DNA - TeacherWeb
... Messenger RNA carries the code that directs the order in which the amino acids bond b. Ribosomal RNA makes up Ribosomes, where proteins are built c. Transfer RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to build the protein. 3. Cells use only the genes that directs the making of proteins needed by that c ...
... Messenger RNA carries the code that directs the order in which the amino acids bond b. Ribosomal RNA makes up Ribosomes, where proteins are built c. Transfer RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to build the protein. 3. Cells use only the genes that directs the making of proteins needed by that c ...
Visualizing DNA
... Thus, larger fragments will move slower than smaller fragments. This allows separation of all different sizes of DNA fragments. ...
... Thus, larger fragments will move slower than smaller fragments. This allows separation of all different sizes of DNA fragments. ...
Jatropha genotyping In Gh Pu QR In Gh Pu QR 13 primer pairs
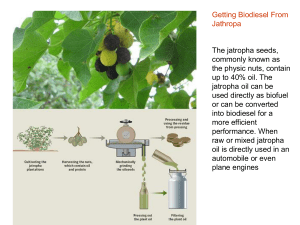
... commonly known as the physic nuts, contain up to 40% oil. The jatropha oil can be used directly as biofuel or can be converted into biodiesel for a more efficient performance. When raw or mixed jatropha oil is directly used in an automobile or even plane engines ...
... commonly known as the physic nuts, contain up to 40% oil. The jatropha oil can be used directly as biofuel or can be converted into biodiesel for a more efficient performance. When raw or mixed jatropha oil is directly used in an automobile or even plane engines ...
Epigenetics - Hospital Melaka Department of Medicine Haematology
... the US Department of Energy and the National Institutes of Health A 'rough draft' of the genome was finished in 2000, announced jointly by U.S. President Bill Clinton and the British Prime Minister Tony Blair on June 26, ...
... the US Department of Energy and the National Institutes of Health A 'rough draft' of the genome was finished in 2000, announced jointly by U.S. President Bill Clinton and the British Prime Minister Tony Blair on June 26, ...
Modeling DNA
... How does the DNA in a bacteria differ from the DNA in a human? How could you have predicted these differences based on what you know about humans, and bacteria? ...
... How does the DNA in a bacteria differ from the DNA in a human? How could you have predicted these differences based on what you know about humans, and bacteria? ...
Go to - Net Start Class
... This explore is best when the students can use computers but can be done globally if necessary. ...
... This explore is best when the students can use computers but can be done globally if necessary. ...
Your genes
... Date _______________________________ Objectives 1. Identify the different structures that make up genetic ...
... Date _______________________________ Objectives 1. Identify the different structures that make up genetic ...
Renal transplant recipients
... Cystic Fibrosis - background • 'Single most common autosomal recessive disorder among Caucasians.' • 1:2500 live births • Defective Gene: - Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) - Chloride Ion Channel - Chromosome 7 - 250,000 base pairs - 27 exons - 1480 amino acids ...
... Cystic Fibrosis - background • 'Single most common autosomal recessive disorder among Caucasians.' • 1:2500 live births • Defective Gene: - Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) - Chloride Ion Channel - Chromosome 7 - 250,000 base pairs - 27 exons - 1480 amino acids ...
Bio 220 MiniQuiz 1
... _____8. A medium for which the chemical composition is unknown is called a ______ medium. a. chemically defined b. sustaining c. selective d. complex _____9. A medium which allows the growth of only certain organisms is called a _____medium. a. chemically defined b. selective d. differential d. comp ...
... _____8. A medium for which the chemical composition is unknown is called a ______ medium. a. chemically defined b. sustaining c. selective d. complex _____9. A medium which allows the growth of only certain organisms is called a _____medium. a. chemically defined b. selective d. differential d. comp ...
Genetic Disorders - West Lake Eagles
... disorder. Caused by a recessive gene on the X chromosome. There are about 20,000 hemophilia patients in the United States. One can bleed to death with small cuts. ...
... disorder. Caused by a recessive gene on the X chromosome. There are about 20,000 hemophilia patients in the United States. One can bleed to death with small cuts. ...
Genetic engineering - Mad River Local Schools
... lives. As a gene therapist, you'll treat human patients with genetic illnesses. Otherwise, you might work in a non-medical environment as a biochemist or biophysicist, exploring living organisms such as plants used as food crops. You'll typically work full-time with a ...
... lives. As a gene therapist, you'll treat human patients with genetic illnesses. Otherwise, you might work in a non-medical environment as a biochemist or biophysicist, exploring living organisms such as plants used as food crops. You'll typically work full-time with a ...
4.4 Genetic engineering and biotechnology - McLain
... (SL p1 May07 TZ1 16) B. Genetic screening C. Gel electrophoresis D. Polymerase chain reaction 11. What was the original goal of the Human Genome Project? (SL p1 May07 TZ1 17) A. To determine the function of genes B. To determine the nucleotide sequence of all human chromosome ...
... (SL p1 May07 TZ1 16) B. Genetic screening C. Gel electrophoresis D. Polymerase chain reaction 11. What was the original goal of the Human Genome Project? (SL p1 May07 TZ1 17) A. To determine the function of genes B. To determine the nucleotide sequence of all human chromosome ...
Reporting Category 2
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA in the nucleus DNA is too big to leave the nucleus mRNA then leaves the nucleus to take the information to the ribosome (in the ...
