Chapter 12 SWBAT`s and Standards
... Students know how to apply base-pairing rules to explain precise copying of DNA during semi conservative replication and transcription of information from DNA into mRNA. ...
... Students know how to apply base-pairing rules to explain precise copying of DNA during semi conservative replication and transcription of information from DNA into mRNA. ...
Advances in Genetics
... • The process of selecting organisms with desired traits to be parents of the next generation is called selective breeding • The corn we use today is a great example! • 2 techniques • Inbreeding • hybridization ...
... • The process of selecting organisms with desired traits to be parents of the next generation is called selective breeding • The corn we use today is a great example! • 2 techniques • Inbreeding • hybridization ...
REVIEW OF MOLECULAR GENETICS - Pascack Valley Regional
... DNA library - a random collection of DNA fragments from an organism cloned into a vector Ideally contains at least one copy of every DNA sequence. Easily maintained in the laboratory Can be manipulated in various ways to facilitate the isolation of a DNA fragment of interest to a scientist. Num ...
... DNA library - a random collection of DNA fragments from an organism cloned into a vector Ideally contains at least one copy of every DNA sequence. Easily maintained in the laboratory Can be manipulated in various ways to facilitate the isolation of a DNA fragment of interest to a scientist. Num ...
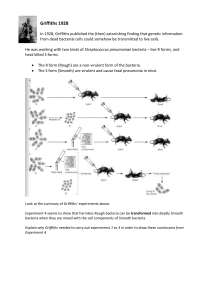
DNA experiments exercise
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
Fill-in-Notes - Pearland ISD
... 2. An electrical current is applied 3. DNA is separated by size. Shorter fragments move farther down the ____________ than longer fragments Used in: DNA _ _________________ DNA Fingerprinting • Best way to determine if two people are genetically ______________ • Used in _______________counseling, pa ...
... 2. An electrical current is applied 3. DNA is separated by size. Shorter fragments move farther down the ____________ than longer fragments Used in: DNA _ _________________ DNA Fingerprinting • Best way to determine if two people are genetically ______________ • Used in _______________counseling, pa ...
Mutations and DNA Technology Notes
... • Inbreeding- continued breeding of ind. with similar characteristics. – Ex- different dog breeds – Can be dangerous due to increased chance for genetic defects. ...
... • Inbreeding- continued breeding of ind. with similar characteristics. – Ex- different dog breeds – Can be dangerous due to increased chance for genetic defects. ...
Gen.1303 Genome: The total genetic content contained in a haploid
... A hereditary unit consisting of a sequence of DNA that occupies a specific location on a chromosome and determines a particular characteristic in an organism. Genes undergo mutation when their DNA sequence changes. Chromatin: A complex of nucleic acids and proteins, primary histones, in the cell nuc ...
... A hereditary unit consisting of a sequence of DNA that occupies a specific location on a chromosome and determines a particular characteristic in an organism. Genes undergo mutation when their DNA sequence changes. Chromatin: A complex of nucleic acids and proteins, primary histones, in the cell nuc ...
14-3 Human Molecular Genetics
... In gene therapy, an absent or faulty gene is replaced by a normal, working gene. - This way the body can make the correct protein or enzyme it needs, which eliminates the cause of the disorder. ...
... In gene therapy, an absent or faulty gene is replaced by a normal, working gene. - This way the body can make the correct protein or enzyme it needs, which eliminates the cause of the disorder. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 14. T - DNA is found in _______________________ 15. Kanamycin can be used as a ___________________ marker ...
... 14. T - DNA is found in _______________________ 15. Kanamycin can be used as a ___________________ marker ...
1 Genetics (BIL-250) Review Questions #1 (2
... major components: (1) 5’ and 3’ ends of each strand, (2) leading strand, (3) lagging strand, (4) single-stranded binding proteins, (5) DNA polymerase, (6)Okazaki fragments, (7) RNA primer, (8) DNA helicase, (9) DNA ligase, (10) primase. (3-2) How did the Meselson-Stahl experiment demonstrate that DN ...
... major components: (1) 5’ and 3’ ends of each strand, (2) leading strand, (3) lagging strand, (4) single-stranded binding proteins, (5) DNA polymerase, (6)Okazaki fragments, (7) RNA primer, (8) DNA helicase, (9) DNA ligase, (10) primase. (3-2) How did the Meselson-Stahl experiment demonstrate that DN ...
