Epigenetics
... • The second kind of mark, called histone modification, indirectly affects the DNA in your genome. • Histones are proteins which enable DNA's molecules to be wound up neatly into chromosomes inside the cell nucleus. • A variety of chemical tags can grab hold of the tails of histones, changing how t ...
... • The second kind of mark, called histone modification, indirectly affects the DNA in your genome. • Histones are proteins which enable DNA's molecules to be wound up neatly into chromosomes inside the cell nucleus. • A variety of chemical tags can grab hold of the tails of histones, changing how t ...
Chapter 12 Review 1. The replication of DNA molecules
... 15. RNA contains which sugar? 16. How many main types of RNA are there? 17. What is produced during transcription? 18. What are anticodons? 19. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? 20. Why is it possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than one kind of codon? 21. What h ...
... 15. RNA contains which sugar? 16. How many main types of RNA are there? 17. What is produced during transcription? 18. What are anticodons? 19. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? 20. Why is it possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than one kind of codon? 21. What h ...
No Slide Title
... Denaturation at 94º C DNA disassociates to SS Add annealing primers at 54 º C :enables polymerase to attach Extensions at ~72 º C :taq polymerase & lots of nucleotides ...
... Denaturation at 94º C DNA disassociates to SS Add annealing primers at 54 º C :enables polymerase to attach Extensions at ~72 º C :taq polymerase & lots of nucleotides ...
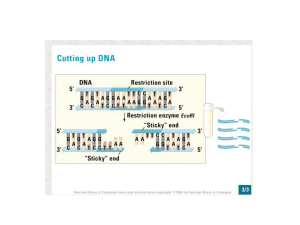
Biological information
... Transcriptional control can be modified by the insertion of transposable elements (e.g. Alu sequences) or mutation. ...
... Transcriptional control can be modified by the insertion of transposable elements (e.g. Alu sequences) or mutation. ...
Plant transposons
... (1) At the beginning of kernel development, the Ds transposon is inserted into the colored (C) gene, resulting in colorless tissue. (2) Ds transposition early in kernel development restores the C gene, giving rise to a large colored sector. (3) Transposition later in kernel development results in sm ...
... (1) At the beginning of kernel development, the Ds transposon is inserted into the colored (C) gene, resulting in colorless tissue. (2) Ds transposition early in kernel development restores the C gene, giving rise to a large colored sector. (3) Transposition later in kernel development results in sm ...
If we should succeed in helping ourselves through applied genetics
... Most DNA manipulation is done in bacteria Bacterial Advantages: 1.) rapid growth on simple substrates 2.) stable extrachromosomal DNA (plasmids) 3.) molecular tools, some model bacteria, particularly E. coli, are very well understood at the cellular level The most significant molecular tool was the ...
... Most DNA manipulation is done in bacteria Bacterial Advantages: 1.) rapid growth on simple substrates 2.) stable extrachromosomal DNA (plasmids) 3.) molecular tools, some model bacteria, particularly E. coli, are very well understood at the cellular level The most significant molecular tool was the ...
Nucleic acid worksheet
... 1. ___________________ are the monomers of all nucleic acids. 2. These monomers of DNA contain the bases: __________________, ___________________, ________________________, and _____________________. 3. _________________________ is the sugar found in all DNA molecules. 4. The shape of a DNA molecule ...
... 1. ___________________ are the monomers of all nucleic acids. 2. These monomers of DNA contain the bases: __________________, ___________________, ________________________, and _____________________. 3. _________________________ is the sugar found in all DNA molecules. 4. The shape of a DNA molecule ...
Chapter 22
... Some retroposons directly resemble retroviruses in their use of LTRs, whereas others do not have LTRs. Other elements can be found that were generated by an RNA-mediated transposition event, but they do not themselves code for enzymes that can catalyze transposition. Transposons and retroposons cons ...
... Some retroposons directly resemble retroviruses in their use of LTRs, whereas others do not have LTRs. Other elements can be found that were generated by an RNA-mediated transposition event, but they do not themselves code for enzymes that can catalyze transposition. Transposons and retroposons cons ...
Exon prediction problem using genetic algorithm as an
... machinery from those actually not functional. In order to predict gene structure by processing only DNA sequence signals often results in a computationally intractable combinatorial explosion of potential products. As a result, any gene prediction method that relies on these signals has to be able t ...
... machinery from those actually not functional. In order to predict gene structure by processing only DNA sequence signals often results in a computationally intractable combinatorial explosion of potential products. As a result, any gene prediction method that relies on these signals has to be able t ...
