* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ME 557 Howmwork #1
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Confocal microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Reflector sight wikipedia , lookup
Optical amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Optical rogue waves wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
3D optical data storage wikipedia , lookup
Ellipsometry wikipedia , lookup
Birefringence wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Optical coherence tomography wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Silicon photonics wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Image stabilization wikipedia , lookup
Optical fiber wikipedia , lookup
Optical tweezers wikipedia , lookup
Photon scanning microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Fiber Bragg grating wikipedia , lookup
Lens (optics) wikipedia , lookup
Optical aberration wikipedia , lookup
Schneider Kreuznach wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
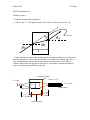
Winter 2006 W.Wang ME 557 Howmwork #1 Geometric Optics 1. Consider an optical flat of thickness t = 0.01 m. If n = 1.5 for light incident at 30 o what is the lateral shift in the ray? θ1 Lateral shift θ2 θ1 t 2. Light coupling into optical fiber and integrated waveguide structure is one of the most time consuming task. Assume that the fiber has a core diameter of 100m and a NA of 0.25, and trhe design requires that the total distance from the source to the fiber be 100mm, which lenses are appropriate (find lens’s focal length, f-number and numeric apeture magnification and clear aperature )? Acceptance angle NAfiber= 0.25 h = 1mm h’ =0.1mm =? Optical fiber Light source p = 100mm q = 10mm Optical system Winter 2006 W.Wang 3. Fiber coupling spheres. Tiny glass balls are often used as lenses to couple light into and out of optical fibers. The fiber end is located at a distance f from the sphere. For a sphere of radius a=1 mm and refractive index n =1.8, determine f such that a ray parallel to the optical axis at a distance y=0.7mm is focused onto the fiber, as illustrated in figure Ball lens fiber y 4. Derive the focal length for the general and bi-concave lenses. 5. Derive expression for effective focal length for two or more lenses system. 6. Show the graphical location of image for a three lenses system (thin lens approximation) Winter 2006 W.Wang Matrix Optics 1. Using ray- transfer matrix and find a relationship between radius R in terms of indices of nair, nlens and d where a diverging beam after going through this planar-convex lens can be collimated. 2. Remember the beam is diverge from a fiber, and after going through the lens system, the beam is a collimated with a beam diameter D. please find the ray-transfer matrix for the following lens system. fiber convex concave convex convex