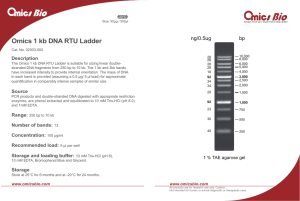
This is to serve as a general overview of important topics. I highly
... Gene Conversion is a special type of __________________________________ recombination. This conversion is (unidirectional/ bidirectional). Gene conversions usually occur within paralogs- need to be similar in genetic sequences. ...
... Gene Conversion is a special type of __________________________________ recombination. This conversion is (unidirectional/ bidirectional). Gene conversions usually occur within paralogs- need to be similar in genetic sequences. ...
7th grade Ch. 5 section 2 and 3 Notes
... same genes as the organism in which it was produced by. • Researchers have cloned sheep and pigs. ...
... same genes as the organism in which it was produced by. • Researchers have cloned sheep and pigs. ...
DNA Technology
... So what does all this mean? • We can already economically sequence a human genome. • These technologies present a huge variety of opportunities and dangers. • Your generation must be aware of these technologies as you will make the ultimate decisions about how these technologies are used. ...
... So what does all this mean? • We can already economically sequence a human genome. • These technologies present a huge variety of opportunities and dangers. • Your generation must be aware of these technologies as you will make the ultimate decisions about how these technologies are used. ...
Principles and Practices of Biosafety
... are unlikely to be involved in pathogenicity may not require additional safety measures. In cases where these sequences are not characterized, a situation that is typically encountered when a library of genomic DNA of an organism is being established, a higher BSL will be required. Cloning of genes ...
... are unlikely to be involved in pathogenicity may not require additional safety measures. In cases where these sequences are not characterized, a situation that is typically encountered when a library of genomic DNA of an organism is being established, a higher BSL will be required. Cloning of genes ...
Document
... evolution. This has been proven to be particularly true in the case of multicellular eukaryotes to which we, the humans, belong. The reasons for this conceptual change are many. First of all genes have been shown to be “ambiguous” in many ways in the sense that a single sequence may be coding for mo ...
... evolution. This has been proven to be particularly true in the case of multicellular eukaryotes to which we, the humans, belong. The reasons for this conceptual change are many. First of all genes have been shown to be “ambiguous” in many ways in the sense that a single sequence may be coding for mo ...
Slide 1
... a start and stop codon – Compare sequences found in one organism and look for similar sequence in other organsims • Microarray assay: microscope slide with known genes in wells – mRNA from a cell is obtained, reacted with cDNA, if bases match they will pair up and when hybrid DNA is placed on slide ...
... a start and stop codon – Compare sequences found in one organism and look for similar sequence in other organsims • Microarray assay: microscope slide with known genes in wells – mRNA from a cell is obtained, reacted with cDNA, if bases match they will pair up and when hybrid DNA is placed on slide ...
Unit 7 Study Guide ANSWERS 2014
... 15. Mutations that can affect the offspring of an organism occur in what cell type? Germ/Sex Cells 16. Give an example of a mutagen? UV light, radiation 17. Define gene. A segment of DNA that contains the information necessary to produce a protein 18. Where are genes located? Chromosomes 19 Where is ...
... 15. Mutations that can affect the offspring of an organism occur in what cell type? Germ/Sex Cells 16. Give an example of a mutagen? UV light, radiation 17. Define gene. A segment of DNA that contains the information necessary to produce a protein 18. Where are genes located? Chromosomes 19 Where is ...
DNA!
... • DNA is identical in all of your cells. • BUT … sometimes, random changes can occur … MUTATIONS • A mutation is a random change in a cell’s genetic information ...
... • DNA is identical in all of your cells. • BUT … sometimes, random changes can occur … MUTATIONS • A mutation is a random change in a cell’s genetic information ...
Italian Association for Cancer Research NETWORK OF
... identification of relevant interactions between genes and the environment through studies of molecular epidemiology in Italy; (b) to rationalize and improve the quality of laboratory measurements by referring to reference laboratories; (c) to pool existing data sets; (d) to create a network web site ...
... identification of relevant interactions between genes and the environment through studies of molecular epidemiology in Italy; (b) to rationalize and improve the quality of laboratory measurements by referring to reference laboratories; (c) to pool existing data sets; (d) to create a network web site ...
centromere
... Genome Organisation II • Eukaryotic genomes are completely different in their organisation compared to prokaryotic, and also much bigger • Their genes are mostly “split” into exons and introns • It is not certain which came first in evolution genes with introns/exons or genes without • Exons may all ...
... Genome Organisation II • Eukaryotic genomes are completely different in their organisation compared to prokaryotic, and also much bigger • Their genes are mostly “split” into exons and introns • It is not certain which came first in evolution genes with introns/exons or genes without • Exons may all ...
Chapter 24 Applied Genetics I. Plant and animal
... 1. Crossing of plants or animals with desirable traits 2. Offspring contain those desirable traits B. Hybridization 1. Crossing of two genetically different related species 2. Produce organism with best traits of both parents (hybrid) C. Inbreeding 1. Crossing of two organisms with the same or simil ...
... 1. Crossing of plants or animals with desirable traits 2. Offspring contain those desirable traits B. Hybridization 1. Crossing of two genetically different related species 2. Produce organism with best traits of both parents (hybrid) C. Inbreeding 1. Crossing of two organisms with the same or simil ...
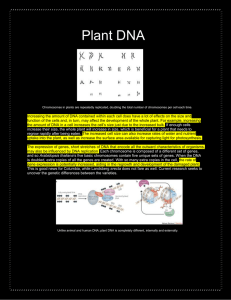
Plant DNA - The uniqueness of DNA
... The expression of genes, short stretches of DNA that encode all the outward characteristics of organisms, may also be influenced by DNA replication. Each chromosome is composed of a different set of genes, and so Arabidopsis thaliana’s five basic chromosomes contain five unique sets of genes. When t ...
... The expression of genes, short stretches of DNA that encode all the outward characteristics of organisms, may also be influenced by DNA replication. Each chromosome is composed of a different set of genes, and so Arabidopsis thaliana’s five basic chromosomes contain five unique sets of genes. When t ...
This examination paper consists of 4 pages
... 15. All eukaryotic nuclear chromosomes are circular have only one origin of replication have only one centromer end in telomeres ...
... 15. All eukaryotic nuclear chromosomes are circular have only one origin of replication have only one centromer end in telomeres ...
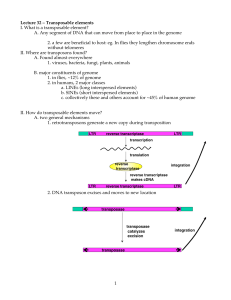
Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element?
... I. What is a transposable element? A. Any segment of DNA that can move from place to place in the genome 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, anim ...
... I. What is a transposable element? A. Any segment of DNA that can move from place to place in the genome 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, anim ...
Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... DNA is a Helix • The three dimensional structure of DNA was first determined with the assistance of X-ray crystallography. Data collected by Rosalind Franklin • James Watson and Francis Crick described it as a double helix (1953) ...
... DNA is a Helix • The three dimensional structure of DNA was first determined with the assistance of X-ray crystallography. Data collected by Rosalind Franklin • James Watson and Francis Crick described it as a double helix (1953) ...
DNA – The Double Helix
... DNA controls the production of proteins within the cell; which proteins are made is determined by the sequence of the DNA. Proteins are the building blocks of an organism. How you look is largely determined by the proteins that are made. ...
... DNA controls the production of proteins within the cell; which proteins are made is determined by the sequence of the DNA. Proteins are the building blocks of an organism. How you look is largely determined by the proteins that are made. ...