* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review sheet Semester 2 Exam
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
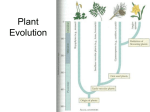
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Review sheet Semester 2 Exam Life Science Name:________________________ Period: _________ ******Complete this sheet to study for the final exam. We will work on it each day in class- so don’t loose it! I will offer help after school until 3:30 to answer any questions you might have. Completed review packets can be turned in on the day of the final for the last grade of your quarter 4 grade.************ The final includes Chapters 6 through 13 and human reproduction. 1. Go over all of the bold words for each chapter listed. 2. Go over your class notes, old review sheets, final notes, and diagrams. Chapter 6 1. What is classification and binomial nomenclature? Organization of organisms by similarities ; Linnaeus’ naming system where each organism is given a two part name, the genus and species 2. What is the proper way to write a scientific name? Use the genus and then species names in italics with the first letter of the genus capitalized and the species name 3. What are the two kingdoms of bacteria? How do they differ in cell structure from the rest of the living organisms found on Earth? Eubacteria and Archaebacteria; they are both prokaryotes 4. What are the three bacteria shapes ? spherical, spiral and rod shaped 5. Bacteria hibernate using an __endospore__________________ cell. Bacteria reproduce by using a form of asexual reproduction called __binary__________ _fission____________ and can trade genetic information using __conjugation__________________. 6. Why are bacteria helpful and important for planet Earth? They decompose dead organic matter to be recycled into carbon cycle. 7. How does nitrogen fixation help a plant? Bacteria in the roots of a plant change gaseous nitrogen in to a solid form. The solid nitrogen form is used by the plant like a man-made fertilizer. 8. What is a virus and how does it reproduce? A non-living particle that invades cells and uses them to reproduce. It takes control of the genetic material of the cell. 9. Name two bacterial diseases and two viral diseases. Look at list page 210 10. What is the relationship between a parasite, and a host? Parasite harms the host and gets benefits where as the host is harmed. 11. Is a virus living or nonliving? Explain Non-living it can not reproduce by itself and does not respond to external stimuli Chapter 7 1. What are the main characteristics of the Protista kingdom? And, why is it the “junk drawer kingdom”? They are a collection of misfits organisms. They share characteristics from all the kingdoms. They are all eukaryotes. 2. How do plant-like protists differ from animal-like protists? Plant-like are autotrophs and animal eat other organisms and have motility 3. Define: flagellum, lichen, hyphae, budding Flagellum- a whip like tail Lichen- a symbioticc relationship between a blue green alga and a fungus Hyphae- the threadlike structures of fungus Budding- the asexual reproduction of yeast cells by splitting unevenly 4. Place each organism in the correct box. amoeba, paramecium, euglena, diatoms, red algae, green algae, brown algae, zooflagelates, sporozoans, dinoflagellates Animal-like protists Sarcodines (with psuedopod )- amoeba Ciliates- paramecium Zooflagellates- giardia Sporozoans- are parasitic – cause malaria Plant-like protists All algae: Euglenoids- euglena Dinoflagellates – cause red tide Diatoms – used in toothpaste, polish etc. Green algae Brown algae - kelp Red algae- used in ice cream 5. What products are made from diatoms? Toothpaste, polish, pool filters, diatomaceous earth, insecticide 6. What are the characteristics of the Fungi kingdom? decomposers, moist areas, use spores to reproduce 7. What are the four main groups of fungi? Their spore producing organs are called_fruiting__ _bodies____. 8. How are fungi grouped into their phyla? By the spore producing structure’s shape Chapter 8 1. How do simple plants in differ from complex plants in chapter 9? Simple- spores Complex use seeds and are all vascular 2. What are the gametophyte’s and sporophyte’s functions? Gametophyte makes gametes Sporeophyte makes spores 3. What is alteration of generations? And, why is it beneficial for a simple plant to use alteration of generations? Alternating the plant forms using one form(sporophyte), than the other (gametophyte) 4. ___gametes_____________ are the sex cells produced by the gametophyte. 5. What is the difference between ferns and mosses? Ferns are vascular and mosses are not Chapter 9 1. What is the difference between seed plants and simple plants. And, what are some examples of seed plants? Oak tree, pine tree, apple tree, grass, etc. 2. Fill in the chart comparing how angiosperms and gymnosperms are different and alike? Give 2 examples of each. Gymnosperm characteristics “naked seed” many use cones to reproduce many have scales or needles instead of leaves Angiosperm characteristics “covered seed” produce flowers 3. What are 5 ways to identify a monocot from a dicot? Name 2 examples of each. Monocot Dicot Mult. of 3 petals Mult. of 3 sepals Parallel veins 1 cotyledon tap root vascular bundles are scattered Mult. of 4,5 petals Mult. of 4,5 sepals Branched veins 2 cotyledons fibrous roots vascular bundles are in a ring 4. What do the phloem, xylem and cambium do for a plant? Transports food; transports water and nutrient;, makes new vascular tissues 6. What are the functions of the roots, stems, leaves, and flowers? Roots- anchor plant, collect water and nutrients Stems- hold vascular tissues, hold up plant Leaves- collect sunlight, photosynthesis, respiration Flowers- reproduction for plant 7.On a separate piece of paper, draw a flower. Diagram the parts of a flower and label each part’s function. Look at page 290 8. What are the forms of seed dispersal? And, why is it important? “Hitch hiker”, wind, water to move the seeds away from the parent plant to lower competition 11. What is the difference between fertilization and pollination? Fertilization is the combination of egg and sperm. Pollination is the transfer of pollen to the stigma. 