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA in the nucleus DNA is too big to leave the nucleus mRNA then leaves the nucleus to take the information to the ribosome (in the ...
Gypsy Vanner Horse Society DNA Analysis Form
... the test will be held by the Gypsy Vanner Horse Society and the University of Kentucky. The University may use the samples in its research. The GVHS does authorize the University of Kentucky to share this DNA information with certain other registries as needed to verify parentage. Hair samples are c ...
... the test will be held by the Gypsy Vanner Horse Society and the University of Kentucky. The University may use the samples in its research. The GVHS does authorize the University of Kentucky to share this DNA information with certain other registries as needed to verify parentage. Hair samples are c ...
DNA Replication Graphic Organizer
... REVIEW: Explain the TWO things an enzyme does in chemical reactions in the body… ...
... REVIEW: Explain the TWO things an enzyme does in chemical reactions in the body… ...
to view and/or print October 2016 eDay assignment.
... QUESTION 3 – WHAT IS INHERITANCE? Play the video and answer the following questions: 1. How is DNA passed to offspring? 2. Explain the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. 3. We have how many copies of each gene? 4. Each parent passes _____ copy of each gene to his/her offspring. 5. W ...
... QUESTION 3 – WHAT IS INHERITANCE? Play the video and answer the following questions: 1. How is DNA passed to offspring? 2. Explain the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. 3. We have how many copies of each gene? 4. Each parent passes _____ copy of each gene to his/her offspring. 5. W ...
Slide 1
... that have the characteristics of both species, some people have bred buffalo and cattle together. ...
... that have the characteristics of both species, some people have bred buffalo and cattle together. ...
Genetics
... What's the center of heredity in a cell? In eukaryotic organisms it is the nucleus, in prokaryotes it is the nucleoid region. What is the genetic material? In eukaryotes & prokaryotes it is DNA, in viruses it can be either DNA or RNA. What do DNA & RNA stand for? DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid / RNA: ri ...
... What's the center of heredity in a cell? In eukaryotic organisms it is the nucleus, in prokaryotes it is the nucleoid region. What is the genetic material? In eukaryotes & prokaryotes it is DNA, in viruses it can be either DNA or RNA. What do DNA & RNA stand for? DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid / RNA: ri ...
Genetic Engineering
... – sample of DNA is cut using restriction enzymes – fragments are separated using electrophoresis to create a pattern of bands (negatively-charged DNA moves towards positive-end of apparatus) – Shortest segments travel the furthest (easier to move through gel) ...
... – sample of DNA is cut using restriction enzymes – fragments are separated using electrophoresis to create a pattern of bands (negatively-charged DNA moves towards positive-end of apparatus) – Shortest segments travel the furthest (easier to move through gel) ...
DNA Web
... 14. Approximately how many genes are encoded in the DNA of humans? 15. ____________________________ is a genetic disease that results in the mutation of hemoglobin protein within our red blood cells. 16. Other than providing instructions for building a hemoglobin molecule, what are two other example ...
... 14. Approximately how many genes are encoded in the DNA of humans? 15. ____________________________ is a genetic disease that results in the mutation of hemoglobin protein within our red blood cells. 16. Other than providing instructions for building a hemoglobin molecule, what are two other example ...
Unit 9 Completed Vocabulary - WAHS
... RNA polymerase – enzyme similar to DNA polymerase that binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands during transcription. promoter – region of DNA that indicates to an enzyme where to bind to make RNA. intron – intervening sequence of DNA; does not code for a protein. exon – expressed sequence of DNA; ...
... RNA polymerase – enzyme similar to DNA polymerase that binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands during transcription. promoter – region of DNA that indicates to an enzyme where to bind to make RNA. intron – intervening sequence of DNA; does not code for a protein. exon – expressed sequence of DNA; ...
which together form the gene "stories" NOTE
... 1) the DNA strand will 'unzip' as the chemical bonds are broken between each of the nitrogen bases ...
... 1) the DNA strand will 'unzip' as the chemical bonds are broken between each of the nitrogen bases ...
How are protein made in our cells?
... in the nucleus. This code must send the message to the ribosome mRNA. mRNA is released into the cytoplasm. mRNA attaches to a ribosome. rRNA Codons will move through the ribosome by tRNA. Codons on mRNA will attach to anticodon on tRNA molecule. After this occurs, the amino acid on (top) tRNA will “ ...
... in the nucleus. This code must send the message to the ribosome mRNA. mRNA is released into the cytoplasm. mRNA attaches to a ribosome. rRNA Codons will move through the ribosome by tRNA. Codons on mRNA will attach to anticodon on tRNA molecule. After this occurs, the amino acid on (top) tRNA will “ ...
Development Through the Lifespan
... Genetic make-up of an individual Phenotype Observable characteristics of an individual Genetic Foundations Chromosomes – store and transmit genetic information. Genes – segments of DNA located along the chromosomes DNA – substance of which genes and chromosomes are made. Dominant-Recessive Inh ...
... Genetic make-up of an individual Phenotype Observable characteristics of an individual Genetic Foundations Chromosomes – store and transmit genetic information. Genes – segments of DNA located along the chromosomes DNA – substance of which genes and chromosomes are made. Dominant-Recessive Inh ...