cataract
... 11. The Nile River is the world’s longest river. 12. The Nile River flows from South to North. 13. The Nile flooded about the same time every year. 14. The Nile’s flood pattern was predictable. 15. The Nile River was used for trade and travel. 16. The hot desert protected Egypt from foreign attacks. ...
... 11. The Nile River is the world’s longest river. 12. The Nile River flows from South to North. 13. The Nile flooded about the same time every year. 14. The Nile’s flood pattern was predictable. 15. The Nile River was used for trade and travel. 16. The hot desert protected Egypt from foreign attacks. ...
Pharaohs/Gods/Places - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... Mediterranean Sea – large body of water north of Egypt; Nile flows into it Red Sea – large body of water east of Egypt Nile River – longest river in the world (4,160 mi.), runs away from Equator (north), annual floods Nile Delta – triangle/fan shaped area at end of Nile River (ends at Mediterranean ...
... Mediterranean Sea – large body of water north of Egypt; Nile flows into it Red Sea – large body of water east of Egypt Nile River – longest river in the world (4,160 mi.), runs away from Equator (north), annual floods Nile Delta – triangle/fan shaped area at end of Nile River (ends at Mediterranean ...
Ancient Egypt - Maple River Schools
... Benefits of the Nile River • Transportation – Used to travel to other villages – Trade – developed friendly relations with others along the Nile ...
... Benefits of the Nile River • Transportation – Used to travel to other villages – Trade – developed friendly relations with others along the Nile ...
Between Lines THE PHARAOHS OF EGYPT
... The Nile is the thread of life that has kept the Delta and her people alive for thousands of years, Here's a few interesting facts and random thoughts about that ancient and monumental stream... Tlie Nile is 4,132 miles long, with the headwaters called "The Blue Nile" and the lower stream known as " ...
... The Nile is the thread of life that has kept the Delta and her people alive for thousands of years, Here's a few interesting facts and random thoughts about that ancient and monumental stream... Tlie Nile is 4,132 miles long, with the headwaters called "The Blue Nile" and the lower stream known as " ...
Geofarming
... The three seasons of farming The Egyptians had three seasons of farming, with four months in each season. ...
... The three seasons of farming The Egyptians had three seasons of farming, with four months in each season. ...
Egypt`s Nile Valley Basin Irrigation
... about four to six week later. At its peak, the flood would cover the entire floodplain to a depth of 1.5 meters. The waters would begin to recede in the south by early October, and by late November most of the valley was drained dry. Egyptian farmers then had before them well-watered fields that had ...
... about four to six week later. At its peak, the flood would cover the entire floodplain to a depth of 1.5 meters. The waters would begin to recede in the south by early October, and by late November most of the valley was drained dry. Egyptian farmers then had before them well-watered fields that had ...
classroom tutorials
... Even though Upper and Lower Egypt were unified early in Egyptian history, the pharaohs always claimed that they ruled over “the two lands.” A design element employed by the ancient Egyptians clearly illustrates this point. The sema tawy sign, seen here between the legs of the painted, white wooden c ...
... Even though Upper and Lower Egypt were unified early in Egyptian history, the pharaohs always claimed that they ruled over “the two lands.” A design element employed by the ancient Egyptians clearly illustrates this point. The sema tawy sign, seen here between the legs of the painted, white wooden c ...
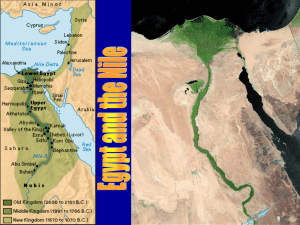
Egypt Study Guide 1. Be able to locate the following on a map and
... e. Libyan Desert (Western Desert) f. Arabian Desert (Eastern Desert) g. Nubia h. Cairo i. Giza j. Memphis k. Thebes l. Valley of the Kings 2. Be able to define the following: a. Canopic Jars b. Cartouche c. Cataract d. Cubit e. Delta f. Drought g. Economy h. Emergence i. Harvest j. ...
