File - MRS. WILSON Science
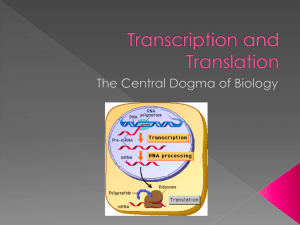
... DNA provides the instructions needed by a cell to make proteins. But the instructions are not made directly into proteins. First, a DNA message is converted into RNA in a process called transcription. Then, the RNA message is converted into proteins in a process called translation. The relationship ...
... DNA provides the instructions needed by a cell to make proteins. But the instructions are not made directly into proteins. First, a DNA message is converted into RNA in a process called transcription. Then, the RNA message is converted into proteins in a process called translation. The relationship ...
Science Notebook DNA, RNA, and Protein
... one amino acid nucleic acid made of ribose, phosphate, and one of four nitrogenous bases—adenine, cytosine, guanine, or uracil intervening DNA sequences that are transcribed and then removed from the final mRNA process by which mRNA directs the synthesis of a protein long strands of RNA that are com ...
... one amino acid nucleic acid made of ribose, phosphate, and one of four nitrogenous bases—adenine, cytosine, guanine, or uracil intervening DNA sequences that are transcribed and then removed from the final mRNA process by which mRNA directs the synthesis of a protein long strands of RNA that are com ...
Chapter 8. Manipulating DNA, RNA and proteins
... Transfecting cells, including bacteria Living bacteria (and other cells) can be transfected with DNA Cells can be treated to enable them to take up DNA (competent cells) Cells can be permeabilized by high voltage (electroporated) to take up DNA DNA can be packaged in liposomes that get incorporated ...
... Transfecting cells, including bacteria Living bacteria (and other cells) can be transfected with DNA Cells can be treated to enable them to take up DNA (competent cells) Cells can be permeabilized by high voltage (electroporated) to take up DNA DNA can be packaged in liposomes that get incorporated ...
Chapter 21 (part 1) - Nevada Agricultural Experiment
... Nucleoplasm III others Mitochondrial RNA Mitochondrial gene Mitochondria polymerase transcripts Chloroplast RNA polymerase ...
... Nucleoplasm III others Mitochondrial RNA Mitochondrial gene Mitochondria polymerase transcripts Chloroplast RNA polymerase ...
One Step Quantitative Real-Time PCR Protocol
... crucial for reverse transcription. Doing NRC once is enough, if the same RNA samples are used in experiments with different genes. In addition, NTC must be included in each plate every time for each tested gene. This is a good control for checking for any contamination in primer/probe mix or formati ...
... crucial for reverse transcription. Doing NRC once is enough, if the same RNA samples are used in experiments with different genes. In addition, NTC must be included in each plate every time for each tested gene. This is a good control for checking for any contamination in primer/probe mix or formati ...
Slide 1
... There are 64 possible ‘triplets’ that can be formed from the 4 different bases, but there are only 20 amino acids (AA) In most cases, more than one type of triplet codes for a given AA For example, CAA and CAG both code for the same AA, glutamine A substitution of a G for the second A in CAA would c ...
... There are 64 possible ‘triplets’ that can be formed from the 4 different bases, but there are only 20 amino acids (AA) In most cases, more than one type of triplet codes for a given AA For example, CAA and CAG both code for the same AA, glutamine A substitution of a G for the second A in CAA would c ...
lesson x - MisterSyracuse.com
... 1. What we need to find out is how genes are controlled. We don’t want them on all the time, but we don’t want them off all the time, either. 2. In prokaryotes, things called operons control the process. 3. There is an operator gene that must be active in order for anything to happen. 4. There is pr ...
... 1. What we need to find out is how genes are controlled. We don’t want them on all the time, but we don’t want them off all the time, either. 2. In prokaryotes, things called operons control the process. 3. There is an operator gene that must be active in order for anything to happen. 4. There is pr ...
E.coli
... MicF RNA and his target gene OmpF: OmpF is a major E.coli outer membrane porin. MicF RNA inhibits OmpF expression in response to the environment. Unlike most other cases MicF and OmpF are partially complementary. The mechanism of inhibition is not completely clear. DicF and his target gene FtsZ: Th ...
... MicF RNA and his target gene OmpF: OmpF is a major E.coli outer membrane porin. MicF RNA inhibits OmpF expression in response to the environment. Unlike most other cases MicF and OmpF are partially complementary. The mechanism of inhibition is not completely clear. DicF and his target gene FtsZ: Th ...
