Genetic Technology
... animals with human diseases and animals that can produce human materials. ...
... animals with human diseases and animals that can produce human materials. ...
DNA technology notes
... are taken from a cell sample, cut out and matched up in pairs • Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes • Karyotypes can be used to determine if genetic disorder is present • If too many are present can indicate Down’s syndrome • If some are missing can indicate Turner’s syndrome ...
... are taken from a cell sample, cut out and matched up in pairs • Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes • Karyotypes can be used to determine if genetic disorder is present • If too many are present can indicate Down’s syndrome • If some are missing can indicate Turner’s syndrome ...
DNA Jeopardy Review
... 2.May facilitate the evolution of new and potentially useful proteins as a result of exon shuffling 3.Introns also increase the benefit of ...
... 2.May facilitate the evolution of new and potentially useful proteins as a result of exon shuffling 3.Introns also increase the benefit of ...
DNA/RNA Worksheet TACGGCACCGTTAGGATT
... If you are given the following codon, what would the anticodon be? Codon: AUC Anticodon: _________________ ...
... If you are given the following codon, what would the anticodon be? Codon: AUC Anticodon: _________________ ...
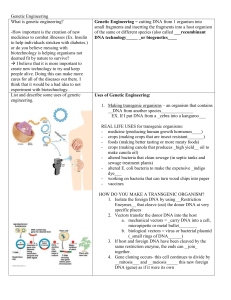
Genetic Engineering Guied Notes
... 1. Isolate the foreign DNA by using __Restriction Enzymes__ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = _carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet________ b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid ...
... 1. Isolate the foreign DNA by using __Restriction Enzymes__ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = _carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet________ b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid ...
Nucleotide - Jackson County School District
... Process by which a strand of mRNA is copied from a section of DNA enough information to code for 1 protein ...
... Process by which a strand of mRNA is copied from a section of DNA enough information to code for 1 protein ...
Genetic disorder/testing PPT
... features of the developing fetus including size, anatomy, number of appendages/parts, sex, and heartbeat. ...
... features of the developing fetus including size, anatomy, number of appendages/parts, sex, and heartbeat. ...
History of Genetics
... • 1910: Thomas Hunt Morgan: proved that genes are located on the chromosome • 1941: Beadle and Tatum - show how genes direct the synthesis of enzymes that control metabolic processes “1 gene = 1 enzyme” • 1952: Hershey and Chase - conducted experiments which helped to confirm that DNA was the geneti ...
... • 1910: Thomas Hunt Morgan: proved that genes are located on the chromosome • 1941: Beadle and Tatum - show how genes direct the synthesis of enzymes that control metabolic processes “1 gene = 1 enzyme” • 1952: Hershey and Chase - conducted experiments which helped to confirm that DNA was the geneti ...
Gene Expression Jeopardy
... What is the difference in premRNA and mRNS Pre-mRNA includes the introns ...
... What is the difference in premRNA and mRNS Pre-mRNA includes the introns ...
Q on Genetic Control of Protein Structure and function – Chapter 5
... What do DNA and RNA stand for? Draw a diagram of a single DNA nucleotide. Which enzyme turns DNA nucleotides into a polynucleotide? Explain what is meant by “complementary base pairing”. What type of bond holds the two DNA strands together? What are the 2 essential functions of DNA? What are the 2 m ...
... What do DNA and RNA stand for? Draw a diagram of a single DNA nucleotide. Which enzyme turns DNA nucleotides into a polynucleotide? Explain what is meant by “complementary base pairing”. What type of bond holds the two DNA strands together? What are the 2 essential functions of DNA? What are the 2 m ...
Recombination
... A. The sizes of DNA molecules can be determined by the position to which they migrate in a gel. B. Smaller DNA molecules move faster and farther than larger ones. C. Gels used for electrophoresis of DNA are made out of agarose. D. DNA molecules move through the gel towards the negative electrode. ...
... A. The sizes of DNA molecules can be determined by the position to which they migrate in a gel. B. Smaller DNA molecules move faster and farther than larger ones. C. Gels used for electrophoresis of DNA are made out of agarose. D. DNA molecules move through the gel towards the negative electrode. ...
forensics - bayo2pisay
... short sequence in the introns of DNA that is repeated in a head-to-tail manner at a specific chromosomal locus interspersed in genome Number of repeated units vary per human Loci – VNTR’s One VNTR – 17 bp, repeated 70 to 450 times Total: 1190 to 7650 base pairs ...
... short sequence in the introns of DNA that is repeated in a head-to-tail manner at a specific chromosomal locus interspersed in genome Number of repeated units vary per human Loci – VNTR’s One VNTR – 17 bp, repeated 70 to 450 times Total: 1190 to 7650 base pairs ...
