User Management
... Each time DNA gathers Inventory data it compares the current details against information already held on the server and if there are any differences they are recorded in the History. ...
... Each time DNA gathers Inventory data it compares the current details against information already held on the server and if there are any differences they are recorded in the History. ...
Mitosis
... 19. During transcription, DNA serves as a template for producing mRNA, which leaves the nucleus. mRNA carries coded instructions from DNA to ribosome. ...
... 19. During transcription, DNA serves as a template for producing mRNA, which leaves the nucleus. mRNA carries coded instructions from DNA to ribosome. ...
Genes and Chromosomes Justified True or False Worksheet
... The cells in a person’s eyes only have the eye color gene, all other cells do not have that gene. ...
... The cells in a person’s eyes only have the eye color gene, all other cells do not have that gene. ...
Test 3
... 9. Compare and contrast control of mRNA transcription in eukaryotes as prokaryotes. Prokaryotes * Most regulation achieved by modulating binding of RNA polymerase to DNA * mostly negative control -(Gene is usually on, and most regulators turn off) *Genes for related proteins usually on one contiguou ...
... 9. Compare and contrast control of mRNA transcription in eukaryotes as prokaryotes. Prokaryotes * Most regulation achieved by modulating binding of RNA polymerase to DNA * mostly negative control -(Gene is usually on, and most regulators turn off) *Genes for related proteins usually on one contiguou ...
Genetics - Mrs. Yu`s Science Classes
... MOLECULAR GENETICS RNA (ribose nucleic acid) Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, Cytosine mRNA – provides instructions for assembling amino acids into a polypeptide chain; linear structure tRNA – delivers amino acids to a ribosome for their addition into a polypeptide chain; “clover-leaf ” shape struc ...
... MOLECULAR GENETICS RNA (ribose nucleic acid) Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, Cytosine mRNA – provides instructions for assembling amino acids into a polypeptide chain; linear structure tRNA – delivers amino acids to a ribosome for their addition into a polypeptide chain; “clover-leaf ” shape struc ...
EOC Checklist
... Biological magnification is when concentrations of a harmful substance ______________ as it moves up the trophic levels in a food web or chain. Organisms at the top will be _______________ likely to be affected and harmed. I remember what can happen when you introduce a nonnative species into an ...
... Biological magnification is when concentrations of a harmful substance ______________ as it moves up the trophic levels in a food web or chain. Organisms at the top will be _______________ likely to be affected and harmed. I remember what can happen when you introduce a nonnative species into an ...
Document
... Proofreading Ability Replication errors can result in mutations – is a change in a nucleotide sequence) DNA polymerase has proofreading ability 1 mistake per 10,000 base pairs occurs DNA polymerase can repair damage If errors are not fixed you get mutations ...
... Proofreading Ability Replication errors can result in mutations – is a change in a nucleotide sequence) DNA polymerase has proofreading ability 1 mistake per 10,000 base pairs occurs DNA polymerase can repair damage If errors are not fixed you get mutations ...
Exchange of genetic material between harmless bacteria could be
... exchanging its DNA in a process known as recombination. This can include the gain of antibiotic-resistant genetic variants and increase the risk of wider spread of antibiotic resistance. In this study, a seemingly harmless strain of the bacterium, known as non-typable or NT, was the most common type ...
... exchanging its DNA in a process known as recombination. This can include the gain of antibiotic-resistant genetic variants and increase the risk of wider spread of antibiotic resistance. In this study, a seemingly harmless strain of the bacterium, known as non-typable or NT, was the most common type ...
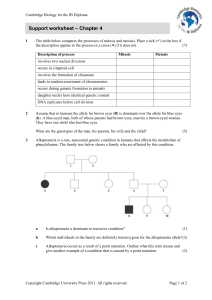
Support worksheet – Chapter 4 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... Assume that in humans the allele for brown eyes (B) is dominant over the allele for blue eyes (b). A blue-eyed man, both of whose parents had brown eyes, marries a brown-eyed woman. They have one child who has blue eyes. What are the genotypes of the man, his parents, his wife and the child? ...
... Assume that in humans the allele for brown eyes (B) is dominant over the allele for blue eyes (b). A blue-eyed man, both of whose parents had brown eyes, marries a brown-eyed woman. They have one child who has blue eyes. What are the genotypes of the man, his parents, his wife and the child? ...
18.1 Mutations Are Inherited Alterations in the DNA Sequence
... Adenine is replaced by thymine. Cytosine is replaced by adenine. Guanine is replaced by adenine. Three nucleotide pairs are inserted into DNA. ...
... Adenine is replaced by thymine. Cytosine is replaced by adenine. Guanine is replaced by adenine. Three nucleotide pairs are inserted into DNA. ...
Slide 1
... fashion, although many gene clusters exist which seem to aid coordinate expression: globin, histone, immunoglobulin, MHC, etc. Some chromosomes are more rich in genes than others, although chromosome size roughly correlates with gene number A gene’s location is termed its locus as we have touched up ...
... fashion, although many gene clusters exist which seem to aid coordinate expression: globin, histone, immunoglobulin, MHC, etc. Some chromosomes are more rich in genes than others, although chromosome size roughly correlates with gene number A gene’s location is termed its locus as we have touched up ...
