CHEM523 Test 3
... Your answers must be well organized and concise. You have 75 minutes to complete the exam. 1) (10 points) Draw the mechanism of the reaction catalyzed by DNA polymerase that occurs between deoxyribose at the end of a DNA chain and a deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate. Include the chemical structure of ...
... Your answers must be well organized and concise. You have 75 minutes to complete the exam. 1) (10 points) Draw the mechanism of the reaction catalyzed by DNA polymerase that occurs between deoxyribose at the end of a DNA chain and a deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate. Include the chemical structure of ...
DNA RNA structure
... DNA is in the nucleus. RNA is made in the nucleus but travels to the cytoplasm • RNA is made in the nucleoli but can travel out to the cytoplasm ...
... DNA is in the nucleus. RNA is made in the nucleus but travels to the cytoplasm • RNA is made in the nucleoli but can travel out to the cytoplasm ...
Chapter 13 DNA Technology
... - “sticky ends” (single chain segments or tails created on the cut piece of DNA….easily bind to complementary strands of DNA. ** Pieces of DNA cut with the same restriction enzyme can bind to form a new sequence of nucleotides…..therefore, DNA HAS BEEN TRANSFERRED OR ISOLATED!!!!!!! See fig.13-1 on ...
... - “sticky ends” (single chain segments or tails created on the cut piece of DNA….easily bind to complementary strands of DNA. ** Pieces of DNA cut with the same restriction enzyme can bind to form a new sequence of nucleotides…..therefore, DNA HAS BEEN TRANSFERRED OR ISOLATED!!!!!!! See fig.13-1 on ...
Heredity
... • Sperm Cells (male gametes)- contain half of the genetic information for organisms • Egg Cells (female gametes)- contain half of the genetic information for organisms • How many chromosomes do we have? • How are these cells produced? ...
... • Sperm Cells (male gametes)- contain half of the genetic information for organisms • Egg Cells (female gametes)- contain half of the genetic information for organisms • How many chromosomes do we have? • How are these cells produced? ...
Nucleic Acids DNA & RNA
... that codes for a protein, which in turn codes for a trait (skin tone, eye color..etc), a gene is a stretch of DNA. ...
... that codes for a protein, which in turn codes for a trait (skin tone, eye color..etc), a gene is a stretch of DNA. ...
DNA Replication
... fragment. A complex containing helicase and 2 DNA polymerases carries out the coordinated synthesis of both strands. The two polymerases are attached to each other and move with the replication fork. The fidelity of DNA polymerization is very high, one error per 109 bases ...
... fragment. A complex containing helicase and 2 DNA polymerases carries out the coordinated synthesis of both strands. The two polymerases are attached to each other and move with the replication fork. The fidelity of DNA polymerization is very high, one error per 109 bases ...
DNA- (Deoxyribonucleic acid)- genetic material that carries the
... Guanine (G), Cytosine (C) are the nitrogen bases. Adenine always pairs with Thymine and Guanine always pairs with Cytosine. With these four base pairs, there are 8,000,000 possible outcomes between two parents and the arrangement of chromosomes. The order of the nitrogen bases is a genetic code to p ...
... Guanine (G), Cytosine (C) are the nitrogen bases. Adenine always pairs with Thymine and Guanine always pairs with Cytosine. With these four base pairs, there are 8,000,000 possible outcomes between two parents and the arrangement of chromosomes. The order of the nitrogen bases is a genetic code to p ...
El Diamante Biology
... a. Which organism is a producer? Where does it get its energy? What is that process called? b. Of the 3 organisms illustrated by this food chain, which type has the smallest population? 14. Study the food web on page 410 (figure 13.11) and answer the following questions: a. Which type of organism co ...
... a. Which organism is a producer? Where does it get its energy? What is that process called? b. Of the 3 organisms illustrated by this food chain, which type has the smallest population? 14. Study the food web on page 410 (figure 13.11) and answer the following questions: a. Which type of organism co ...
Questions - Vanier College
... C) occurs continuously in the cell. D) does not result in the production of enzymes. E) starts when the pathway's product is present. 4. Gene expression might be altered at the level of post-transcriptional processing in eukaryotes rather than prokaryotes because of which of the following? A) Prokar ...
