DNA Assessment - WordPress.com
... 6) Individual genes store bits of information that make cells function. Identify which of the following describes a gene. A) a segment of DNA B) a segment of RNA C) a segment of protein D) a segment of carbohydrate 7) Genetic information is stored in________________. A) DNA molecules B) RNA molecule ...
... 6) Individual genes store bits of information that make cells function. Identify which of the following describes a gene. A) a segment of DNA B) a segment of RNA C) a segment of protein D) a segment of carbohydrate 7) Genetic information is stored in________________. A) DNA molecules B) RNA molecule ...
CHANGES IN DNA CAN PRODUCE VARIATIONS
... and a person’s behavior can bring on or prevent the disease. ...
... and a person’s behavior can bring on or prevent the disease. ...
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 16 OUTLINE
... AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 16 OUTLINE THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE I. DNA AS THE GENETIC MATERIAL A. The search for the genetic material led to DNA: science as a process Proteins were thought to be the genetic material because: ...
... AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 16 OUTLINE THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE I. DNA AS THE GENETIC MATERIAL A. The search for the genetic material led to DNA: science as a process Proteins were thought to be the genetic material because: ...
Sc9 - a 3.1(student notes)
... Learning outcomes: 1 I can describe the relationship among chromosomes, genes and DNA, and their role in storing genetic information. ...
... Learning outcomes: 1 I can describe the relationship among chromosomes, genes and DNA, and their role in storing genetic information. ...
Some No-Nonsense Facts on
... between tiny single-celled organisms like yeast and large multi-cellular organisms like ourselves. The similarities reflect a common ancestry to be shared by all life on ...
... between tiny single-celled organisms like yeast and large multi-cellular organisms like ourselves. The similarities reflect a common ancestry to be shared by all life on ...
DNA Vocabulary Study Option
... 2. Have your child mix up the cards and try to match the correct definition with the correct vocabulary term. (A second chart can be printed to act as a key) ...
... 2. Have your child mix up the cards and try to match the correct definition with the correct vocabulary term. (A second chart can be printed to act as a key) ...
DNA,RNA & Protein synthesis game
... the debate regarding hereditary material over these two molecules ...
... the debate regarding hereditary material over these two molecules ...
Protein Synthesis 1 - Transcription Translation
... ___________________________________________ 3) Where does translation take place? ___________________________________________ MAKING PROTEINS 4) First, the DNA (genetic code) gets transcribed into mRNA. 5) Why do we need to make a coded copy of DNA? __________________________________________________ ...
... ___________________________________________ 3) Where does translation take place? ___________________________________________ MAKING PROTEINS 4) First, the DNA (genetic code) gets transcribed into mRNA. 5) Why do we need to make a coded copy of DNA? __________________________________________________ ...
Human Genetics and Genetic Technology Test Review Jeopardy
... season ended. DNA from this blood was compared to meat and blood found in the suspect’s freezer. Was the suspect guilty? Why or why not? ...
... season ended. DNA from this blood was compared to meat and blood found in the suspect’s freezer. Was the suspect guilty? Why or why not? ...
Biology Study Guide CH 12 Part I DNA-RNA
... 17. Why is it possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than one kind of codon? 18. During the process of ________________, the cell uses information from mRNA to produce proteins. 19. During translation, the type of amino acid that is added to the growing polypeptide depends on the ______ ...
... 17. Why is it possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than one kind of codon? 18. During the process of ________________, the cell uses information from mRNA to produce proteins. 19. During translation, the type of amino acid that is added to the growing polypeptide depends on the ______ ...
PPT
... list of some of the more common genetic diseases that can be detected. Any gene disorder in which the DNA base pairs or code is known, can be detected by PND & ...
... list of some of the more common genetic diseases that can be detected. Any gene disorder in which the DNA base pairs or code is known, can be detected by PND & ...
DNA - heredity2
... repeats are termed pre-mutation (will most likely pass it on to next generation), 200+ is full mutation causing physical mental and emotional disability the severity of which increases with the number of repeats present. – Most children with excessive repetition die before they reach adulthood. ...
... repeats are termed pre-mutation (will most likely pass it on to next generation), 200+ is full mutation causing physical mental and emotional disability the severity of which increases with the number of repeats present. – Most children with excessive repetition die before they reach adulthood. ...
