Applied Genetics
... DNA Fingerprinting • Hair, skin and blood can all be used to make a DNA fingerprint • No 2 people have the exact same DNA • A DNA finger print consists of a series of bands, something like a bar code. • DNA finger prints can be used to show whether people are related, identify people and solve crim ...
... DNA Fingerprinting • Hair, skin and blood can all be used to make a DNA fingerprint • No 2 people have the exact same DNA • A DNA finger print consists of a series of bands, something like a bar code. • DNA finger prints can be used to show whether people are related, identify people and solve crim ...
Chapter 27 Bacteria
... What was Frederick Griffith’s contribution to our understanding of DNA? (Refer back to Ch. 16) ...
... What was Frederick Griffith’s contribution to our understanding of DNA? (Refer back to Ch. 16) ...
Bacteria - sandsbiochem
... What was Frederick Griffith’s contribution to our understanding of DNA? (Refer back to Ch. 16) ...
... What was Frederick Griffith’s contribution to our understanding of DNA? (Refer back to Ch. 16) ...
DNA - VanityWolveriine
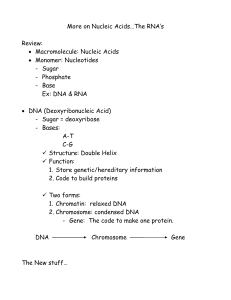
... genetic characteristics in all life forms, constructed of two nucleotide strands coiled around each other in a ladder like arrangement with the sidepieces composed of alternating phosphate and deoxyribose units and the rungs composed of the perinea and pyrimidine bases adenine, guanine, cytosine, an ...
... genetic characteristics in all life forms, constructed of two nucleotide strands coiled around each other in a ladder like arrangement with the sidepieces composed of alternating phosphate and deoxyribose units and the rungs composed of the perinea and pyrimidine bases adenine, guanine, cytosine, an ...
Lecture 1 Genetics – An Overview Professor Jane Farrar School of
... The same 3 billion base pairs of DNA are present in every cell of your body. Approximately 25,000 genes present in 23 pairs of human chromosomes in the 3 billion DNBA base pairs How does each cell function so differently? Not all genes are active in all cell types. Genes make RNA which is translate ...
... The same 3 billion base pairs of DNA are present in every cell of your body. Approximately 25,000 genes present in 23 pairs of human chromosomes in the 3 billion DNBA base pairs How does each cell function so differently? Not all genes are active in all cell types. Genes make RNA which is translate ...
6CDE Transcription and Translation
... substitutions like point mutations and immediately change a gene sequence. Insertion or deletion mutations result in a frame-shift and may result in an incorrect amino acid sequence in the synthesized protein. 4. Gene expression is a regulated process, and most of DNA is made up of regulatory sequen ...
... substitutions like point mutations and immediately change a gene sequence. Insertion or deletion mutations result in a frame-shift and may result in an incorrect amino acid sequence in the synthesized protein. 4. Gene expression is a regulated process, and most of DNA is made up of regulatory sequen ...
REPLICATION, TRANSCRIPTION, TRANSLATION TAKS
... F* 3' TCTACGTAG 5' G 5' CTACGTAGA 3' H 3' AGATGCATC 5' J 5' AGACGTCTA 3' SPRING 2003 – 11: 26 If a cat has 38 chromosomes in each of its body cells, how many chromosomes will be in each daughter cell after mitosis? F 11 G 19 H* 38 J 76 APRIL 2004 – 11: ...
... F* 3' TCTACGTAG 5' G 5' CTACGTAGA 3' H 3' AGATGCATC 5' J 5' AGACGTCTA 3' SPRING 2003 – 11: 26 If a cat has 38 chromosomes in each of its body cells, how many chromosomes will be in each daughter cell after mitosis? F 11 G 19 H* 38 J 76 APRIL 2004 – 11: ...
Problem 3: Why do pre-mRNAs get smaller during RNA processing?
... Problem 7: Features of nuclear RNA processing Which of the following is not part of RNA processing in eukaryotes? A. splicing of exons B. reverse transcription C. addition of a 5' cap D. addition of a poly A tail E. intron removal ...
... Problem 7: Features of nuclear RNA processing Which of the following is not part of RNA processing in eukaryotes? A. splicing of exons B. reverse transcription C. addition of a 5' cap D. addition of a poly A tail E. intron removal ...
A Genomic Timeline
... James Gusella and co-workers locate a genetic marker for Huntington’s disease on chromosome 4. This leads to scientists having the ability to screen people for a disease without being able ot cure it. Kary Mullis conceives of the polymerase chain reaction, a chemical DNA replication process that gr ...
