Impacts of aortic stenosis and hypertension on left ventricular
... Concentric left ventricular hypertrophy is an adaptive mechanism compensating for pressure overload mainly by an increase of the myocardial wall thickness. But ultimately, left ventricular hypertrophy may lead to the development of myocardial ischemia, symptoms (i.e. angina, shortness of breath, diz ...
... Concentric left ventricular hypertrophy is an adaptive mechanism compensating for pressure overload mainly by an increase of the myocardial wall thickness. But ultimately, left ventricular hypertrophy may lead to the development of myocardial ischemia, symptoms (i.e. angina, shortness of breath, diz ...
Specialty Training Curriculum Paediatric Cardiology
... The most important function of the specialist training programme is to educate individuals who will become consultants capable of providing the highest standard of service to children with cardiac disorders and adolescents and adults with congenital heart disease. The educational process set out in ...
... The most important function of the specialist training programme is to educate individuals who will become consultants capable of providing the highest standard of service to children with cardiac disorders and adolescents and adults with congenital heart disease. The educational process set out in ...
Heart 2016 – Deactivation of Devices
... importance of providing clear and consistent guidance on management of CIEDs towards the end of life, during cardiorespiratory arrest and after death. This document has been developed to provide guidance for the full range of healthcare professionals who may encounter people with CIEDs in the situat ...
... importance of providing clear and consistent guidance on management of CIEDs towards the end of life, during cardiorespiratory arrest and after death. This document has been developed to provide guidance for the full range of healthcare professionals who may encounter people with CIEDs in the situat ...
Cardiovascular Responses to Exercise
... stimulation. Thus, changes in stroke volume occur because left ventricular end–diastolic volume increases and left ventricular end–systolic volume decreases (Poliner, et al., 1980). Left ventricular end–diastolic volume increases because of the return of blood to the heart by the active muscle pump, ...
... stimulation. Thus, changes in stroke volume occur because left ventricular end–diastolic volume increases and left ventricular end–systolic volume decreases (Poliner, et al., 1980). Left ventricular end–diastolic volume increases because of the return of blood to the heart by the active muscle pump, ...
Effects of Ischemia and Hypercarbic Acidosis on Myocyte Calcium
... The time courses of changes in pHI and cytosolic calcium were compared in isolated perfused rabbit hearts with the use of the calcium-sensitive fluorescent indicator indo-1 and the pH indicator 2',7'-bis(2-carboxyethyl)-5(6)-carboxyfluorescein (BCECF). Cell-permeant forms of these indicators were lo ...
... The time courses of changes in pHI and cytosolic calcium were compared in isolated perfused rabbit hearts with the use of the calcium-sensitive fluorescent indicator indo-1 and the pH indicator 2',7'-bis(2-carboxyethyl)-5(6)-carboxyfluorescein (BCECF). Cell-permeant forms of these indicators were lo ...
Comparison of estimations versus measured resting oxygen
... LVEF (HFpEF)], and represents the severest stage of several disorders/diseases of the heart (Bui, Horwich, & Fonarow, 2011; Hunt et al., 2009; Lindenfeld et al., 2010). In physiological terms, the Heart Failure Society of America describes HF as the presence of elevated cardiac filling pressure (typ ...
... LVEF (HFpEF)], and represents the severest stage of several disorders/diseases of the heart (Bui, Horwich, & Fonarow, 2011; Hunt et al., 2009; Lindenfeld et al., 2010). In physiological terms, the Heart Failure Society of America describes HF as the presence of elevated cardiac filling pressure (typ ...
Arrhythmogenesis by single ectopic beats originating in the Purkinje
... Several experimental (14, 24) and computer modeling (2, 28, 37, 49) studies have documented how EADs generated in PS cells propagate to coupled myocytes and induce ectopic activity. However, the behavior of the PS changes significantly when it is coupled to a large mass of ventricular muscle due to ...
... Several experimental (14, 24) and computer modeling (2, 28, 37, 49) studies have documented how EADs generated in PS cells propagate to coupled myocytes and induce ectopic activity. However, the behavior of the PS changes significantly when it is coupled to a large mass of ventricular muscle due to ...
Implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs)
... Before you have the ICD fitted, you can discuss any issues or concerns that you may have about having an ICD implanted. The doctor will explain the procedure to you and will discuss with you the risks and benefits of the procedure. He or she will ask you to sign a consent form saying that you agree ...
... Before you have the ICD fitted, you can discuss any issues or concerns that you may have about having an ICD implanted. The doctor will explain the procedure to you and will discuss with you the risks and benefits of the procedure. He or she will ask you to sign a consent form saying that you agree ...
Principles of Cardiac Pacing
... – Pacemaker not sensitive enough to detect the patient’s intrinsic electrical activity (mV) – Insufficient myocardial voltage – Dislodged, loose, fibrotic, or fractured electrode – Electrolyte abnormalities – Low battery voltage ...