12. What adaptations of flowers help pollination? High anthers and stigma Colored petals Fragrance 13. What are photosynthesis and respiration? And, what’s their purpose? What are the chemical equations? Sunlight + CO2 + water = O2 + sugars (Respiration is the reverse.) 14. On a separate sheet of paper. Draw a diagram of a leaf and label the parts. Know what each part does for the plant. Look at page 279 15. The ___ovary___________-develops into the fruit of the plant. 16. What are stomata and from what kind of cells are they made? Holes in leaf made by two guard cells 17. Define: phototropism, thigmotropism, gravitropism, transpiration complete flower, incomplete flower a. b. c. d. e. f. a plant’s response to light a plant’s response to touch a plant’s response to gravity (roots go down and leaves go up) the loss of water vapor from a plant a flower with both genders a flower with one gender Human Reproduction 1.Be able to label all of the female and male reproductive parts on a diagram. Look at the worksheet given out in class 2. For each part listed, write down its function in the body. Placenta – the organ in mother that supports fetus; gives food and oxygen and removes waste in blood Ovaries- makes and releases eggs in female fallopian tubes = oviducts – tubes to transport eggs to uterus uterus- large muscled organ holds fetus when pregnant vagina = birth canal – used to birth baby and to deposit sperm penis – deposits sperm in female testes – makes testosterone and sperm in male sperm – holds male’s genetic information Vas deferens – tubes to transport sperm from testes to glands to make semen epididymus – top area of testes prostate gland – makes basic fluid for semen urethra – tube for urination and sperm ejaculation scrotum – skin sac around testes semen – fluids and sperm 3. What are the male and female sex hormones and from where are they secreted? Estrogen from ovaries, progesterone from uterus, and testosterone from testes 4. Put these terms in order from youngest to oldest. (fetus, zygote, embryo, baby) zygote to embryo to fetus to baby 5. Which hormones are released at the onset of puberty? LH and FSH 6. What are four secondary sexual characteristics of both males and of females? Male- Pubic hair, facial hair, voice lowers, muscle mass, acne Female- breasts, hips widen, fat layer added, acne 7.What is the main purpose of the reproduction system? To make new organisms of the same kind 8. What are the five characteristics for the animal kingdom? Motility, many celled, heterotophs, most reproduce sexually, eukayotes 9.What does each phylum name in the animal kingdom mean? And, what is an example of each phylum? a. Porifera - Sponges b. Cnidaria – jellyfish c. Platyhelminthes – flatworms like tapewormor planaria d. Nematoda – round worm like nematods e. Annelida – segmented worms like earthworm or leech f. Molluska - snail g. Arthropoda – insects, arachnids, crustaceans, millipedes, centipedes h. Chordata – mammals, monotremes, marsupials 9. Describe how a sponge catches and eats its food. What is this called? Filters out food with collar cells by moving water through the body and out the pores “Filter-feeding” 10. What is the function of the collar cells, spicules, and outer layer of cells on a sponge? Look at page 321 11. What are the characteristics of a cnidarian? And, what are two examples? Stinging cells on tentacles, radial symmetry, invertebrete 12. Draw a picture of the two body plans of a cnidarian. Look at page 324 13. How does an echinoderm use its water vascular system and tube feet? The water is pumped it to the tubes inside the starfish and pressurized to move and retract the tube feet Look at page 367 14. What characteristics do all echinoderms share? Spiny looking skin, radial symmetry, water vascular system, invertebrete, incomplete digestive track 15. What are the characteristics of the Arthropoda ? (What are the main identifying features of an arthropod?) It means “jointed foot” so have jointed appendages, segmented bodies, invertebrates, exoskeleton, open circulatory system 16. The five classes of Arthropods are insecta, chilopoda, diplopoda, crustacea, arachnida. What is an example of each class? Insects (bee), millipeds, centipedes, crustaceans (crab), arachnids (spiders) 17. What are the features used to identify mollusks? Soft bodies, foot, mantle, invertebrte, Look at page 343 18. What is the function of the radula, mantle, foot, shell, gills in a mollusk? a. b. c. d. Rows of teeth that scrape away food Soft fleshy, muscular part of organism Muscle moves organism Respiration /collect O2 19. What are the noticeable features of annelids? Are segmented worms with segmented bodies, complete digestive track, invertebret 20. How does an arthropod breathe? Uses spiracles on sides of body 21. What is metamorphosis and how is it beneficial to the animals that use it? The change from one life form to another; lowers competition with same species 22. What are the characteristics of the phylum Chordata? Have notochord, nerve cord, gill slits at some time in their life (A vertebrate has a backbone in addition to the list above.)