MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DOCTORAL GENERAL EXAMINATION PART 1 SEPTEMBER 7, 2000
... An 55 Fe x-ray source which emits 5.9 keV x-rays is located at sea-level. An absorber is located 30 m directly above the source. a) Find the fractional energy shift of the x-ray photon when it reaches the absorber. Make any reasonable approximation. b) The absorber has a very narrow resonance. How f ...
... An 55 Fe x-ray source which emits 5.9 keV x-rays is located at sea-level. An absorber is located 30 m directly above the source. a) Find the fractional energy shift of the x-ray photon when it reaches the absorber. Make any reasonable approximation. b) The absorber has a very narrow resonance. How f ...
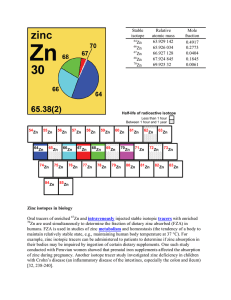
Zinc isotopes in biology Oral tracers of enriched Zn and
... the atomic nucleus. A pure chemical substance composed of atoms with the same number of protons in the atomic nucleus [703]. gamma rays (gamma radiation) – a stream of high-energy electromagnetic radiation given off by an atomic nucleus undergoing radioactive decay. The energies of gamma rays are hi ...
... the atomic nucleus. A pure chemical substance composed of atoms with the same number of protons in the atomic nucleus [703]. gamma rays (gamma radiation) – a stream of high-energy electromagnetic radiation given off by an atomic nucleus undergoing radioactive decay. The energies of gamma rays are hi ...
Tutorial for Chapter 8
... A Gaussian beam of Rayleigh range z0 = 50 cm and wavelength = 488 nm is converted into another Gaussian beam with using a lens of focal length f = 5 cm at a distance z = 75 cm. Find the beam waist and location (from the lens) for the new Gaussian beam. ...
... A Gaussian beam of Rayleigh range z0 = 50 cm and wavelength = 488 nm is converted into another Gaussian beam with using a lens of focal length f = 5 cm at a distance z = 75 cm. Find the beam waist and location (from the lens) for the new Gaussian beam. ...
Sample
... intensity would average to that of two bulbs. If you scanned over the whole volume with a detector small enough to see the variations on the scale of a wavelength, you would see intensity varying continually between total darkness and peak light. 2. One photon is a wave packet that doesn't last very ...
... intensity would average to that of two bulbs. If you scanned over the whole volume with a detector small enough to see the variations on the scale of a wavelength, you would see intensity varying continually between total darkness and peak light. 2. One photon is a wave packet that doesn't last very ...
Wave nature of light
... - since E = hf, photon’s energy for red light is not big enough to overcome forces attracting electron to metal so it can’t be ejected. But f is greater for violet and uv, so photon gives more energy to the electron can be ejected. (explains 2 & 4) - the brighter the light, i.e more intense, means ...
... - since E = hf, photon’s energy for red light is not big enough to overcome forces attracting electron to metal so it can’t be ejected. But f is greater for violet and uv, so photon gives more energy to the electron can be ejected. (explains 2 & 4) - the brighter the light, i.e more intense, means ...
www.osa-opn.org 36 | OPN Optics & Photonics News Illustration by Phil Saunders/ spacechannel.org
... quantum information processing protocols. In the presence of photon-pair entanglement, each of the constituent single photons becomes a statistical mixture of the relevant spectral and spatial modes, so that the detection of one of the photons heralds (i.e., announces the presence of) a single photo ...
... quantum information processing protocols. In the presence of photon-pair entanglement, each of the constituent single photons becomes a statistical mixture of the relevant spectral and spatial modes, so that the detection of one of the photons heralds (i.e., announces the presence of) a single photo ...
Slides1 - University of Guelph
... • To understand from basic principles how a quantum information protocol works in theory and in practice using optics • I chose quantum teleportation where we can understand the discrete (polarization) and continuous variable versions of this ...
... • To understand from basic principles how a quantum information protocol works in theory and in practice using optics • I chose quantum teleportation where we can understand the discrete (polarization) and continuous variable versions of this ...
Atomic number
... How many protons does Calcium have? What element has 17 protons and 18 neutrons? What is its atomic number? What is its atomic mass? ...
... How many protons does Calcium have? What element has 17 protons and 18 neutrons? What is its atomic number? What is its atomic mass? ...
Chapter 5 * Electrons in Atoms
... configuration of elements? 2. Explain why the actual electron configurations for some elements differ from those assigned using the Aufbau principle. 3. Arrange the following sublevels in order of decreasing energy: 2p, 4s, 3s, 3d, and 3p. 4. Why does one electron in a potassium atom go into the fou ...
... configuration of elements? 2. Explain why the actual electron configurations for some elements differ from those assigned using the Aufbau principle. 3. Arrange the following sublevels in order of decreasing energy: 2p, 4s, 3s, 3d, and 3p. 4. Why does one electron in a potassium atom go into the fou ...
