Topic_Social_Structure
... status set: all of the statuses or positions that an individual occupies (101) Discussion Topics to Encourage Student Participation Have your students look around the class for status symbols their classmates may be wearing or displaying. Did they find designer labels and expensive jewelry on stud ...
... status set: all of the statuses or positions that an individual occupies (101) Discussion Topics to Encourage Student Participation Have your students look around the class for status symbols their classmates may be wearing or displaying. Did they find designer labels and expensive jewelry on stud ...
session five- social psychology part one
... 10% of real subjects fully complied with the orders ...
... 10% of real subjects fully complied with the orders ...
It is really confusing!!!
... can be distorted under certain circumstances. Factors that effect time passed: level of fatigue; level of concentration; Depression and Happiness Work setting: work situation influences productivity the most à assess how workers perceive their jobs as correct as possible. Social setting: How an ind ...
... can be distorted under certain circumstances. Factors that effect time passed: level of fatigue; level of concentration; Depression and Happiness Work setting: work situation influences productivity the most à assess how workers perceive their jobs as correct as possible. Social setting: How an ind ...
SOC4044 Sociological Theory Georg Simmel Dr. Ronald Keith
... By virtue of his partial involvement in group affairs he can attain an objectivity that other members cannot reach… Moreover, being distant and near at the same time, the stranger will often be called upon as a confidant… the stranger may be a better judge between conflicting parties than full ...
... By virtue of his partial involvement in group affairs he can attain an objectivity that other members cannot reach… Moreover, being distant and near at the same time, the stranger will often be called upon as a confidant… the stranger may be a better judge between conflicting parties than full ...
Document
... • When we know how to act, life runs smoothly. How is this true? When is it not true? • Bold statement: Behavior is contagious. Give three examples! • Conformity: Define • Chameleon effect: Define • Mood linkage & mood contagion (sometimes we try to make this happen unnaturally) ...
... • When we know how to act, life runs smoothly. How is this true? When is it not true? • Bold statement: Behavior is contagious. Give three examples! • Conformity: Define • Chameleon effect: Define • Mood linkage & mood contagion (sometimes we try to make this happen unnaturally) ...
view pdf pages 40-45 - European/American Journals
... human behaviour is based largely on the interaction of people with their meaningful environments. Rotter believes that, although personality can change at any time, it has a basic unity that preserves it from changing as a result of minor experiences. McLeod (2011) supported Rotter’s work with the v ...
... human behaviour is based largely on the interaction of people with their meaningful environments. Rotter believes that, although personality can change at any time, it has a basic unity that preserves it from changing as a result of minor experiences. McLeod (2011) supported Rotter’s work with the v ...
Social Skills Training
... corrective action (e.g. steering a car. Social Skill: Skilled performer corrects performance in relation to social feedback from others. (Note importance of non-verbal feedback). ...
... corrective action (e.g. steering a car. Social Skill: Skilled performer corrects performance in relation to social feedback from others. (Note importance of non-verbal feedback). ...
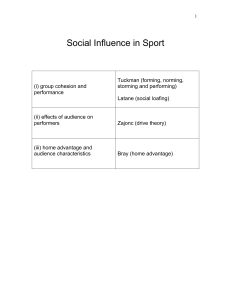
f) Social influence in sport
... actually like each other and offer support and trust to one another) It is possible to have one type of cohesion without the other, for example, as an individual you might be very committed to winning but not really like the other people in the team. There are a number of external factors that may a ...
... actually like each other and offer support and trust to one another) It is possible to have one type of cohesion without the other, for example, as an individual you might be very committed to winning but not really like the other people in the team. There are a number of external factors that may a ...
The Unity of Self and Object1
... consequences, among these being the 'reasons' commonly treated as antecedent motives. As a corollary, we are more likely to find in the background of or as antecedent to current practical, need-satisfying, instrumental activity a sense of play or experimentation. We tried to emphasize the sense in w ...
... consequences, among these being the 'reasons' commonly treated as antecedent motives. As a corollary, we are more likely to find in the background of or as antecedent to current practical, need-satisfying, instrumental activity a sense of play or experimentation. We tried to emphasize the sense in w ...
