Timing and Development of Growth
... • Enzyme that transcribes DNA (RNA Polymerase) requires transcription factors • Activation of transcription factors triggers transcription, thus expressing the gene. ...
... • Enzyme that transcribes DNA (RNA Polymerase) requires transcription factors • Activation of transcription factors triggers transcription, thus expressing the gene. ...
DNA cr.eu updated plg latest
... with approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wound around them; in euchromatin, this wrapping is loose so that the raw DNA may be accessed. • Each core histone possesses a `tail' structure, which can vary in several ways; it is thought that these variations act as "master control switches," which determ ...
... with approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wound around them; in euchromatin, this wrapping is loose so that the raw DNA may be accessed. • Each core histone possesses a `tail' structure, which can vary in several ways; it is thought that these variations act as "master control switches," which determ ...
Glossary of Genetic Terms
... Haldane's law: the generalization that if first generation hybrids are produced between two species, but one sex is absent, rare, or sterile, that sex is the heterogamic sex. ...
... Haldane's law: the generalization that if first generation hybrids are produced between two species, but one sex is absent, rare, or sterile, that sex is the heterogamic sex. ...
Name:
... 11. What is a codon and what does each one stand for on an mRNA strand? 12. What amino acid does the CAG codon code for? 13. What is the first codon in all mRNA sequences? 14. What transports the amino acids to the ribosome during translation? ...
... 11. What is a codon and what does each one stand for on an mRNA strand? 12. What amino acid does the CAG codon code for? 13. What is the first codon in all mRNA sequences? 14. What transports the amino acids to the ribosome during translation? ...
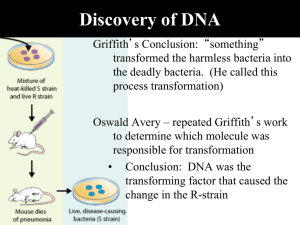
Discovery of DNA
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
to view and/or print October 2016 eDay assignment.
... 3. We have how many copies of each gene? 4. Each parent passes _____ copy of each gene to his/her offspring. 5. Why do children resemble their parents and each other? ...
... 3. We have how many copies of each gene? 4. Each parent passes _____ copy of each gene to his/her offspring. 5. Why do children resemble their parents and each other? ...
Biochemistry
... Eukaryotic Gene Expression in Bacteria • An eukaryotic gene from the eukaryotic genome will not express correctly in the bacterium • Eukaryotic genes have – Exons: coding regions – Introns: noncoding regions • Introns in eukaryouric gene pose problems • Bacteria cannot splice introns out • mRNA is ...
... Eukaryotic Gene Expression in Bacteria • An eukaryotic gene from the eukaryotic genome will not express correctly in the bacterium • Eukaryotic genes have – Exons: coding regions – Introns: noncoding regions • Introns in eukaryouric gene pose problems • Bacteria cannot splice introns out • mRNA is ...
Chromatin Structure and Gene Regulation
... • Methylation (attachment of a methyl group to DNA) causes most genes to be inactive • Removal of the methyl group on these genes will cause expression • Methylation or demethylation during embryonic development is responsible for if maternal or paternal alleles are expressed – genomic imprinting ...
... • Methylation (attachment of a methyl group to DNA) causes most genes to be inactive • Removal of the methyl group on these genes will cause expression • Methylation or demethylation during embryonic development is responsible for if maternal or paternal alleles are expressed – genomic imprinting ...
Human Genome Project, Gene Therapy, and Cloning
... Adapted from the University of Utah Genetic Science Learning Center and The National Genome Research Institute, National Institutes of Health ...
... Adapted from the University of Utah Genetic Science Learning Center and The National Genome Research Institute, National Institutes of Health ...
DNA Unit Study Guide 2017 - Liberty Union High School District
... DNA T A C T A T T C C T C G T C T C G G C G T A T T mRNA_______________________________________________________________________ tRNA________________________________________________________________________ rRNA/aa______________________________________________________________________ 24. What is a gen ...
... DNA T A C T A T T C C T C G T C T C G G C G T A T T mRNA_______________________________________________________________________ tRNA________________________________________________________________________ rRNA/aa______________________________________________________________________ 24. What is a gen ...
