Gene Expression/Transcription & Translation Practice PowerPoint
... In 1917 the biologist Thomas Hunt Morgan conducted studies in which he kept some caterpillars in the dark and placed other under red, green, or blue lights. Exposure to red light produced butterflies with brightly colored wings. Exposure to green light resulted in dark-colored wings. Exposure to bl ...
... In 1917 the biologist Thomas Hunt Morgan conducted studies in which he kept some caterpillars in the dark and placed other under red, green, or blue lights. Exposure to red light produced butterflies with brightly colored wings. Exposure to green light resulted in dark-colored wings. Exposure to bl ...
[pdf]
... and Holliday junction resolvase, and the enzymes of this family have important roles in many processes. However, little is known regarding their mechanism of substrate recognition and metal-ion-dependent catalysis. Despite continuous efforts to gain structural insights, there hasn’t been a structure ...
... and Holliday junction resolvase, and the enzymes of this family have important roles in many processes. However, little is known regarding their mechanism of substrate recognition and metal-ion-dependent catalysis. Despite continuous efforts to gain structural insights, there hasn’t been a structure ...
No Slide Title
... DNA IS USED AS A TEMPLATE RNA is edited by removing introns Transcription YouTube ...
... DNA IS USED AS A TEMPLATE RNA is edited by removing introns Transcription YouTube ...
Slide 1
... Identify the main product on a western blot and other components (subunits) that can be co-purified ...
... Identify the main product on a western blot and other components (subunits) that can be co-purified ...
Document
... RNA transcripts thus maintaining the genome stability. RNAi application RNAi holds many promises as antiviral treatment and for controlling gene expression in eukaryotic cells. However, for the time being it is only used as experimental tool. There is hardly any molecular biology or molecular geneti ...
... RNA transcripts thus maintaining the genome stability. RNAi application RNAi holds many promises as antiviral treatment and for controlling gene expression in eukaryotic cells. However, for the time being it is only used as experimental tool. There is hardly any molecular biology or molecular geneti ...
Walk the Dogma - Nutley Public Schools
... information is copied from DNA to RNA • DNA double-strand “unzips” • RNA polymerase (an enzyme) binds to a specific region on DNA called a promoter • RNA polymerase travels along the gene, creating a chain of mRNA that is complementary to the strand of DNA • RNA polymerase reaches the termination si ...
... information is copied from DNA to RNA • DNA double-strand “unzips” • RNA polymerase (an enzyme) binds to a specific region on DNA called a promoter • RNA polymerase travels along the gene, creating a chain of mRNA that is complementary to the strand of DNA • RNA polymerase reaches the termination si ...
(A) + RNA
... Most gene expression assays are based on the comparison of two or more samples and require uniform sampling conditions for this comparison to be valid. Many factors can contribute to variability in the analysis of samples, making the results difficult to reproduce between experiments: Sample degrada ...
... Most gene expression assays are based on the comparison of two or more samples and require uniform sampling conditions for this comparison to be valid. Many factors can contribute to variability in the analysis of samples, making the results difficult to reproduce between experiments: Sample degrada ...
Wed 12-2 Computers Lab (40 points if all correct or 0 if not) Open up
... RNA is transcribed from DNA by enzymes called RNA polymerases and is generally further processed by other enzymes. RNA is central to protein synthesis. Here, a type of RNA called messenger RNA carries information from DNA to structures called ribosomes. These ribosomes are made from proteins and rib ...
... RNA is transcribed from DNA by enzymes called RNA polymerases and is generally further processed by other enzymes. RNA is central to protein synthesis. Here, a type of RNA called messenger RNA carries information from DNA to structures called ribosomes. These ribosomes are made from proteins and rib ...
Gene Expression
... Prokaryotic Gene Regulation Operons, specific sets of clustered genes, are the controlling unit Promoter: sequence where RNA polymerase binds Requirement for initiation of transcription ...
... Prokaryotic Gene Regulation Operons, specific sets of clustered genes, are the controlling unit Promoter: sequence where RNA polymerase binds Requirement for initiation of transcription ...
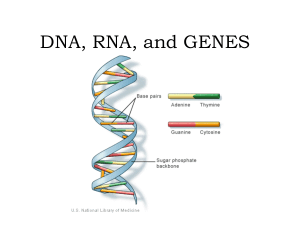
DNA, RNA, and GENES
... • Ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes, where proteins are built. • Transfer RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to build the proteins. ...
... • Ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes, where proteins are built. • Transfer RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to build the proteins. ...
Review Questions
... DNA, the recipe for making proteins, never leaves the nucleus (nucleoid region in bacteria). Yet all the protein-making machinery is located out in the cytoplasm. So how does the information get to the cytoplasm? DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA. 2. What is a transcript? A transcript is not a c ...