... – Pacemaker not sensitive enough to detect the patient’s intrinsic electrical activity (mV) – Insufficient myocardial voltage – Dislodged, loose, fibrotic, or fractured electrode – Electrolyte abnormalities – Low battery voltage ...
Normal Sinus Rhythm
... • Etiology: Recent theories suggest that it is due to multiple re-entrant wavelets conducted between the R & L atria. Either way, impulses are formed in a totally unpredictable fashion. The AV node allows some of the impulses to pass through at variable intervals (so rhythm is irregularly irregular) ...
... • Etiology: Recent theories suggest that it is due to multiple re-entrant wavelets conducted between the R & L atria. Either way, impulses are formed in a totally unpredictable fashion. The AV node allows some of the impulses to pass through at variable intervals (so rhythm is irregularly irregular) ...
Normalization of the EKG in patients with right bundle branch block
... marked reduction in left ventricular (LV) pump function. RVA pacing bypasses the His-Purkinje system resulting in a left bundle branch block like pattern on surface on the EKG.5 Pacing from the RV apex produces an abnormal activation of the lateral wall of the left ventricle (LV), with ventricular r ...
... marked reduction in left ventricular (LV) pump function. RVA pacing bypasses the His-Purkinje system resulting in a left bundle branch block like pattern on surface on the EKG.5 Pacing from the RV apex produces an abnormal activation of the lateral wall of the left ventricle (LV), with ventricular r ...
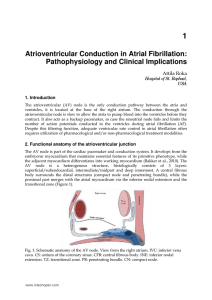
Atrioventricular Conduction in Atrial Fibrillation: Pathophysiology
... prognosis (Nerheim et al., 2004). Although it would be clinically important to identify patients where high ventricular rate plays the major role in the development of heart failure, thus may benefit from aggressive rate and/or rhythm control, prospective identification of these cases is difficult, ...
... prognosis (Nerheim et al., 2004). Although it would be clinically important to identify patients where high ventricular rate plays the major role in the development of heart failure, thus may benefit from aggressive rate and/or rhythm control, prospective identification of these cases is difficult, ...
as a PDF
... Methods Endocardial single-site pacing was performed in anesthetized swine (n ¼ 7) from the RV septum and RV apex. Biventricular pacing was performed using an epicardial left ventricular (LV) lead and a RV lead. High-resolution, non-contact mapping was employed to record LV activation sequences simu ...
... Methods Endocardial single-site pacing was performed in anesthetized swine (n ¼ 7) from the RV septum and RV apex. Biventricular pacing was performed using an epicardial left ventricular (LV) lead and a RV lead. High-resolution, non-contact mapping was employed to record LV activation sequences simu ...
Single-site ventricular and biventricular pacing
... Methods Endocardial single-site pacing was performed in anesthetized swine (n ¼ 7) from the RV septum and RV apex. Biventricular pacing was performed using an epicardial left ventricular (LV) lead and a RV lead. High-resolution, non-contact mapping was employed to record LV activation sequences simu ...
... Methods Endocardial single-site pacing was performed in anesthetized swine (n ¼ 7) from the RV septum and RV apex. Biventricular pacing was performed using an epicardial left ventricular (LV) lead and a RV lead. High-resolution, non-contact mapping was employed to record LV activation sequences simu ...
special article
... the papillary muscle from the right ventricle of the cat, and skeletal muscle, as represented by the sartorius muscle of the frog.' However, the maximum force of contraction of heart muscle is less than that of skeletal muscle. Recently we have found that this lesser maximum force development of car ...
... the papillary muscle from the right ventricle of the cat, and skeletal muscle, as represented by the sartorius muscle of the frog.' However, the maximum force of contraction of heart muscle is less than that of skeletal muscle. Recently we have found that this lesser maximum force development of car ...
QT interval variability in body surface ECG
... Temporal QT interval variations may differ between recording sites reflecting local repolarization signal heterogeneity, lead-specific respiration effects and noise (e.g. myopotentials).19 Short-term QTV analysis of 12-lead ECG suggests considerable inter-lead differences.20 Short-term QTV from ambu ...
... Temporal QT interval variations may differ between recording sites reflecting local repolarization signal heterogeneity, lead-specific respiration effects and noise (e.g. myopotentials).19 Short-term QTV analysis of 12-lead ECG suggests considerable inter-lead differences.20 Short-term QTV from ambu ...
Brief Review Determinants of Left Ventricular Filling and of the
... between the volume and equilibrium volume, Vo, is increased. As a result of this increased strain, diastolic wall stress and end-diastolic pressure increase. Over time, cardiac myocytes respond by elongating and thickening in a way that effectively increases Vo with little or no increase in wall thi ...
... between the volume and equilibrium volume, Vo, is increased. As a result of this increased strain, diastolic wall stress and end-diastolic pressure increase. Over time, cardiac myocytes respond by elongating and thickening in a way that effectively increases Vo with little or no increase in wall thi ...
