction which occurs a piece of an organism will develop into a new organism. sperm male sex cell. spermatogenesis production of sperm in males by the process of meiosis. syngamy a type o sexual reproduction between two unicellular organisms that temporarily fuse to exchange genetic material. zygote a fertilized egg; a diploid cell formed by the union of egg and sperm.