Social Influence and Persuasion - Donna Vandergrift Psychology
... Techniques Based on Reciprocation Door-in-the-Face Technique – Start with an inflated request and then retreat to a smaller one that appears to be a concession – Does not work if the first request is viewed as unreasonable or if requests are made by different people That’s-Not-All Technique – Begin ...
... Techniques Based on Reciprocation Door-in-the-Face Technique – Start with an inflated request and then retreat to a smaller one that appears to be a concession – Does not work if the first request is viewed as unreasonable or if requests are made by different people That’s-Not-All Technique – Begin ...
Review of Identity Economics by Akerlof and Kranton
... that people understood as collections of preferences are distinct and individual. Yet one cannot show a person to be distinct and individual in virtue of having some single set of preferences, since two different people could have identical preferences. A person’s preferences only mark them off as d ...
... that people understood as collections of preferences are distinct and individual. Yet one cannot show a person to be distinct and individual in virtue of having some single set of preferences, since two different people could have identical preferences. A person’s preferences only mark them off as d ...
Mathematical Modeling in Social and Behavioral Sciences
... research and systems analysis, that is for example, for optimal scheduling of production processes, for determining the best way for transporting a certain commodity. Optimization theory is closely related to the calculus of variations, control theory, convex optimization theory, decision theory, ga ...
... research and systems analysis, that is for example, for optimal scheduling of production processes, for determining the best way for transporting a certain commodity. Optimization theory is closely related to the calculus of variations, control theory, convex optimization theory, decision theory, ga ...
Social Behavior
... relationship, partner’s beliefs/attitudes will shift in the direction of the other person’s belief/attitude. EX. A conservative, gun-toting member of the NRA marries a bleeding-heart liberal. In 20 years, the conservative may insist on putting solar panels on the house and the liberal may enjoy go ...
... relationship, partner’s beliefs/attitudes will shift in the direction of the other person’s belief/attitude. EX. A conservative, gun-toting member of the NRA marries a bleeding-heart liberal. In 20 years, the conservative may insist on putting solar panels on the house and the liberal may enjoy go ...
AP Psychology - Airport High School
... • A dispositional cause is an explanation of behavior based on the internal personality characters of the person being observed. • Fundamental attribution errors is the tendency to overestimate the influence of internal factors on behavior while underestimating the influence of the situation • Ways ...
... • A dispositional cause is an explanation of behavior based on the internal personality characters of the person being observed. • Fundamental attribution errors is the tendency to overestimate the influence of internal factors on behavior while underestimating the influence of the situation • Ways ...
Learning Objectives Ch. 1
... As a scientific discipline, sociology seeks to explain why something happens, attempts to make generalizations that can be applied to a broader group or situation, and predict what will happen based on the knowledge received. Sociology specifically seeks to explain the causes of human behavior and ...
... As a scientific discipline, sociology seeks to explain why something happens, attempts to make generalizations that can be applied to a broader group or situation, and predict what will happen based on the knowledge received. Sociology specifically seeks to explain the causes of human behavior and ...
learning objectives chapter 14
... 23. Define assistance and altruism. Discuss the arousal: cost-reward theory of helping behavior. Describe the situational factors and personality characteristics that influence helping behavior. Define bystander effect and diffusion of responsibility. (see “Altruism and Assistance” and “Why Do Peopl ...
... 23. Define assistance and altruism. Discuss the arousal: cost-reward theory of helping behavior. Describe the situational factors and personality characteristics that influence helping behavior. Define bystander effect and diffusion of responsibility. (see “Altruism and Assistance” and “Why Do Peopl ...
Self, identity and Interpersonal relationship in individualized
... Theory of categorization and social identity Apart from interactionalist perspective of analyzing how an individuals internalizes role expectations and performances into their selves and constitutes her role-based identity, Henri Tajfel and his followers most notably John C. Turner look at forma ...
... Theory of categorization and social identity Apart from interactionalist perspective of analyzing how an individuals internalizes role expectations and performances into their selves and constitutes her role-based identity, Henri Tajfel and his followers most notably John C. Turner look at forma ...
The societal context of xenophobia
... zero-sum belief has also been identified as a mediator in the relationship between social dominance orientation – the individual preference for hierarchy within social systems – and attitudes towards immigrants (Esses et al., 1998). Concern over material threats may be a relevant criterion for diffe ...