14-3 Human Molecular Genetics
... is replaced by a normal, working gene. - This way the body can make the correct protein or enzyme it needs, which eliminates the cause of the disorder. ...
... is replaced by a normal, working gene. - This way the body can make the correct protein or enzyme it needs, which eliminates the cause of the disorder. ...
... the genome. Since the last century the replicon model has been proposed in order to explain the general mechanism of genome duplication in bacteria. Later work in yeast lead to identifying proteins and dna sequences that participate in the initiation of replication in a similar fashion to what has b ...
Mutations Can Change the Meaning of Genes
... 3. Excluding the stop sequence, how many nucleotides are necessary to code for a polypeptide that is 100 amino acids long? a. 33 b. 66 c. 100 d. 300 ...
... 3. Excluding the stop sequence, how many nucleotides are necessary to code for a polypeptide that is 100 amino acids long? a. 33 b. 66 c. 100 d. 300 ...
Composite Transposons
... Insertion sequences (IS) are short DNA sequences, about 700 to 5000 bp which can move from one location in a DNA sequence to another. They have short 16-41 bp inverted repeats on their ends. They encode a transposase which catalyses site-specific recombination. ...
... Insertion sequences (IS) are short DNA sequences, about 700 to 5000 bp which can move from one location in a DNA sequence to another. They have short 16-41 bp inverted repeats on their ends. They encode a transposase which catalyses site-specific recombination. ...
Genetics - FAQ`s - El Camino College
... A threadlike structure found in the nucleus of the cell that contains the hereditary material. A chromosome is made up of one tightly coiled DNA molecule. Humans have 46 chromosomes, which occur in 23 pairs. WHAT IS A GENE? Even scientists disagree on how to define a gene. Generally, a gene is defin ...
... A threadlike structure found in the nucleus of the cell that contains the hereditary material. A chromosome is made up of one tightly coiled DNA molecule. Humans have 46 chromosomes, which occur in 23 pairs. WHAT IS A GENE? Even scientists disagree on how to define a gene. Generally, a gene is defin ...
The Molecular Study and Sequence Analysis of Wdhn13 (LEA
... LEA proteins in wheat and cotton were identified and discussed as the first report in late embryonic proteins. Public classification for more LEA genes was inferred from the structure of the protein domain or chemically derived characters. Bioinformatics methods in genome research methods are useful ...
... LEA proteins in wheat and cotton were identified and discussed as the first report in late embryonic proteins. Public classification for more LEA genes was inferred from the structure of the protein domain or chemically derived characters. Bioinformatics methods in genome research methods are useful ...
Transposons - iPlant Pods
... • Subtle impact on the expression of many genes • Produces stress-inducible networks (cold, salt, others?) • Generates dominant alleles Naito et al, Nature, 2009 ...
... • Subtle impact on the expression of many genes • Produces stress-inducible networks (cold, salt, others?) • Generates dominant alleles Naito et al, Nature, 2009 ...
Genetic selection and variation
... Genes are a specific sequences of DNA located on the chromosomes. Chromosomes consist of proteins (histones) combined with two complementary chains of DNA. ...
... Genes are a specific sequences of DNA located on the chromosomes. Chromosomes consist of proteins (histones) combined with two complementary chains of DNA. ...
DNA Technology
... 2. Research an example of how the technique has been used by humans. You can use one of the examples listed above or find your own. Be specific in explaining how the technique was used. Cite your sources – not the textbook. This is the major part of your report. DO NOT USE INSULIN or INDENTIFYING CR ...
... 2. Research an example of how the technique has been used by humans. You can use one of the examples listed above or find your own. Be specific in explaining how the technique was used. Cite your sources – not the textbook. This is the major part of your report. DO NOT USE INSULIN or INDENTIFYING CR ...
7 Self study questions
... 1. Explain why ORF scanning is a feasible way of identifying genes in a prokaryotic DNA sequence. 2. What modifications are introduced when ORF scanning is applied to a eukaryotic DNA sequence? 3. Describe how homology searching is used to locate genes in a DNA sequence and to assign possible functi ...
... 1. Explain why ORF scanning is a feasible way of identifying genes in a prokaryotic DNA sequence. 2. What modifications are introduced when ORF scanning is applied to a eukaryotic DNA sequence? 3. Describe how homology searching is used to locate genes in a DNA sequence and to assign possible functi ...