... James Gusella and co-workers locate a genetic marker for Huntington’s disease on chromosome 4. This leads to scientists having the ability to screen people for a disease without being able ot cure it. Kary Mullis conceives of the polymerase chain reaction, a chemical DNA replication process that gr ...
... the genome. Since the last century the replicon model has been proposed in order to explain the general mechanism of genome duplication in bacteria. Later work in yeast lead to identifying proteins and dna sequences that participate in the initiation of replication in a similar fashion to what has b ...
Control of Gene Expression
... Cells are very different because each cell makes certain proteins and not others ...
... Cells are very different because each cell makes certain proteins and not others ...
ANNEX B: Selected Biotechnology Terms
... Antibodies destroy or weaken bacteria and neutralize organic poisons, thus forming the basis of immunity. Bioregulators – chemicals or enzymes that control physiological functions, such as pain, sleep, or mood. Cloning – the process of preparing a largely identical group of organisms, cells, viruses ...
... Antibodies destroy or weaken bacteria and neutralize organic poisons, thus forming the basis of immunity. Bioregulators – chemicals or enzymes that control physiological functions, such as pain, sleep, or mood. Cloning – the process of preparing a largely identical group of organisms, cells, viruses ...
Fast Facts about Human Genetics • DNA stands for Deoxy
... The nucleus, or control centre, of a cell, is where the DNA is coiled up into chromosomes. With the exception of reproductive cells, every cell has 46 chromosomes. Twenty-two pairs of the chromosomes are similar in terms of size, shape and genetic content. The twenty-third pair determines the sex of ...
... The nucleus, or control centre, of a cell, is where the DNA is coiled up into chromosomes. With the exception of reproductive cells, every cell has 46 chromosomes. Twenty-two pairs of the chromosomes are similar in terms of size, shape and genetic content. The twenty-third pair determines the sex of ...
When Is a Genome Project Finished?
... 4. What is the name of the gene prediction method that uses a statistical analysis of the nucleotide base sequence to determine likely locations for genes, including the position of exons and introns? ________________________________________________________________________ 5. What is the name of the ...
... 4. What is the name of the gene prediction method that uses a statistical analysis of the nucleotide base sequence to determine likely locations for genes, including the position of exons and introns? ________________________________________________________________________ 5. What is the name of the ...
here
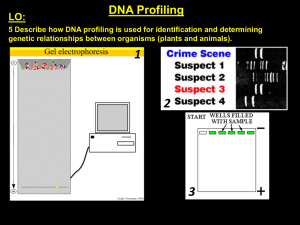
... DNA profiling is a technique that allows an individual’s genes to be visualised, this allows someone's genetic makeup to be compared to known genes to see if they too have it. This technique can be used to identify genetic disorders in individuals or match DNA samples to individuals. We usually sam ...
... DNA profiling is a technique that allows an individual’s genes to be visualised, this allows someone's genetic makeup to be compared to known genes to see if they too have it. This technique can be used to identify genetic disorders in individuals or match DNA samples to individuals. We usually sam ...
Chapter 21
... Three types of RNA – Ribosomal (rRNA): joins with proteins to form ribosomes – Messenger (mRNA): carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes ...
... Three types of RNA – Ribosomal (rRNA): joins with proteins to form ribosomes – Messenger (mRNA): carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes ...
ENCODE Project - HudsonAlpha Institute for Biotechnology
... high-quality description of genomic activity that will be useful throughout many biological and disease research areas. The next step is to figure out how the various players in this regulatory symphony interact. For example, if a binding site is altered or deleted through mutation, is there an effe ...
... high-quality description of genomic activity that will be useful throughout many biological and disease research areas. The next step is to figure out how the various players in this regulatory symphony interact. For example, if a binding site is altered or deleted through mutation, is there an effe ...
2-3 DNA to Proteins - Lighthouse Christian Academy
... chromosome so that a copy of the needed gene can be made. This is copy is called RNA (ribonucleic acid). RNA is similar to DNA except it is only one strand. o RNA to Ribosome – The RNA then leaves the nucleus and attaches to a ribosome which “reads” the code on the ...
... chromosome so that a copy of the needed gene can be made. This is copy is called RNA (ribonucleic acid). RNA is similar to DNA except it is only one strand. o RNA to Ribosome – The RNA then leaves the nucleus and attaches to a ribosome which “reads” the code on the ...
Chapter 20
... What would you look for if you wanted to find an unknown protein coding gene? Scientists use computers to search for short coding sequences similar to those present in known genes. these are called “express service tags” ...
... What would you look for if you wanted to find an unknown protein coding gene? Scientists use computers to search for short coding sequences similar to those present in known genes. these are called “express service tags” ...