... e. Libyan Desert (Western Desert) f. Arabian Desert (Eastern Desert) g. Nubia h. Cairo i. Giza j. Memphis k. Thebes l. Valley of the Kings 2. Be able to define the following: a. Canopic Jars b. Cartouche c. Cataract d. Cubit e. Delta f. Drought g. Economy h. Emergence i. Harvest j. ...
Chapter 2 Study Guide – EGYPT
... Who was responsible for combining these two lands? What was his capital city? ...
... Who was responsible for combining these two lands? What was his capital city? ...
Class Notes: Chapter 3, Lesson 1
... Class Notes: Chapter 3, Lesson 1 1. Ancient Egypt flourished for nearly 3000 years in the Nile River Valley of Africa. 2. People began to move into the Nile River Valley after 10,000 BC, during the New Stone Age, and by 4500 BC many small villages formed. 3. People were drawn to the Nile River Valle ...
... Class Notes: Chapter 3, Lesson 1 1. Ancient Egypt flourished for nearly 3000 years in the Nile River Valley of Africa. 2. People began to move into the Nile River Valley after 10,000 BC, during the New Stone Age, and by 4500 BC many small villages formed. 3. People were drawn to the Nile River Valle ...
Farming - Grade4-BCA
... Crops that were grown included wheat, barley, flax, onions, leeks, garlic, beans, lettuce, lentils, cabbages, radishes, turnips, grapes, figs, plums and melons. The Egyptians had plenty of food with great variety! Since Egypt didn’t get much rain, they had to find a way of watering the crops once a ...
... Crops that were grown included wheat, barley, flax, onions, leeks, garlic, beans, lettuce, lentils, cabbages, radishes, turnips, grapes, figs, plums and melons. The Egyptians had plenty of food with great variety! Since Egypt didn’t get much rain, they had to find a way of watering the crops once a ...
Cornell Notes – Geography and Early Egypt
... Without the “gift” of flooding that provided the rich soil for crops, civilization probable would not have developed in Egypt. ...
... Without the “gift” of flooding that provided the rich soil for crops, civilization probable would not have developed in Egypt. ...
WH4
... Scribes were the few Egyptians who knew how to read and write. Being a scribe was an extremely difficult job because in total, there were hundreds of different hieroglyphs to remember. A scribe's job was highly regarded in Ancient Egypt. Although being a scribe was rewarding, the training could take ...
... Scribes were the few Egyptians who knew how to read and write. Being a scribe was an extremely difficult job because in total, there were hundreds of different hieroglyphs to remember. A scribe's job was highly regarded in Ancient Egypt. Although being a scribe was rewarding, the training could take ...
Chapter 1 Study Guide
... o What was the staple [main] food of ancient Egyptians? o Why did farmers build the pyramids? (Why were they not farming?) o What other famous Egyptian monument is near the Great Pyramid? What does it look like? o What were 2 daily uses of the Nile River? What were 2 uses of the river for farmers? o ...
... o What was the staple [main] food of ancient Egyptians? o Why did farmers build the pyramids? (Why were they not farming?) o What other famous Egyptian monument is near the Great Pyramid? What does it look like? o What were 2 daily uses of the Nile River? What were 2 uses of the river for farmers? o ...
Ancient Egypt : The Old Kingdom
... Floods of the Nile • Most of Egypt was desert. • The Nile’s floods were easier to predict than flood in Mesopotamia. • The Nile flooded upper Egypt in midsummer and lower Egypt in the fall. • The silt from the Nile made the soil ideal for farming. • Without floods, people never could have settled i ...
... Floods of the Nile • Most of Egypt was desert. • The Nile’s floods were easier to predict than flood in Mesopotamia. • The Nile flooded upper Egypt in midsummer and lower Egypt in the fall. • The silt from the Nile made the soil ideal for farming. • Without floods, people never could have settled i ...
egypt test study guide key
... Weak leadership Egypt attacked by other more powerful groups, with more and better weapons Loss of land (only left with Nile delta) 2. What two things were the Hyksos known for? Iron weapons and horse drawn chariots ...
... Weak leadership Egypt attacked by other more powerful groups, with more and better weapons Loss of land (only left with Nile delta) 2. What two things were the Hyksos known for? Iron weapons and horse drawn chariots ...
