Oral cancer is one of the leading cancers around the world and
... ideal molecular markers. DNA methylation frequently leads to transcriptional changes in both tumor suppressor genes and oncogenes. Some of the techniques developed thus far enable the identification of novel cancer genes altered by DNA methylation alone or in combination with genetic events. They ma ...
... ideal molecular markers. DNA methylation frequently leads to transcriptional changes in both tumor suppressor genes and oncogenes. Some of the techniques developed thus far enable the identification of novel cancer genes altered by DNA methylation alone or in combination with genetic events. They ma ...
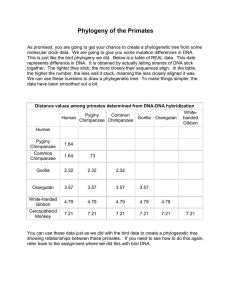
Phylogeny of the Primates
... As promised, you are going to get your chance to create a phylogenetic tree from some molecular clock data. We are going to give you some mutation differences in DNA. This is just like the bird phylogeny we did. Below is a table of REAL data. This date represents difference in DNA. It is obtained by ...
... As promised, you are going to get your chance to create a phylogenetic tree from some molecular clock data. We are going to give you some mutation differences in DNA. This is just like the bird phylogeny we did. Below is a table of REAL data. This date represents difference in DNA. It is obtained by ...
Unit 4
... 11. Explain how viruses may cause disease symptoms, and describe some medical weapons used to fight viral infections. Damage or kill cells. In response to a viral infection, lysosomes may release hydrolytic enzymes. Be toxic themselves or cause infected cells to produce toxins. Cause varying degrees ...
... 11. Explain how viruses may cause disease symptoms, and describe some medical weapons used to fight viral infections. Damage or kill cells. In response to a viral infection, lysosomes may release hydrolytic enzymes. Be toxic themselves or cause infected cells to produce toxins. Cause varying degrees ...
Lecture Notes - Course Notes
... the mitochondrial genome which contains 37 genes. Mitochondrial DNA is circular and is maternally inherited, unlike nuclear DNA. ...
... the mitochondrial genome which contains 37 genes. Mitochondrial DNA is circular and is maternally inherited, unlike nuclear DNA. ...
Spring 2011 Midterm Review Answers
... mRNA attaches to a ribosome and the message starts being read (AUG codon) For each codon on the mRNA strand, the corresponding tRNA with the anticodon pairs up with the mRNA sequence The tRNA molecules carry the amino acids which are then bound together with a peptide bond to form the protein When t ...
... mRNA attaches to a ribosome and the message starts being read (AUG codon) For each codon on the mRNA strand, the corresponding tRNA with the anticodon pairs up with the mRNA sequence The tRNA molecules carry the amino acids which are then bound together with a peptide bond to form the protein When t ...
DNA Workshop
... The single molecule of DNA in the bacteria, E. coli contains 4.7 x 106 nucleotide pairs. DNA replication begins at a single, fixed location in this molecule, called the replication origin, it proceeds at about _______ nucleotides per second, and thus is done in approximately _____ minutes. The avera ...
... The single molecule of DNA in the bacteria, E. coli contains 4.7 x 106 nucleotide pairs. DNA replication begins at a single, fixed location in this molecule, called the replication origin, it proceeds at about _______ nucleotides per second, and thus is done in approximately _____ minutes. The avera ...
Genetics Genetics, a discipline of biology, is the science of genes
... DNA is held in the sequence of pieces of DNA called genes. A gene is a sequence of DNA that contains genetic information and can influence the phenotype of an organism. Transmission of genetic information in genes is achieved via complementary base pairing. For example, in transcription, when a cell ...
... DNA is held in the sequence of pieces of DNA called genes. A gene is a sequence of DNA that contains genetic information and can influence the phenotype of an organism. Transmission of genetic information in genes is achieved via complementary base pairing. For example, in transcription, when a cell ...
A2 5.2.3 Genetic Engineering
... • Plasmids cut with restriction enzyme and mixed with cDNA, then sealed with ligase forming recombinant plasmids as they have new DNA in them • Plasmids mixed with bacteria and are taken up • Bacteria grown on agar plates producing a colony of clones ...
... • Plasmids cut with restriction enzyme and mixed with cDNA, then sealed with ligase forming recombinant plasmids as they have new DNA in them • Plasmids mixed with bacteria and are taken up • Bacteria grown on agar plates producing a colony of clones ...
DNA Review Questions
... A. Genes to specify the portion of the organism in which they are found B. All of the information needed for growing the whole organism C. All of the chromosomes except sex chromosomes which are restricted to sex organs D. Single stranded DNA E. One euchromatin except in the case of the Y-chromosome ...
... A. Genes to specify the portion of the organism in which they are found B. All of the information needed for growing the whole organism C. All of the chromosomes except sex chromosomes which are restricted to sex organs D. Single stranded DNA E. One euchromatin except in the case of the Y-chromosome ...