Study Guide Foldable .Answer Key
... information for the inheritance of traits. A gene has the information for making a specific protein. 5. Chromosomes where genes are located ...
... information for the inheritance of traits. A gene has the information for making a specific protein. 5. Chromosomes where genes are located ...
What is RNA? - Biology for Life
... • The first genetic information and enzymes were RNA molecules • Why RNA? RNA can act as a catalyst to: ...
... • The first genetic information and enzymes were RNA molecules • Why RNA? RNA can act as a catalyst to: ...
Retroviruses - stephen fleenor
... Draw the lytic cycle of the HIV virus (as you did yesterday), showing reverse transcriptase. Also indicate the point at which the genetic material can acquire mutations much more rapidly than DNA-based viruses. ...
... Draw the lytic cycle of the HIV virus (as you did yesterday), showing reverse transcriptase. Also indicate the point at which the genetic material can acquire mutations much more rapidly than DNA-based viruses. ...
CS 262—Lecture 1 Notes • 4-‐5 HWs, 3 late days • (Optional
... • DNA in nucleus and each cell has copies of DNA o Although we have trillions of cells, an average somatic cell only has 30-‐60 differences from the “pure”, original genome • DNA packed into chromosom ...
... • DNA in nucleus and each cell has copies of DNA o Although we have trillions of cells, an average somatic cell only has 30-‐60 differences from the “pure”, original genome • DNA packed into chromosom ...
Postdoc position in Regulation of Gene Transcription by RNA
... (mainly Cdk9 and Cdk12) involved in the regulation of gene transcription by RNA Polymerase II and their roles in modulation of DNA damage responses (see our recent paper: Blazek et al., Genes and Development. 2011; 25(20):2158-72). The successful candidate will join a team of young motivated people ...
... (mainly Cdk9 and Cdk12) involved in the regulation of gene transcription by RNA Polymerase II and their roles in modulation of DNA damage responses (see our recent paper: Blazek et al., Genes and Development. 2011; 25(20):2158-72). The successful candidate will join a team of young motivated people ...
rna interference
... the form of double-stranded RNA, so it is likely that the RNA interference machinery evolved as a defense against these viruses. The machinery is however also used by the cell itself to regulate gene activity: certain parts of the genome are transcribed into microRNAs, short RNA molecules that fold ...
... the form of double-stranded RNA, so it is likely that the RNA interference machinery evolved as a defense against these viruses. The machinery is however also used by the cell itself to regulate gene activity: certain parts of the genome are transcribed into microRNAs, short RNA molecules that fold ...
10 Useful RNA Facts
... 6. RNA is found in both the nucleus and cytoplasm of human’s cells. DNA is found in the cell nucleus and mitochondria. ...
... 6. RNA is found in both the nucleus and cytoplasm of human’s cells. DNA is found in the cell nucleus and mitochondria. ...
Modern Genetics Outline
... Most genetic diseases in humans are __________ as __________ genes and involve __________ in enzyme formation. When there is a mistake in __________ formation, the person’s metabolism is ___________. The presence of many genetic disorders can be detected either before or after birth. _______ ...
... Most genetic diseases in humans are __________ as __________ genes and involve __________ in enzyme formation. When there is a mistake in __________ formation, the person’s metabolism is ___________. The presence of many genetic disorders can be detected either before or after birth. _______ ...
NAME Period___________ Modern Genetics Outline
... Most genetic diseases in humans are __________ as __________ genes and involve __________ in enzyme formation. When there is a mistake in __________ formation, the person’s metabolism is ___________. The presence of many genetic disorders can be detected either before or after birth. _______ ...
... Most genetic diseases in humans are __________ as __________ genes and involve __________ in enzyme formation. When there is a mistake in __________ formation, the person’s metabolism is ___________. The presence of many genetic disorders can be detected either before or after birth. _______ ...
PG1005 Lecture 17 Gene Transcription
... • Define transcription as the key event in gene expression during which the genetic code is read and transcribed into a portable template set of instructions for protein synthesis • Detail the sequence of events occurring during the initiation, elongation and termination of transcription • Descri ...
... • Define transcription as the key event in gene expression during which the genetic code is read and transcribed into a portable template set of instructions for protein synthesis • Detail the sequence of events occurring during the initiation, elongation and termination of transcription • Descri ...