Genetics EQ
... see a Security Warning click HERE on Options… and then click on Enable this content ...
... see a Security Warning click HERE on Options… and then click on Enable this content ...
Gen.1303 Genome: The total genetic content contained in a haploid
... A hereditary unit consisting of a sequence of DNA that occupies a specific location on a chromosome and determines a particular characteristic in an organism. Genes undergo mutation when their DNA sequence changes. Chromatin: A complex of nucleic acids and proteins, primary histones, in the cell nuc ...
... A hereditary unit consisting of a sequence of DNA that occupies a specific location on a chromosome and determines a particular characteristic in an organism. Genes undergo mutation when their DNA sequence changes. Chromatin: A complex of nucleic acids and proteins, primary histones, in the cell nuc ...
DNA/RNA Worksheet TACGGCACCGTTAGGATT
... Which type of RNA has an amino acid attached at one end and the anticodon at the other end? ________________________ ...
... Which type of RNA has an amino acid attached at one end and the anticodon at the other end? ________________________ ...
DNA Structure and Function Vocabulary
... Base pair • To form the DNA molecule, bases pair together across the double helix structure. Adenine (A) always pairs with Thymine (T), and Cytosine (C) always pairs with Guanine (G). These are the only pairs possible. ...
... Base pair • To form the DNA molecule, bases pair together across the double helix structure. Adenine (A) always pairs with Thymine (T), and Cytosine (C) always pairs with Guanine (G). These are the only pairs possible. ...
LEQ: How does RNA help to make a protein?
... The type of RNA that carriers the genetic information/message from DNA and coveys it to ribosomes where the information is translated into amino acid sequences ...
... The type of RNA that carriers the genetic information/message from DNA and coveys it to ribosomes where the information is translated into amino acid sequences ...
Insects and genetics
... d. mutation 4. genetic make-up of an organism-e e. genotype 5. alternative state of a gene or trait-c f. phenotype 6. segment of DNA on a chromosome coding for a protein or RNA-a g. chromosome 7. group of coiled DNA strands containing genes-g 9. genome 8. entire DNA complement of an organism-9 11. T ...
... d. mutation 4. genetic make-up of an organism-e e. genotype 5. alternative state of a gene or trait-c f. phenotype 6. segment of DNA on a chromosome coding for a protein or RNA-a g. chromosome 7. group of coiled DNA strands containing genes-g 9. genome 8. entire DNA complement of an organism-9 11. T ...
lecture0
... The various genome projects have yielded the complete DNA sequences of many organisms. ...
... The various genome projects have yielded the complete DNA sequences of many organisms. ...
Introduction to DNA webquest: Name http://learn.genetics.utah.
... 2. What is the protein in red blood cells called, and what does it ...
... 2. What is the protein in red blood cells called, and what does it ...
Genomics
... a) Systematic identification of all common variants in human genes, both the coding and non-coding regions. These are the "isotopes" to gene "elements" b) resequencing of entire genomes of individuals c) comparison of fully sequenced genomes of related (and unrelated) species EG: man and chimp This ...
... a) Systematic identification of all common variants in human genes, both the coding and non-coding regions. These are the "isotopes" to gene "elements" b) resequencing of entire genomes of individuals c) comparison of fully sequenced genomes of related (and unrelated) species EG: man and chimp This ...
The modern synthesis
... One of the key assumptions of the theory of natural selection. How does that work? Genes! ...
... One of the key assumptions of the theory of natural selection. How does that work? Genes! ...
Chromosomal Structure HWK
... (b) A telomere is a long sequence of repetitive, noncoding DNA that is found at the end of chromosomes, while a centromere is a constricted region of a chromosome that holds two replicated chromosome strands together (c) A LINE is a DNA sequence of 5000 to 7000 nucleotides that are repetitive and al ...
... (b) A telomere is a long sequence of repetitive, noncoding DNA that is found at the end of chromosomes, while a centromere is a constricted region of a chromosome that holds two replicated chromosome strands together (c) A LINE is a DNA sequence of 5000 to 7000 nucleotides that are repetitive and al ...