Sources of DNA
... for transferring genes used for genetic engineering and gene therapy. Recombinant virus technology is used in the process gene therapy The genetic engineering process includes the following: identification ...
... for transferring genes used for genetic engineering and gene therapy. Recombinant virus technology is used in the process gene therapy The genetic engineering process includes the following: identification ...
Study Guide for LS
... - In a pedigree, a solid black square or circle indicates that the person has a certain trait. - In a pedigree, squares represent males. - In a pedigree, circles represent females. - In a pedigree, a half-filled square or circle indicates that the person is a carrier of a certain trait. ...
... - In a pedigree, a solid black square or circle indicates that the person has a certain trait. - In a pedigree, squares represent males. - In a pedigree, circles represent females. - In a pedigree, a half-filled square or circle indicates that the person is a carrier of a certain trait. ...
NAME CH11 In class assignment Due 2/18/14 Across 1. Initials of
... 2) When a restriction enzyme cuts a piece of DNA, portions of the ends are single stranded. Another term for these single stranded sections is: a) “single ends” b) “lonely ends” c) “sticky ends” d) “fragmented ends” 3) In order to produce a transgenic animal, DNA must be injected into the __________ ...
... 2) When a restriction enzyme cuts a piece of DNA, portions of the ends are single stranded. Another term for these single stranded sections is: a) “single ends” b) “lonely ends” c) “sticky ends” d) “fragmented ends” 3) In order to produce a transgenic animal, DNA must be injected into the __________ ...
Defined - cloudfront.net
... • Where: Single genes or entire chromosomes – Some gene mutations change phenotype (physical characteristics) • Example: Can cause a premature stop codon – Some gene mutations don’t change phenotype. • Example: Could be silent or occur in a non-coding region ...
... • Where: Single genes or entire chromosomes – Some gene mutations change phenotype (physical characteristics) • Example: Can cause a premature stop codon – Some gene mutations don’t change phenotype. • Example: Could be silent or occur in a non-coding region ...
DNA Review Cards
... potential least effect on the protein. Describe the process of transcription. What is a mutagen? What is the primary enzyme in transcription. Give examples of mutagens. What type of cell must a mutation occur in to be passed on to offspring? ...
... potential least effect on the protein. Describe the process of transcription. What is a mutagen? What is the primary enzyme in transcription. Give examples of mutagens. What type of cell must a mutation occur in to be passed on to offspring? ...
DOC
... Write your name on this quiz and then answer the following questions in three sentences or LESS. You have fifteen minutes to answer ten questions. 1. When you input the mRNA sequence of your gene of interest into Ambion’s website, what nucleotide pattern does it look for to come up with a list of ca ...
... Write your name on this quiz and then answer the following questions in three sentences or LESS. You have fifteen minutes to answer ten questions. 1. When you input the mRNA sequence of your gene of interest into Ambion’s website, what nucleotide pattern does it look for to come up with a list of ca ...
Study Guide: The Cell
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
Review for Post Exam 10 on iLearn
... Write the following questions on your own paper and answer them. 1. What differences in DNA gives each organism its own unique look? 2. Why is DNA called a universal code? 3. What macromolecule is DNA and RNA? 4. How are genes coded for in DNA 5. Why does DNA replicate? 6. How is DNA inherited? 7. D ...
... Write the following questions on your own paper and answer them. 1. What differences in DNA gives each organism its own unique look? 2. Why is DNA called a universal code? 3. What macromolecule is DNA and RNA? 4. How are genes coded for in DNA 5. Why does DNA replicate? 6. How is DNA inherited? 7. D ...
Chapter 10 Protein Synthesis Test Study Guide THERE WILL BE 21
... 13. Using pg. 207 in your textbook, determine the series of amino acids encoded for by the mRNA sequence CUCAAGUGCUUC. 14. Using pg. 207 in your textbook, determine the series of amino acids encoded for by the mRNA sequence AUGGACAAUUCG. 15. What would the sequence of DNA be from which the mRNA stra ...
... 13. Using pg. 207 in your textbook, determine the series of amino acids encoded for by the mRNA sequence CUCAAGUGCUUC. 14. Using pg. 207 in your textbook, determine the series of amino acids encoded for by the mRNA sequence AUGGACAAUUCG. 15. What would the sequence of DNA be from which the mRNA stra ...
Clinical Applications of Genetic Test
... Types of Genetic Tests • Diagnostic- establishes the basis of an existing disorder • Predictive- determines the presence of genetic condition when there are no obvious symptoms • Carrier- identifies heterozygotes • Prenatal- assesses a fetus for abnormalities ...
... Types of Genetic Tests • Diagnostic- establishes the basis of an existing disorder • Predictive- determines the presence of genetic condition when there are no obvious symptoms • Carrier- identifies heterozygotes • Prenatal- assesses a fetus for abnormalities ...