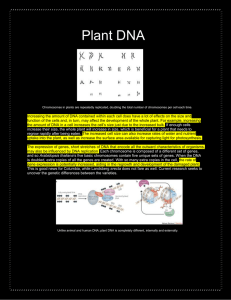
Plant DNA - The uniqueness of DNA
... uptake into the plant, as well as increase the surface area available for capturing light for photosynthesis. The expression of genes, short stretches of DNA that encode all the outward characteristics of organisms, may also be influenced by DNA replication. Each chromosome is composed of a differen ...
... uptake into the plant, as well as increase the surface area available for capturing light for photosynthesis. The expression of genes, short stretches of DNA that encode all the outward characteristics of organisms, may also be influenced by DNA replication. Each chromosome is composed of a differen ...
molecular genetics unit review
... g) Hershey and Chase Describe the contributions of the following scientists to our current knowledge of DNA structure and DNA replication: a) Chargaff b) Rosalind Franklin c) Watson and Crick d) Meselson and Stahl Describe the structure of DNA. Include terms like anti-parallel, nucleotide (phosphate ...
... g) Hershey and Chase Describe the contributions of the following scientists to our current knowledge of DNA structure and DNA replication: a) Chargaff b) Rosalind Franklin c) Watson and Crick d) Meselson and Stahl Describe the structure of DNA. Include terms like anti-parallel, nucleotide (phosphate ...
DNA Paper Model Activity Try to attach and mode the Gene Reading
... DNA ribbon that is not spooled around a histone or covered by a methyl. Can the machinery read any significant stretch of DNA? No, it cannot. 2. Refer to question 1, would this be an active or inactive gene? Explain. It’s inactive, because the methyl groups make the DNA inaccessible. 3. Try to attac ...
... DNA ribbon that is not spooled around a histone or covered by a methyl. Can the machinery read any significant stretch of DNA? No, it cannot. 2. Refer to question 1, would this be an active or inactive gene? Explain. It’s inactive, because the methyl groups make the DNA inaccessible. 3. Try to attac ...
DNA
... *is passed from one generation to the next in chromosomes. *looks like a ladder, twisted around itself, called a double helix DNA Timeline Facts… Early 1950’s o 1st picture of DNA taken by Rosalind Franklin using an X-ray machine. ...
... *is passed from one generation to the next in chromosomes. *looks like a ladder, twisted around itself, called a double helix DNA Timeline Facts… Early 1950’s o 1st picture of DNA taken by Rosalind Franklin using an X-ray machine. ...
Chapter 14 - The Biology Corner
... f. Huntingtons Disease g. Hemophilia h. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy i. Colorblindness ...
... f. Huntingtons Disease g. Hemophilia h. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy i. Colorblindness ...
AP BIO Unit 6 Review Ch. 14,15,16,18,19 Westbrook Gene
... Gene expression includes what processes? For transcription to occur, the DNA is read from what end? What is the 3-nucleotide sequence in an mRNA that codes for an amino acid? How does protein synthesis proceeds once the ribosome has attached to the mRNA strand? What is the site where the empty RNA m ...
... Gene expression includes what processes? For transcription to occur, the DNA is read from what end? What is the 3-nucleotide sequence in an mRNA that codes for an amino acid? How does protein synthesis proceeds once the ribosome has attached to the mRNA strand? What is the site where the empty RNA m ...
Aim: How do scientists use biotechnology to manipulate genomes?
... Does that lead to variation in offspring? No, it leads to clones ...
... Does that lead to variation in offspring? No, it leads to clones ...
Biotechnology Key Terms and Concepts
... an organism. 1. Humans create genetically modified plants and animals (GMOs) for a variety of reasons. including increased nutrition and pest resistance 2. Transgenic-an organism that has genes from more than one species due to genetic modification C. Gel Electrophoresis 1. Process used to separate ...
... an organism. 1. Humans create genetically modified plants and animals (GMOs) for a variety of reasons. including increased nutrition and pest resistance 2. Transgenic-an organism that has genes from more than one species due to genetic modification C. Gel Electrophoresis 1. Process used to separate ...
Things to Cover for Exam 1
... Diploid (2n) cells or haploid (n) cells? Genetically identical or genetically different? If the chromosome number of a diploid cell is 102, what is its haploid chromosome number? What is a zygote and when is it formed? Meiosis involves a single duplication of DNA followed by two successive cel ...
... Diploid (2n) cells or haploid (n) cells? Genetically identical or genetically different? If the chromosome number of a diploid cell is 102, what is its haploid chromosome number? What is a zygote and when is it formed? Meiosis involves a single duplication of DNA followed by two successive cel ...