Unit 2 MI Study Guide
... What is the purpose of PCR? List the steps and what occurs during each step. ...
... What is the purpose of PCR? List the steps and what occurs during each step. ...
Protein Synthesis
... Both are directions for how to make something Recipes are directions to make food, DNA are directions for how to make proteins Proteins are one of the four building blocks of the cell ...
... Both are directions for how to make something Recipes are directions to make food, DNA are directions for how to make proteins Proteins are one of the four building blocks of the cell ...
Intro Biology Review for Final
... Somatic cells, gametes Mitosis phases Main steps of photosynthesis End products of photosynthesis Locus Homologous chromosomes Sister chromatids Haploid, diploid Meiosis I and II Centromere 3 mechanisms that contribute to genetic variation Why Mendel studied peas Alleles ...
... Somatic cells, gametes Mitosis phases Main steps of photosynthesis End products of photosynthesis Locus Homologous chromosomes Sister chromatids Haploid, diploid Meiosis I and II Centromere 3 mechanisms that contribute to genetic variation Why Mendel studied peas Alleles ...
Name:
... 1. __ Found the proportion of Adenine to be equal to that of Thymine, and the proportion of Cytosine to be equal to that of Guanine. __ Proposed the Theory of Natural Selection. __ The father of modern genetics. __ Disproved the theory of spontaneous generation with his experiment involving flies an ...
... 1. __ Found the proportion of Adenine to be equal to that of Thymine, and the proportion of Cytosine to be equal to that of Guanine. __ Proposed the Theory of Natural Selection. __ The father of modern genetics. __ Disproved the theory of spontaneous generation with his experiment involving flies an ...
Concept 20.1 A. -Plasmid is the cloning vector.
... -mRNA is used to make single stranded transcripts of DNA using reverse transcriptase in vitro. The mRNA is then degraded and a second DNA strand is made by DNA polymerase. This ds DNA is complementary DNA ( cDNA). To overcome eukaryote-prokaryote incompatability scientists use eukaryotic cells such ...
... -mRNA is used to make single stranded transcripts of DNA using reverse transcriptase in vitro. The mRNA is then degraded and a second DNA strand is made by DNA polymerase. This ds DNA is complementary DNA ( cDNA). To overcome eukaryote-prokaryote incompatability scientists use eukaryotic cells such ...
BIO_Protein_Synthesis_Outline - Cole Camp R-1
... connected. The Rungs are connected by weak ___________________________________ ...
... connected. The Rungs are connected by weak ___________________________________ ...
Enterococcus faecalis VRE, Genomic DNA
... genomic tips. This control is supplied in TE Buffer and should be frozen at -20°C or below. DNA concentration and 260/280 ratios are determined using a NanoDrop ND-1000®. The extracted DNA ...
... genomic tips. This control is supplied in TE Buffer and should be frozen at -20°C or below. DNA concentration and 260/280 ratios are determined using a NanoDrop ND-1000®. The extracted DNA ...
Techniques
... - Green spot: only expressed in no O2 Red spot: expressed only in plus O2 Yellow: Expressed in both condition ...
... - Green spot: only expressed in no O2 Red spot: expressed only in plus O2 Yellow: Expressed in both condition ...
UNIT 4 PART 2 APPLIED GENETICS
... trace a condition through a family and predict where it may occur in the future: ...
... trace a condition through a family and predict where it may occur in the future: ...
Selling Genzyme Genetics` Maternal Serum Screening Program
... Confined placental mosaicism with CVS Cytogenetic success over 99% ...
... Confined placental mosaicism with CVS Cytogenetic success over 99% ...
Genetic Engineering
... A. Selective Breeding – allowing only those individuals with desired characteristics to produce the next generation 1. Inbreeding – cross two of the same type of individual to preserve the characteristics (Risky!) 2. Cross-breeding / Hybridization – cross two different types of individuals to get th ...
... A. Selective Breeding – allowing only those individuals with desired characteristics to produce the next generation 1. Inbreeding – cross two of the same type of individual to preserve the characteristics (Risky!) 2. Cross-breeding / Hybridization – cross two different types of individuals to get th ...