EOC Review Part 3
... Cloning- making an identical individual (remember mimi the mouse) When a nucleus of a body cell is placed into an egg. This allows scientists to make identical copies of an organism quickly. The first clone was Dolly, a sheep. It could allow us to bring back extinct or endangered organisms. ...
... Cloning- making an identical individual (remember mimi the mouse) When a nucleus of a body cell is placed into an egg. This allows scientists to make identical copies of an organism quickly. The first clone was Dolly, a sheep. It could allow us to bring back extinct or endangered organisms. ...
Ecology
... – Enzymes act to speed up (catalyze) chemical reactions in the body • Ex. Digestion of food, making DNA, and regulating ...
... – Enzymes act to speed up (catalyze) chemical reactions in the body • Ex. Digestion of food, making DNA, and regulating ...
CLARK LAP Wednesday March 26 2014 STRAWBERRY DNA
... through the cheesecloth and into the tall glass until there is very little liquid left in the funnel (only wet pulp remains). How does the filtered strawberry liquid look? • Pour the filtered strawberry liquid from the tall glass into the small glass jar so that the jar is one quarter full. • Measur ...
... through the cheesecloth and into the tall glass until there is very little liquid left in the funnel (only wet pulp remains). How does the filtered strawberry liquid look? • Pour the filtered strawberry liquid from the tall glass into the small glass jar so that the jar is one quarter full. • Measur ...
Table II Transformation of various derived strains OSU Strain Outcrossed with
... in: Genetic Engineering of Microorganisms for Chemicals, eds. Hollaender et al. pp. 87-100 Plenum, New York) with slight modifications. Two inl+ transformants (Tl and T3) were obtained. They were back-crossed to an inl (89601) strain and several inl+ ascospores from the F1 progeny were selected for ...
... in: Genetic Engineering of Microorganisms for Chemicals, eds. Hollaender et al. pp. 87-100 Plenum, New York) with slight modifications. Two inl+ transformants (Tl and T3) were obtained. They were back-crossed to an inl (89601) strain and several inl+ ascospores from the F1 progeny were selected for ...
HONORS BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE 2010
... why mitosis does not. 4. If an organism has 80 chromosomes, how would non-disjunction affect the resulting daughter cells during meiosis? Provide a specific example of a human genetic disorder resulting from non-disjunction. 5. Dr. Goldin cuts her big toe. What cellular division process would be use ...
... why mitosis does not. 4. If an organism has 80 chromosomes, how would non-disjunction affect the resulting daughter cells during meiosis? Provide a specific example of a human genetic disorder resulting from non-disjunction. 5. Dr. Goldin cuts her big toe. What cellular division process would be use ...
Chapter 4: DNA, Genes, and Protein Synthesis
... In 1869, a chemist by the name of Friedrich Miescher found a substance in the cell nucleus that he called "nuclein." This substance became known as deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA. In the 1950s, several researchers were attempting to discover the structure of DNA and exactly how it or some other molec ...
... In 1869, a chemist by the name of Friedrich Miescher found a substance in the cell nucleus that he called "nuclein." This substance became known as deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA. In the 1950s, several researchers were attempting to discover the structure of DNA and exactly how it or some other molec ...
2657/113 Recombinant DNA……To Exempt or Non
... What is recombinant DNA (rDNA) you may be asking yourself? The National Institutes of Health Office of Biotechnology Activities (NIH-OBA) defines rDNA molecules as either: (i) molecules that are constructed outside living cells by joining natural or synthetic DNA segments to DNA molecules that can r ...
... What is recombinant DNA (rDNA) you may be asking yourself? The National Institutes of Health Office of Biotechnology Activities (NIH-OBA) defines rDNA molecules as either: (i) molecules that are constructed outside living cells by joining natural or synthetic DNA segments to DNA molecules that can r ...
Structure and function of DNA
... Complete the mRNA molecule by filling in the correct base sequence on the diagram. How many amino acids are coded for by this section of mRNA? ...
... Complete the mRNA molecule by filling in the correct base sequence on the diagram. How many amino acids are coded for by this section of mRNA? ...
Section 8.7 Mutations
... Two Categories of Mutations: 1.Single Gene – affects one gene – usually caused by an error in DNA replication 2. Chromosomal – affects chromosomes – usually error in meiosis . Usually more harmful since many genes are affected. ...
... Two Categories of Mutations: 1.Single Gene – affects one gene – usually caused by an error in DNA replication 2. Chromosomal – affects chromosomes – usually error in meiosis . Usually more harmful since many genes are affected. ...
KS4 Chromosomes, Genes and DNA
... In all living things, characteristics are passed on in the chromosomes that offspring inherit from their parents. So all human characteristics, including gender, must be something to do with chromosomes. Where are chromosomes found? 4 of 47 ...
... In all living things, characteristics are passed on in the chromosomes that offspring inherit from their parents. So all human characteristics, including gender, must be something to do with chromosomes. Where are chromosomes found? 4 of 47 ...
Chapter 13 Presentation-Meiosis and Chromosomes
... organism to the next within a species. They are the vehicles of heredity. Minor differences in the sequences of base pairs on these chromosomes is what contributes to variation. ...
... organism to the next within a species. They are the vehicles of heredity. Minor differences in the sequences of base pairs on these chromosomes is what contributes to variation. ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.