Unit 4 Genetics and Heredity Study Guide Below are some key
... 5. Which stage is the longest? Why (what happens during this stage)? 6. How do cells regulate growth normally? 7. What is Cancer? What are some different forms of cancer? What are some cau ...
... 5. Which stage is the longest? Why (what happens during this stage)? 6. How do cells regulate growth normally? 7. What is Cancer? What are some different forms of cancer? What are some cau ...
Cloning and PCR File
... DNA from bacteria. (A plasmid is circular DNA that is not part of a chromosome and can replicate independently.) Ligation is illustrated below. The DNA that results is called recombinant DNA. 3. In transformation, the recombinant DNA is inserted into a living cell, usually a bacterial cell. Changing ...
... DNA from bacteria. (A plasmid is circular DNA that is not part of a chromosome and can replicate independently.) Ligation is illustrated below. The DNA that results is called recombinant DNA. 3. In transformation, the recombinant DNA is inserted into a living cell, usually a bacterial cell. Changing ...
Gel Electrophoresis
... Gel matrix acts as a “seive” for DNA Large DNA molecules cannot pass through the small holes in the gel Small molecules move easily through the gel ...
... Gel matrix acts as a “seive” for DNA Large DNA molecules cannot pass through the small holes in the gel Small molecules move easily through the gel ...
Introduction to Genetics and Genomics
... RNA studies • Presence of any RNA molecule implies that the underlying gene is expressed. • techniques: differential display, SAGE, cDNA ...
... RNA studies • Presence of any RNA molecule implies that the underlying gene is expressed. • techniques: differential display, SAGE, cDNA ...
Genetic modification: an overview for non
... is called genetic modification or genetic engineering. There are three major differences between selective breeding and genetic modification: ...
... is called genetic modification or genetic engineering. There are three major differences between selective breeding and genetic modification: ...
Many practical applications of recombinant DNA are
... Recombinant DNA technology engineers microbial cells for producing foreign proteins, and its success solely depends on the precise reading of equivalent genes made with the help of bacterial cell machinery. This process has been responsible for fueling many advances related to modern molecular biolo ...
... Recombinant DNA technology engineers microbial cells for producing foreign proteins, and its success solely depends on the precise reading of equivalent genes made with the help of bacterial cell machinery. This process has been responsible for fueling many advances related to modern molecular biolo ...
DNA Bank Acquisitions Policy
... Herbarium of NYBG. Any herbarium specimen obtained this way that is duplicated in the NYBG herbarium will be dispersed to another interested herbarium. Please contact Lisa M. Campbell, Plant Research Laboratory, The New York Botanical Garden, Bronx, NY 10458 ([email protected]) prior to sending any ...
... Herbarium of NYBG. Any herbarium specimen obtained this way that is duplicated in the NYBG herbarium will be dispersed to another interested herbarium. Please contact Lisa M. Campbell, Plant Research Laboratory, The New York Botanical Garden, Bronx, NY 10458 ([email protected]) prior to sending any ...
Chapter 12 Study Guide 12.1 Identifying the Substance of Genes
... strand, the strands are said to be complementary. DNA copies itself through the process of replication: The two strands of the double helix unzip, forming replication forks. New bases are added, following the rules of base pairing (A with T and G with C). Each new DNA molecule has one original stran ...
... strand, the strands are said to be complementary. DNA copies itself through the process of replication: The two strands of the double helix unzip, forming replication forks. New bases are added, following the rules of base pairing (A with T and G with C). Each new DNA molecule has one original stran ...
Ch. 6 Section 1 Active Reading/Quiz
... A gene is a segment of DNA that codes for a protein or RNA molecule. A single molecule of DNA has thousands of genes lined up like the cars of a train. When genes are being used, the strand of DNA is stretched out so that the information it contains can be decoded and used to direct the synthesis of ...
... A gene is a segment of DNA that codes for a protein or RNA molecule. A single molecule of DNA has thousands of genes lined up like the cars of a train. When genes are being used, the strand of DNA is stretched out so that the information it contains can be decoded and used to direct the synthesis of ...
Chapter 22
... Retroposons of the viral superfamily are transposons that mobilize via an RNA that does not form an infectious particle. Some retroposons directly resemble retroviruses in their use of LTRs, whereas others do not have LTRs. Other elements can be found that were generated by an RNA-mediated transposi ...
... Retroposons of the viral superfamily are transposons that mobilize via an RNA that does not form an infectious particle. Some retroposons directly resemble retroviruses in their use of LTRs, whereas others do not have LTRs. Other elements can be found that were generated by an RNA-mediated transposi ...
CHAPTER 13
... This image shows a DNA fingerprint where DNA from a bloodstain at a crime scene is compared to suspect DNA. ...
... This image shows a DNA fingerprint where DNA from a bloodstain at a crime scene is compared to suspect DNA. ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.