Chapter 2
... Egypt, Nile River Valley Civilization • Nile River played a key role • Yearly flood deposited rich silt for farming • Egyptians learned how to harness the flood to help instead of harm them (dikes, reservoirs, irrigation ditches) ...
... Egypt, Nile River Valley Civilization • Nile River played a key role • Yearly flood deposited rich silt for farming • Egyptians learned how to harness the flood to help instead of harm them (dikes, reservoirs, irrigation ditches) ...
Egypt Test Study Guide - Warren County Schools
... Egypt Test Study Guide Mr. Davis Social Studies 7 Warriors ...
... Egypt Test Study Guide Mr. Davis Social Studies 7 Warriors ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide: Egypt
... annual flooding, led to development of 3 seasons and a 365 day calendar Nubia was located along the upper Nile River valley. The Nubians were among the first people to make ceramic pottery and offer it for trade. They also traded goods such as hardwoods and animal products that came from places in ...
... annual flooding, led to development of 3 seasons and a 365 day calendar Nubia was located along the upper Nile River valley. The Nubians were among the first people to make ceramic pottery and offer it for trade. They also traded goods such as hardwoods and animal products that came from places in ...
Gift of the Nile questions
... 15. What was the Sun God’s name? Was he the Egyptian’s most important god? Why ...
... 15. What was the Sun God’s name? Was he the Egyptian’s most important god? Why ...
Egypt Notes page Geography • Nile River – 4,100 miles long, flows
... Transportation on the Nile Nile provided a reliable system of transportation. flows north - northbound boats drifted with current wind blows south - boats hoist their sails and wind blows them up river. Upper and Lower Egypt south portion, Upper Egypt, is higher in elevation north portion, ...
... Transportation on the Nile Nile provided a reliable system of transportation. flows north - northbound boats drifted with current wind blows south - boats hoist their sails and wind blows them up river. Upper and Lower Egypt south portion, Upper Egypt, is higher in elevation north portion, ...
Ancient Egyptians and the Environment
... Literally thought to keep the sun rising each morning “Responsible” for the regular flooding of the Nile ...
... Literally thought to keep the sun rising each morning “Responsible” for the regular flooding of the Nile ...
The Nile River “The Gift of the Nile”
... Papyrus was bound together to make rafts. Short lengths of wood were cut from acacia and sycamore and tied together with the papyrus to make rope. ...
... Papyrus was bound together to make rafts. Short lengths of wood were cut from acacia and sycamore and tied together with the papyrus to make rope. ...
Ancient Egypt
... • Scribes held a privileged place in society • Because they were so necessary to the nobles that they lived in the royal palace or temple • They did not have to partake in manual labour • They kept records, transcribed laws, and composed hymns ...
... • Scribes held a privileged place in society • Because they were so necessary to the nobles that they lived in the royal palace or temple • They did not have to partake in manual labour • They kept records, transcribed laws, and composed hymns ...
Aswan Dam

The Aswan Dam is an embankment dam built across the Nile at Aswan, Egypt between 1898 and 1902. Since the 1960s, the name commonly refers to the Aswan High Dam. Construction of the High Dam became a key objective of the Egyptian Government following the Egyptian Revolution of 1952, as the ability to control floods, provide water for irrigation, and generate hydroelectricity were seen as pivotal to Egypt's industrialization. The High Dam was constructed between 1960 and 1970, and has had a significant effect on the economy and culture of Egypt.Before the dams were built, the Nile flooded every year during late summer, when water flowed down the valley from its East African drainage basin. These floods brought high water and natural nutrients and minerals that annually enriched the fertile soil along the floodplain and delta; this had made the Nile valley ideal for farming since ancient times. Because floods vary, in high-water years the whole crop might be wiped out, while in low-water years widespread drought and famine occasionally occurred. As Egypt's population grew and conditions changed, both a desire and ability developed to control the floods, and thus both protect and support farmland and the economically important cotton crop. With the reservoir storage provided by the Aswan dams, the floods could be lessened and the water stored for later release.