... DNA, the recipe for making proteins, never leaves the nucleus (nucleoid region in bacteria). Yet all the protein-making machinery is located out in the cytoplasm. So how does the information get to the cytoplasm? DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA. 2. What is a transcript? A transcript is not a c ...
Chapter 10 - Power Point Presentation
... before making the protein. The portions that remain and ARE used are called exons So, eukaryotes undergo RNA splicing This is one way a gene can have some variability in its outcome ...
... before making the protein. The portions that remain and ARE used are called exons So, eukaryotes undergo RNA splicing This is one way a gene can have some variability in its outcome ...
Distinguish between these 3 root types: - mvhs
... mRNA for this protein contains a signal recognition sequence that is recognized by a signal recognition particle (SRP). The SRP brings the growing polypeptide to the receptor protein in the ___________________. ...
... mRNA for this protein contains a signal recognition sequence that is recognized by a signal recognition particle (SRP). The SRP brings the growing polypeptide to the receptor protein in the ___________________. ...
week2
... The process of using the information stored in DNA to make RNA and then a corresponding protein. Parts of the DNA sequence are used to directly transcribe RNA Part of the DNA sequence help with the Expression Process. ...
... The process of using the information stored in DNA to make RNA and then a corresponding protein. Parts of the DNA sequence are used to directly transcribe RNA Part of the DNA sequence help with the Expression Process. ...
Chapter 10 Lesson 1
... a. One nucleotide is substituted for another. This only changes one a.acid B. Mutagen 1. Def – External agents that cause mutations a. Ex: radiation, high temp, chemicals, environmental factors C. Mutations 1. Body cells – only cause problems in person 2. Sex cells – problems are passed from generat ...
... a. One nucleotide is substituted for another. This only changes one a.acid B. Mutagen 1. Def – External agents that cause mutations a. Ex: radiation, high temp, chemicals, environmental factors C. Mutations 1. Body cells – only cause problems in person 2. Sex cells – problems are passed from generat ...
outline File - selu moodle
... Genetic code is degenerate Stop codon Start codon Wobble effect at third position Near universal 15.3 Prokaryotic Transcription Begins at a promoter transcribes the transcription unit ends at the terminator Promoter – sequence within DNA Elongation uses RNA polymerase to add ribonucleotides that ...
... Genetic code is degenerate Stop codon Start codon Wobble effect at third position Near universal 15.3 Prokaryotic Transcription Begins at a promoter transcribes the transcription unit ends at the terminator Promoter – sequence within DNA Elongation uses RNA polymerase to add ribonucleotides that ...
RNAi - University of Maryland, College Park
... along with its use of genome sequence information, has dramatically changed how these tests are done. RNAi is a form of reverse genetics, meaning researchers can systematically pick genes rather than beginning with mutants and then searching for the genes affected. One major advantage of this method ...
... along with its use of genome sequence information, has dramatically changed how these tests are done. RNAi is a form of reverse genetics, meaning researchers can systematically pick genes rather than beginning with mutants and then searching for the genes affected. One major advantage of this method ...
RNA & Protein Synthesis
... RNA carries copies of genes – acts as “messengers” ◦ Messenger RNA or mRNA ...
... RNA carries copies of genes – acts as “messengers” ◦ Messenger RNA or mRNA ...
Gene silencing - Get Biotech Smart
... • If we want to stop that protein from being made we can disable the sense strand of RNA • RNA can become double stranded • What is needed is an “antisense” strand of RNA to bind with the “sense” strand ...
... • If we want to stop that protein from being made we can disable the sense strand of RNA • RNA can become double stranded • What is needed is an “antisense” strand of RNA to bind with the “sense” strand ...
Section: Gene Regulation and Structure
... instructions for making a protein to an mRNA molecule 10. a three-nucleotide sequence on the mRNA that specifies an amino acid or “start” or “stop” signal 12. piece of DNA that serves as an on-off switch for transcription 14. long segment of nucleotides on a eukaryotic gene that has no coding ...
... instructions for making a protein to an mRNA molecule 10. a three-nucleotide sequence on the mRNA that specifies an amino acid or “start” or “stop” signal 12. piece of DNA that serves as an on-off switch for transcription 14. long segment of nucleotides on a eukaryotic gene that has no coding ...
Chapter 10 Structure and Function of DNA
... What is the backbone Where are the 5’ and 3’ sugars on ribose? DNA replication DNA polymerase Primers 5’ to 3’ direction Helicase Ligase Semiconservative Templates Leading strand ...
... What is the backbone Where are the 5’ and 3’ sugars on ribose? DNA replication DNA polymerase Primers 5’ to 3’ direction Helicase Ligase Semiconservative Templates Leading strand ...
![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008789110_1-03a81e28d94c74d682b307dd66c7080a-300x300.png)