... zero-sum belief has also been identified as a mediator in the relationship between social dominance orientation – the individual preference for hierarchy within social systems – and attitudes towards immigrants (Esses et al., 1998). Concern over material threats may be a relevant criterion for diffe ...
Test 2 - Kellogg Community College
... by Fitzgerald and others (2010), which of the following best explains Abigail’s actions? a. In high-risk scenarios, we are motivated to help anyone. b. In low-risk scenarios, we are willing to help friends and relatives c. In all scenarios, we are unlikely to help someone not genetically related to ...
... by Fitzgerald and others (2010), which of the following best explains Abigail’s actions? a. In high-risk scenarios, we are motivated to help anyone. b. In low-risk scenarios, we are willing to help friends and relatives c. In all scenarios, we are unlikely to help someone not genetically related to ...
Social Psychology Ch. 18 and 19
... authority- even if they violate their own codes of behavior. They would inflict pain on people if ordered to do so. ...
... authority- even if they violate their own codes of behavior. They would inflict pain on people if ordered to do so. ...
I j - Human Capital and Economic Opportunity Global Working Group
... • In the same way some people like apples and others like oranges, some people may not want to work with blacks or women. • Employers might then not want to hire this group because workers with these tastes would require a wage premium… • Blacks/women then have lower benefits of education ...
... • In the same way some people like apples and others like oranges, some people may not want to work with blacks or women. • Employers might then not want to hire this group because workers with these tastes would require a wage premium… • Blacks/women then have lower benefits of education ...
Social Psychology
... In terms of substantive interests and orientations both sociologists and psychologists populate this field of study and have defined its basic character. This situation has resulted in what some analysts refer to as “sociological social psychology” and “psychological social psychology.” In years pas ...
... In terms of substantive interests and orientations both sociologists and psychologists populate this field of study and have defined its basic character. This situation has resulted in what some analysts refer to as “sociological social psychology” and “psychological social psychology.” In years pas ...
AP Psychology
... 22. Which of the following is the most important tenet of Heinz Kohut's theory of self psychology? (A) The development of defense mechanisms protect the ego from overwhelming anxiety (B) The ability to form meaningful and fulfilling attachments is often influenced by the effectiveness of the first a ...
... 22. Which of the following is the most important tenet of Heinz Kohut's theory of self psychology? (A) The development of defense mechanisms protect the ego from overwhelming anxiety (B) The ability to form meaningful and fulfilling attachments is often influenced by the effectiveness of the first a ...
culture, human values and professional ethics
... 39. Of the following which is a primary group political group factory school family 40. A group in which one has a ‘we-feeling’ is called an racial group primary group nationality group inherited group 41. The essential characteristics of primary group is lack of identification a ...
... 39. Of the following which is a primary group political group factory school family 40. A group in which one has a ‘we-feeling’ is called an racial group primary group nationality group inherited group 41. The essential characteristics of primary group is lack of identification a ...
Homework for the Week of February 16-20
... becomes law, then law becomes habit, and finally, habit becomes a matter of the heart (that is emotional). ...
... becomes law, then law becomes habit, and finally, habit becomes a matter of the heart (that is emotional). ...
Self-categorization theory

Self-categorization theory is a social psychological theory that describes the circumstances under which a person will perceive collections of people (including themselves) as a group, as well as the consequences of perceiving people in group terms. Although the theory is often introduced as an explanation of psychological group formation (which was one of its early goals), it is more accurately thought of as general analysis of the functioning of categorization processes in social perception and interaction that speaks to issues of individual identity as much as group phenomena.The theory was developed by John Turner and colleagues, and along with social identity theory it is a constituent part of the social identity approach. It was in part developed to address questions that arose in response to social identity theory about the mechanistic underpinnings of social identification. For example, what makes people define themselves in terms of one group membership rather than another? Self-categorization theory has been influential in the academic field of social psychology and beyond. It was first applied to the topics of social influence, group cohesion, group polarization, and collective action. In subsequent years the theory, often as part of the social identity approach, has been applied to further topics such as leadership, personality, outgroup homogeneity, and power. One tenet of the theory is that the self should not be considered as a foundational aspect of cognition, but rather the self should be seen as a product of the cognitive system at work. Or in other words, the self is an outcome of cognitive processes rather than a ""thing"" at the heart of cognition.