Percutaneous mitral valve repair: an overview of new interventional
... are possible. Clinical improvement has been demonstrated in those patients with improved MR. Several patients have had myocardial infarction from coronary compression, and this has led to a careful screening approach with CT angiography to demonstrate the relationship of the coronary sinus and to t ...
... are possible. Clinical improvement has been demonstrated in those patients with improved MR. Several patients have had myocardial infarction from coronary compression, and this has led to a careful screening approach with CT angiography to demonstrate the relationship of the coronary sinus and to t ...
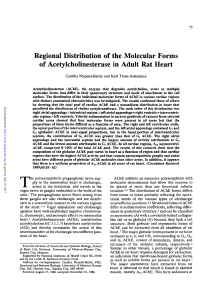
Regional Distribution of the Molecular Forms of Acetylcholinesterase
... forms. Extraction of asymmetric AChE forms from tissue was ensured by the inclusion of 1M NaCl in the homogenization buffer. The nonionic detergent Triton X-100 was included to solubilize the membrane-bound globular forms of AChE. For this analysis, tissue samples from six animals were examined. Fig ...
... forms. Extraction of asymmetric AChE forms from tissue was ensured by the inclusion of 1M NaCl in the homogenization buffer. The nonionic detergent Triton X-100 was included to solubilize the membrane-bound globular forms of AChE. For this analysis, tissue samples from six animals were examined. Fig ...
The Fontan circulation: who controls cardiac output?
... administration of diuretics. Systemic venous pressure, therefore, cannot be an important factor of output regulation at rest. At mild to moderate levels of exercise, invasive studies in normal subjects over a wide age range have shown that the mean pulmonary artery (PA) pressure rarely exceeds 25 mm ...
... administration of diuretics. Systemic venous pressure, therefore, cannot be an important factor of output regulation at rest. At mild to moderate levels of exercise, invasive studies in normal subjects over a wide age range have shown that the mean pulmonary artery (PA) pressure rarely exceeds 25 mm ...
A Cure for the Code Blues? Vasopressin, Steroid and Epinephrine
... i. Activation of cytokines, endotoxins, and reactive species after CA ii. Inflammatory response further damages ischemic organs a. Compounds neurologic damage b. Cytokines associated with mortality and unfavorable neurologic outcomes iii. Normal physiologic response to cytokines is stimulation of co ...
... i. Activation of cytokines, endotoxins, and reactive species after CA ii. Inflammatory response further damages ischemic organs a. Compounds neurologic damage b. Cytokines associated with mortality and unfavorable neurologic outcomes iii. Normal physiologic response to cytokines is stimulation of co ...
Left Ventricular Mass in Normal Children and its
... to weight, height and body surface area (BSA) in children and to determine the sex differences. We evaluated 208 children (143 males and 65 females), aged 1 day to 14 years who had no cardiovascular disease. The end-diastolic left ventricular internal dimension (LVIDd), end-diastolic left ventricula ...
... to weight, height and body surface area (BSA) in children and to determine the sex differences. We evaluated 208 children (143 males and 65 females), aged 1 day to 14 years who had no cardiovascular disease. The end-diastolic left ventricular internal dimension (LVIDd), end-diastolic left ventricula ...
Myocardial infarction

Myocardial infarction (MI) or acute myocardial infarction (AMI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow stops to a part of the heart causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Often it is in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat, or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms, with women more likely than men to present atypically. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, or cardiac arrest.Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, and excessive alcohol intake, among others. The mechanism of an MI often involves the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, leading to complete blockage of a coronary artery. MIs are less commonly caused by coronary artery spasms, which may be due to cocaine, significant emotional stress, and extreme cold, among others. A number of tests are useful to help with diagnosis, including electrocardiograms (ECGs), blood tests, and coronary angiography. An ECG may confirm an ST elevation MI if ST elevation is present. Commonly used blood tests include troponin and less often creatine kinase MB.Aspirin is an appropriate immediate treatment for a suspected MI. Nitroglycerin or opioids may be used to help with chest pain; however, they do not improve overall outcomes. Supplemental oxygen should be used in those with low oxygen levels or shortness of breath. In ST elevation MIs treatments which attempt to restore blood flow to the heart are typically recommended and include angioplasty, where the arteries are pushed open, or thrombolysis, where the blockage is removed using medications. People who have a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) are often managed with the blood thinner heparin, with the additional use angioplasty in those at high risk. In people with blockages of multiple coronary arteries and diabetes, bypass surgery (CABG) may be recommended rather than angioplasty. After an MI, lifestyle modifications, along with long term treatment with aspirin, beta blockers, and statins, are typically recommended.Worldwide, more than 3 million people have ST elevation MIs and 4 million have NSTEMIs each year. STEMIs occur about twice as often in men as women. About one million people have an MI each year in the United States. In the developed world the risk of death in those who have had an STEMI is about 10%. Rates of MI for a given age have decreased globally between 1990 and 2010.