Database Systems Syllabus - Lehman College
... Research Survey Paper Assignment (for graduate students only): Read papers in a specific research topic of database and write a survey-type research paper (around 12 pages). Each paper must have a detailed bibliography and each paper must consult at least 5 references. A paper with creative resea ...
... Research Survey Paper Assignment (for graduate students only): Read papers in a specific research topic of database and write a survey-type research paper (around 12 pages). Each paper must have a detailed bibliography and each paper must consult at least 5 references. A paper with creative resea ...
Lec 1
... Determine whether it matters • Isolate the network element and express it as an overhead on transactions executed on the LAN • Carry out tests locally and then across the links that are expected to be a problem • On an Australian Frame relay network with relatively low bandwidth links, we had a net ...
... Determine whether it matters • Isolate the network element and express it as an overhead on transactions executed on the LAN • Carry out tests locally and then across the links that are expected to be a problem • On an Australian Frame relay network with relatively low bandwidth links, we had a net ...
Lecture 3
... Function SUM returns sum of all values from the beginning of the table until current record Records are sorted by name: OVER (order by ...
... Function SUM returns sum of all values from the beginning of the table until current record Records are sorted by name: OVER (order by ...
Overview of Transaction Management
... Databases default to RC, read-committed, so many apps run that way, can have their read data changed, and phantoms Web apps (JEE, anyway) have a hard time overriding RC, so most are running at RC The 2PL locking scheme we studied was for RR, repeatable read: transaction takes long term read and writ ...
... Databases default to RC, read-committed, so many apps run that way, can have their read data changed, and phantoms Web apps (JEE, anyway) have a hard time overriding RC, so most are running at RC The 2PL locking scheme we studied was for RR, repeatable read: transaction takes long term read and writ ...
ASSOCIATION RULE MINING IN DISTRIBUTED DATABASE SYSTEM
... 4.If an item set has 2 local supports value and if the sum less than the minimum support value it may not be a global frequent itemset if itdoes not satisfies the foll.condn such that globalmin_support-current_minsupport < ...
... 4.If an item set has 2 local supports value and if the sum less than the minimum support value it may not be a global frequent itemset if itdoes not satisfies the foll.condn such that globalmin_support-current_minsupport < ...
CHAPTER 1: The Roles of Data and Database Administrators
... Procedures that process transactions so that outcome is the same as this. Processing transactions using a serializable schedule will give the same results as if the transactions had been processed one after the other. Schedules are designed so that transactions that will not interfere with each othe ...
... Procedures that process transactions so that outcome is the same as this. Processing transactions using a serializable schedule will give the same results as if the transactions had been processed one after the other. Schedules are designed so that transactions that will not interfere with each othe ...
The Cloud Database by Interworks, is a highly available, scalable
... Database operators can quickly start managing provisioned databases using the same tools they have been using for on-premise databases. ...
... Database operators can quickly start managing provisioned databases using the same tools they have been using for on-premise databases. ...
Link to Slides
... ◦ A RESERVED lock means that the process is planning on writing to the database file at some point in the future but that it is currently just reading from the file. Only a single RESERVED lock may be active at one time, though multiple SHARED locks can coexist with a single RESERVED lock. RESERVED ...
... ◦ A RESERVED lock means that the process is planning on writing to the database file at some point in the future but that it is currently just reading from the file. Only a single RESERVED lock may be active at one time, though multiple SHARED locks can coexist with a single RESERVED lock. RESERVED ...
Group-based Replication of On-line Transaction Processing Servers*
... locally and replies to the client. Upon the reception of the remote transaction’s commit outcome each replica applies t’s state changes through the execution of a high priority transaction consisting of updates, inserts and deletes according to t’s previously multicast write-values. The high priori ...
... locally and replies to the client. Upon the reception of the remote transaction’s commit outcome each replica applies t’s state changes through the execution of a high priority transaction consisting of updates, inserts and deletes according to t’s previously multicast write-values. The high priori ...
View File - UET Taxila
... A facility by which DBMS periodically refuses to accept any new transactions. All transactions in progress are completed and the journal files are updates. At this point, system is in a quiet state, and the database & transaction logs are synchronized. The DBMS writes a special record (checkpoint re ...
... A facility by which DBMS periodically refuses to accept any new transactions. All transactions in progress are completed and the journal files are updates. At this point, system is in a quiet state, and the database & transaction logs are synchronized. The DBMS writes a special record (checkpoint re ...
Module 2 Association Rules
... The design strategy of multidatabase is a combination of top-down and bottom-up strategy. Individual database sites are designed independently, but the development of MDMS requires the underlying working knowledge of sites. Thus virtualization of resources is not possible in multidatabase architectu ...
... The design strategy of multidatabase is a combination of top-down and bottom-up strategy. Individual database sites are designed independently, but the development of MDMS requires the underlying working knowledge of sites. Thus virtualization of resources is not possible in multidatabase architectu ...