... C) occurs continuously in the cell. D) does not result in the production of enzymes. E) starts when the pathway's product is present. 4. Gene expression might be altered at the level of post-transcriptional processing in eukaryotes rather than prokaryotes because of which of the following? A) Prokar ...
Top 102 Biology Review
... 55.The Human Genome Project ______________ all of human ______. This information has been used for ________ therapy. 56.What technique can separate DNA molecules of different length based on the size of the molecules? 57.DNA put together from 2 different species is called _________________ DNA. 58.A ...
... 55.The Human Genome Project ______________ all of human ______. This information has been used for ________ therapy. 56.What technique can separate DNA molecules of different length based on the size of the molecules? 57.DNA put together from 2 different species is called _________________ DNA. 58.A ...
DNA, RNA, and Protein
... • RNA polymerase binds to DNA promoter • DNA strands unwind & separate • RNA polymerase adds free RNA nucleotides to complement 1 strand of DNA bases. ...
... • RNA polymerase binds to DNA promoter • DNA strands unwind & separate • RNA polymerase adds free RNA nucleotides to complement 1 strand of DNA bases. ...
Ch. 13 Genetic Engineering
... The Enzymes recognize specific sequences on Human and Bacterial Plasmids The Enzymes cut the strands. The cut produces DNA fragments with short strands on each end that are complementary to each other ...
... The Enzymes recognize specific sequences on Human and Bacterial Plasmids The Enzymes cut the strands. The cut produces DNA fragments with short strands on each end that are complementary to each other ...
dna structure - Siegel Science
... protein & determines a trait • Chromosome: threadlike structure in nucleus that contains genetic info ...
... protein & determines a trait • Chromosome: threadlike structure in nucleus that contains genetic info ...
11-03-11 st bio3 notes
... Chromosome: collection of DNA in your cells, suitcases holding the DNA when the cell divides Genome: your complete collection of DNA/chromosomes in a cell Alleles: different versions of a gene that control the same thing -ex: gene codes for hair color, allele controls WHICH hair color Genotype: all ...
... Chromosome: collection of DNA in your cells, suitcases holding the DNA when the cell divides Genome: your complete collection of DNA/chromosomes in a cell Alleles: different versions of a gene that control the same thing -ex: gene codes for hair color, allele controls WHICH hair color Genotype: all ...
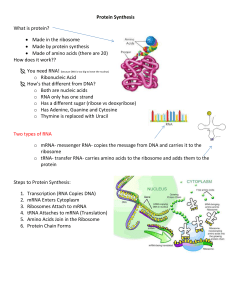
Protein Synthesis - Madison County Schools
... What is protein? Made in the ribosome Made by protein synthesis Made of amino acids (there are 20) How does it work?? You need RNA! (because DNA is too big to leave the nucleus) o Ribonucleic Acid How’s that different from DNA? o Both are nucleic acids o RNA only has one strand o Has a dif ...
... What is protein? Made in the ribosome Made by protein synthesis Made of amino acids (there are 20) How does it work?? You need RNA! (because DNA is too big to leave the nucleus) o Ribonucleic Acid How’s that different from DNA? o Both are nucleic acids o RNA only has one strand o Has a dif ...
File
... Introduction: DNA fingerprinting relies on the fact that the DNA code is universal for all living things and that there are differences between individuals within that code. Because human DNA is very similar to every other human’s DNA, DNA fingerprinting primarily focuses on the areas of the genetic ...
... Introduction: DNA fingerprinting relies on the fact that the DNA code is universal for all living things and that there are differences between individuals within that code. Because human DNA is very similar to every other human’s DNA, DNA fingerprinting primarily focuses on the areas of the genetic ...
How do organisms grow and heal themselves? What instructions do
... Groups of Genes are called Chromosomes All Chromosomes is an organisms DNA ...
... Groups of Genes are called Chromosomes All Chromosomes is an organisms DNA ...
Day 58 - upwardsapbio
... telomere is extended. A telomere is a repeated extra part of the DNA molecule. In humans the telomere sequence is TTAGGG. The reason for telomeres is that an RNA primer is made from the telomere so that the original strand can serve as a template without the daughter strand being shortened with each ...
... telomere is extended. A telomere is a repeated extra part of the DNA molecule. In humans the telomere sequence is TTAGGG. The reason for telomeres is that an RNA primer is made from the telomere so that the original strand can serve as a template without the daughter strand being shortened with each ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.