* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Seedless Plants, Chapter 27
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
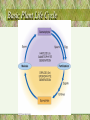
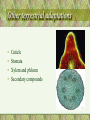
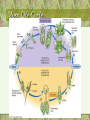
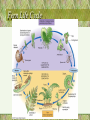
• Chapter #27 ~ The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants Plant Evolution • The Plant Kingdom – Nonvascular plants with a dominant gametophyte generation (Bryophytes) – Vascular plants with a dominant sporophyrte generation • Seedless plants (club mosses, ferns, wisk ferns and horsetails) • Seed plants – Plants with naked seeds (Gymnosperms) – Seeds enclosed within a fruit (Angiosperms) Alternation of Generations 1 • 2 parts of plant life cycle – haploid gametophyte generation – diploid sporophyte generation • Gametophyte plant – produces gametes by mitosis – gametes fuse (fertilization) to form zygote (first stage of sporophyte generation) Basic Plant Life Cycle Plant Evolution • Plants: multicellular, eukaryotic, photosynthetic autotrophs • Terrestrial colonization: • Vascular tissue • The seed • The flower Plant origins • Charophytes: green algae (closest plant ancestor) • Similarities: • 1-Homologous chloroplasts: chlorophyll a & b • 2- Biochemical similarity cellulose composition; peroxisomes • 3- Cell division similarity mitosis; cytokinesis • 4- Sperm similarity ultrastructure • 5- Genetic relationship nuclear genes; rRNA Characteristics that separate plants from algae ancestors • Apical meristems: localized regions of cell division • Multicellular, dependent embryos (embryophytes) • Alternation of generations • Walled spores produced in sporangia • Multicellular gametangia Other terrestrial adaptations • • • • Cuticle Stomata Xylem and phloem Secondary compounds Bryophytes • Mosses, liverworts, and hornworts • 1st to exhibit the embryonic condition (male = antheridium; female = archegonium) • Flagellated (water) sperm • No vascular tissue (imbibe water) • No lignin (short stature) • Haploid gametophyte is the dominant generation Moss Life Cycle Pteridophytes: seedless vascular plants • • • • • Ferns, club ‘moss’, horsetails True roots and leaves Roots have lignified vascular tissue Sporophyte-dominant life cycle Homosporous plants: a single type of spore…. • Sporophyte---->Single type of spore ---->Bisexual gametophyte ---->Eggs; sperm (flagellated; damp locations) • Carboniferous period plants Fern Life Cycle