Download-Database Assignment
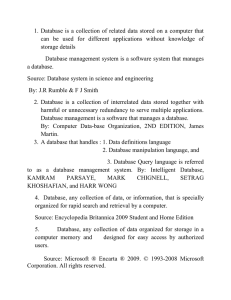
... 1. Database is a collection of related data stored on a computer that can be used for different applications without knowledge of storage details Database management system is a software system that manages a database. Source: Database system in science and engineering By: J.R Rumble & F J Smith 2. ...
... 1. Database is a collection of related data stored on a computer that can be used for different applications without knowledge of storage details Database management system is a software system that manages a database. Source: Database system in science and engineering By: J.R Rumble & F J Smith 2. ...
Database Administration
... Views or Schemas: Which restrict user views of the database Authorization Rules: Which identify users and restrict the action they may take against the database ...
... Views or Schemas: Which restrict user views of the database Authorization Rules: Which identify users and restrict the action they may take against the database ...
H-Store: A High-Performance, Distributed Main Memory Transaction
... more concise description of two of these classes and briefly discuss how H-Store generates an optimal execution strategy for each. Because a query can have unknown parameter values at deployment, the distributed query planner cannot always determine the transaction class before execution time. We pl ...
... more concise description of two of these classes and briefly discuss how H-Store generates an optimal execution strategy for each. Because a query can have unknown parameter values at deployment, the distributed query planner cannot always determine the transaction class before execution time. We pl ...
H-Store: A High-Performance, Distributed Main Memory Transaction
... more concise description of two of these classes and briefly discuss how H-Store generates an optimal execution strategy for each. Because a query can have unknown parameter values at deployment, the distributed query planner cannot always determine the transaction class before execution time. We pl ...
... more concise description of two of these classes and briefly discuss how H-Store generates an optimal execution strategy for each. Because a query can have unknown parameter values at deployment, the distributed query planner cannot always determine the transaction class before execution time. We pl ...
Chapter 15: Concurrency Control
... Select for update (SFU) treats all data read by the query as if it were also updated, preventing concurrent updates ...
... Select for update (SFU) treats all data read by the query as if it were also updated, preventing concurrent updates ...
Distributed Database Integrated Transaction Processing Technology
... Availability, Reliability, Safety, Confidentiality, Integrity and Maintainability. The importance of generating real-time business intelligence is that it is a building block to achieve better business process management and true business process optimization [10,11]. 4. Integrated distributed datab ...
... Availability, Reliability, Safety, Confidentiality, Integrity and Maintainability. The importance of generating real-time business intelligence is that it is a building block to achieve better business process management and true business process optimization [10,11]. 4. Integrated distributed datab ...
Data and Database Administration
... – Database – used during database updates – Table – used for bulk updates – Block or page – very commonly used – Record – only requested row; fairly commonly used – Field – requires significant overhead; impractical Types of locks: – Shared lock - Read but no update permitted. Used when just reading ...
... – Database – used during database updates – Table – used for bulk updates – Block or page – very commonly used – Record – only requested row; fairly commonly used – Field – requires significant overhead; impractical Types of locks: – Shared lock - Read but no update permitted. Used when just reading ...
Document
... has completed (i.e., the transfer of the $50 has taken place), the updates to the database by the transaction must persist even if there are software or hardware failures. ...
... has completed (i.e., the transfer of the $50 has taken place), the updates to the database by the transaction must persist even if there are software or hardware failures. ...
transaction
... • A concurrency control based on view equivalence should provide better performance than one based on conflict equivalence since less reordering is done but … • It is difficult to implement a view equivalence concurrency control • a concurrency control that guarantees conflict equivalence to serial ...
... • A concurrency control based on view equivalence should provide better performance than one based on conflict equivalence since less reordering is done but … • It is difficult to implement a view equivalence concurrency control • a concurrency control that guarantees conflict equivalence to serial ...
National Academy for Software Development
... Concurrency Control Techniques • Two basic concurrency control techniques: • Locking • Used in most RDBMS servers, e.g. Oracle, SQL Server, etc. ...
... Concurrency Control Techniques • Two basic concurrency control techniques: • Locking • Used in most RDBMS servers, e.g. Oracle, SQL Server, etc. ...
Chapter 16
... If a transaction Ti is aborted, all its actions have to be undone. Not only that, if Tj reads an object last written by Ti , Tj must be aborted as well! ...
... If a transaction Ti is aborted, all its actions have to be undone. Not only that, if Tj reads an object last written by Ti , Tj must be aborted as well! ...
Introduction
... statistics, and indexes (special data structures for efficient access) CPSC 310/603 ...
... statistics, and indexes (special data structures for efficient access) CPSC 310/603 ...