ome
... Answer: The “omics” revolution of modern biology refers to the rapid expansion of new disciplines of research that have resulted from genomics studies, as reflected by new terms using the suffix omics or ome. Generally such studies involve a largescale comprehensive analysis. For example, proteomics ...
... Answer: The “omics” revolution of modern biology refers to the rapid expansion of new disciplines of research that have resulted from genomics studies, as reflected by new terms using the suffix omics or ome. Generally such studies involve a largescale comprehensive analysis. For example, proteomics ...
DNA Test Review
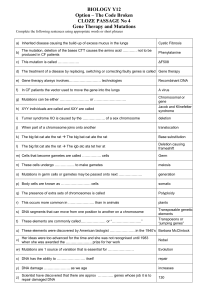
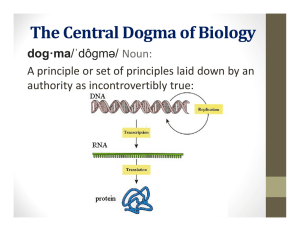
... 1. What are the four nucleotides in DNA? Which goes with which? 2. Describe the Central Dogma of molecular biology. 3. If a DNA molecule has the sequence TACGAACCC, what would be the complimentary mRNA sequence? 4. The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____. 5. What is a codon? 6. ...
... 1. What are the four nucleotides in DNA? Which goes with which? 2. Describe the Central Dogma of molecular biology. 3. If a DNA molecule has the sequence TACGAACCC, what would be the complimentary mRNA sequence? 4. The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____. 5. What is a codon? 6. ...
Red line Introduction
... Gene annotation adds meaning to DNA sequence. Concept of gene continues to evolve. A genome is more than genes. ...
... Gene annotation adds meaning to DNA sequence. Concept of gene continues to evolve. A genome is more than genes. ...
Red Line - iPlant Pods
... Gene annotation adds meaning to DNA sequence. Concept of gene continues to evolve. A genome is more than genes. ...
... Gene annotation adds meaning to DNA sequence. Concept of gene continues to evolve. A genome is more than genes. ...
Natural products and ecological interactions Adaptive evolution (i.e. “rapid”) Scents Colours
... Natural products and ecological interactions Adaptive evolution (i.e. “rapid”) ...
... Natural products and ecological interactions Adaptive evolution (i.e. “rapid”) ...
Brooker Chapter 17
... In 1981, Paul Bingham, Robert Levis and Gerald Rubin use transposon tagging to clone this gene ...
... In 1981, Paul Bingham, Robert Levis and Gerald Rubin use transposon tagging to clone this gene ...
Recombinant DNA Technologies
... d. T- Thymine -put together in a double-helical molecule with A-T & C-G as the “rungs” -form GENES e. We have about 30,000 genes and they are mapped by location on each chromosome -”Human Genome Project” f. We are 99.9% identical; .1% makes us unique and different from Rob Marder (thank heaven!) a. ...
... d. T- Thymine -put together in a double-helical molecule with A-T & C-G as the “rungs” -form GENES e. We have about 30,000 genes and they are mapped by location on each chromosome -”Human Genome Project” f. We are 99.9% identical; .1% makes us unique and different from Rob Marder (thank heaven!) a. ...
Aim: How do scientists use biotechnology to manipulate genomes?
... A gene is a sequence of ____ DNA on a chromosome ___________ that codes for one protein ________. **Remember, not all of the ____ DNA codes for proteins. The parts that do are called ______, genes the parts that don’t are called non-coding regions ___________________. ...
... A gene is a sequence of ____ DNA on a chromosome ___________ that codes for one protein ________. **Remember, not all of the ____ DNA codes for proteins. The parts that do are called ______, genes the parts that don’t are called non-coding regions ___________________. ...
2D Barcode Quiz
... Transcription is the process of making an amino acid sequence from messenger RNA VNTR (Variable Number Tandem Repeat) is a type of mutation used in parental determination or DNA fingerprinting Polymerase Copying Reaction (‘PCR’) is a technique used to synthesise new copies of a DNA template Directed ...
... Transcription is the process of making an amino acid sequence from messenger RNA VNTR (Variable Number Tandem Repeat) is a type of mutation used in parental determination or DNA fingerprinting Polymerase Copying Reaction (‘PCR’) is a technique used to synthesise new copies of a DNA template Directed ...
Name
... Proposed that some human diseases are due to “inborn errors of metabolism” that result from lack of an enzyme ...
... Proposed that some human diseases are due to “inborn errors of metabolism” that result from lack of an enzyme ...
Transposons: Mobile DNA DNA
... DNA transposons are able to transpose in direct, DNA-DNA manner and are present in prokaryotes and eukaryotes Two distinct mechanisms of transposition: •Replicative transposition – direct interaction between the donor transposon and the target site, resulting in copying of the donor ...
... DNA transposons are able to transpose in direct, DNA-DNA manner and are present in prokaryotes and eukaryotes Two distinct mechanisms of transposition: •Replicative transposition – direct interaction between the donor transposon and the target site, resulting in copying of the donor ...
3.5 Genetic Modification and Biotechnology
... Many plant species and some animal species have Design of an experiment to assess one factor natural methods of cloning. affecting the rooting of stem-cuttings. Animals can be cloned at the embryo stage by breaking up the embryo into more than one group of cells. Methods have been developed for clon ...
... Many plant species and some animal species have Design of an experiment to assess one factor natural methods of cloning. affecting the rooting of stem-cuttings. Animals can be cloned at the embryo stage by breaking up the embryo into more than one group of cells. Methods have been developed for clon ...
Biotechnology - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
... A gene is a sequence of ______ protein that codes for one __________. DNA codes for proteins. **Remember, not all of the ______ genes the parts that The parts that do are called ________, don’t are called _________________ non-coding regions. ...
... A gene is a sequence of ______ protein that codes for one __________. DNA codes for proteins. **Remember, not all of the ______ genes the parts that The parts that do are called ________, don’t are called _________________ non-coding regions. ...
Nucleic Acid and Protein - Seattle Central College
... 1. At the beginning of lab you will assemble many nucleotides. A DNA nucleotide consists of deoxyribose sugar, phosphate and one of 4 bases. List the 4 bases: ...
... 1. At the beginning of lab you will assemble many nucleotides. A DNA nucleotide consists of deoxyribose sugar, phosphate and one of 4 bases. List the 4 bases: ...
Dichotomous Keys and DNA to Protein WS
... RNA:_______________________________________________________ Amino Acid:_______________________________________________________ ...
... RNA:_______________________________________________________ Amino Acid:_______________________________________________________ ...