Δk/k
... (N.B.: This function also describes the diffraction pattern from a single slit.) Therefore, under irradiation with frequency ω > 0, the transition probability has non-negligible intensity only 1. for ω0 ω 2 / t , that is at ω0 ω 0 within a width ω 2 / t (uncertainty relation), 2. for ω0 ...
... (N.B.: This function also describes the diffraction pattern from a single slit.) Therefore, under irradiation with frequency ω > 0, the transition probability has non-negligible intensity only 1. for ω0 ω 2 / t , that is at ω0 ω 0 within a width ω 2 / t (uncertainty relation), 2. for ω0 ...
Parallel algorithms for 3D Reconstruction of Asymmetric
... must be abandoned, but also the naive concept of reality which looked upon atomic particles as if they were very small grains of sand. At every instant a grain of sand has a definite position and velocity. This is not the case with an electron. If the position is determined with increasing accuracy, ...
... must be abandoned, but also the naive concept of reality which looked upon atomic particles as if they were very small grains of sand. At every instant a grain of sand has a definite position and velocity. This is not the case with an electron. If the position is determined with increasing accuracy, ...
Advanced Chemistry - Forestville Middle
... But actually Visible light constitutes a very small segment of the electromagnetic spectrum, which is composed of various types of electromagnetic radiation in order of increasing wavelength ...
... But actually Visible light constitutes a very small segment of the electromagnetic spectrum, which is composed of various types of electromagnetic radiation in order of increasing wavelength ...
Problem sets 09-20-2..
... Elastic Raman scattered light provides a useful signal for analytical purposes? ...
... Elastic Raman scattered light provides a useful signal for analytical purposes? ...
PPT
... energy states become available (due to kT) as T increases. Metals Have a partly filled band. Higher energy states are available, even at T = 0. ...
... energy states become available (due to kT) as T increases. Metals Have a partly filled band. Higher energy states are available, even at T = 0. ...
Electronic Structure
... it emits a quantum of energy E in radiation of definite frequency, . Since E for the change from E2 to E1 is always the same in a given atom, and h is a constant , must be a constant. Therefore, radiation always has the same energy and is always of the same frequency for this particular electro ...
... it emits a quantum of energy E in radiation of definite frequency, . Since E for the change from E2 to E1 is always the same in a given atom, and h is a constant , must be a constant. Therefore, radiation always has the same energy and is always of the same frequency for this particular electro ...
Unit 4 - School District of Durand
... • Electrons will remain at the lowest possible energy level that produces the most atomic stability. • More energy is required to exist farther away from the nucleus. This equates to higher potential energy. • Electrons that absorb energy can move to an energy level further away from the nucleus. • ...
... • Electrons will remain at the lowest possible energy level that produces the most atomic stability. • More energy is required to exist farther away from the nucleus. This equates to higher potential energy. • Electrons that absorb energy can move to an energy level further away from the nucleus. • ...
Chapter 7 – Quantum Theory and Atomic Structure Chapters 4 and 6
... becomes c = . Does this make sense? In high frequency light many wave cycles pass a given point in one second. If this is the case, the wavelengths must be short to get them through in the allotted time since the speed is fixed. Most light (e.g. from an incandescent bulb or the sun) contains many ...
... becomes c = . Does this make sense? In high frequency light many wave cycles pass a given point in one second. If this is the case, the wavelengths must be short to get them through in the allotted time since the speed is fixed. Most light (e.g. from an incandescent bulb or the sun) contains many ...
Answers
... It is easier to see interference if the wavelength is large. Therefore the electrons must be moving slowly. 9) The photo below shows the interference pattern produced by an electron double-slit experiment. The electrons were sent through a double-slit apparatus with slit separation of 200 nm. The de ...
... It is easier to see interference if the wavelength is large. Therefore the electrons must be moving slowly. 9) The photo below shows the interference pattern produced by an electron double-slit experiment. The electrons were sent through a double-slit apparatus with slit separation of 200 nm. The de ...
6.1 Organizing the Periodic Table
... increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties ...
... increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties ...
Chapter 4
... Think of orbitals as sort of a "border” for spaces around the nucleus inside which electrons are allowed. No more than 2 electrons can ever be in 1 orbital. The orbital just defines an “area” where you can find an electron. ...
... Think of orbitals as sort of a "border” for spaces around the nucleus inside which electrons are allowed. No more than 2 electrons can ever be in 1 orbital. The orbital just defines an “area” where you can find an electron. ...
Gr 10 Review sheet chemistry
... 2. Formation of a ________________ 3. Formation of _____________ 4. Release or absorption of_____________ ...
... 2. Formation of a ________________ 3. Formation of _____________ 4. Release or absorption of_____________ ...
X-ray fluorescence

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic ""secondary"" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis and chemical analysis, particularly in the investigation of metals, glass, ceramics and building materials, and for research in geochemistry, forensic science and archaeology.