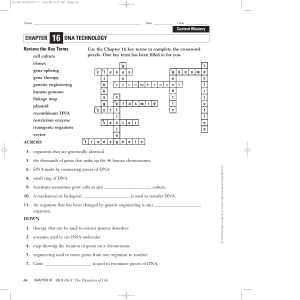
Gene Patenting?
... Only 4% of the total human genome Has their function known. On the other hand, the function of the remainder 96% of the genetic information is unknown. Hence, owning any sequence of them now may be beneficial to a patent holder later, when its function become known ...
... Only 4% of the total human genome Has their function known. On the other hand, the function of the remainder 96% of the genetic information is unknown. Hence, owning any sequence of them now may be beneficial to a patent holder later, when its function become known ...
Worksheet for 4/16
... gel electrophoresis. Diagram a gel including electric charge, and labeled fragments. ...
... gel electrophoresis. Diagram a gel including electric charge, and labeled fragments. ...
Genes and Mutations 1. Define: Genetics – Genetics may be defined
... bacterial culture is usually around 10-9 cells/ml of medium (that’s 1 billion cells/ml). 12. Substitutions/ The substitution of one base for another within a gene may or may not change the amino acid sequence the gene is encoding because the genetic code is redundant (several different codons encode ...
... bacterial culture is usually around 10-9 cells/ml of medium (that’s 1 billion cells/ml). 12. Substitutions/ The substitution of one base for another within a gene may or may not change the amino acid sequence the gene is encoding because the genetic code is redundant (several different codons encode ...
notes
... • First method is by “cloning”, i.e. introduce the gene into a bacterial cell then grow up large amounts and extract DNA (in vivo) • Second method is by “polymerase chain reaction” (PCR) using DNA polymerase to amplify the gene in a test-tube (in vitro) • Both methods have their uses but PCR is pref ...
... • First method is by “cloning”, i.e. introduce the gene into a bacterial cell then grow up large amounts and extract DNA (in vivo) • Second method is by “polymerase chain reaction” (PCR) using DNA polymerase to amplify the gene in a test-tube (in vitro) • Both methods have their uses but PCR is pref ...
When Is a Genome Project Finished?
... Database (OsGDB?) ________________________________________________________________________ 8. If two EST’s are generated from the same mRNA transcript, how will this be indicated in the Genome Context View? ________________________________________________________________________ ...
... Database (OsGDB?) ________________________________________________________________________ 8. If two EST’s are generated from the same mRNA transcript, how will this be indicated in the Genome Context View? ________________________________________________________________________ ...
DNA-RNA-Protein Practice Hwk
... Lysine and arginine make up more than 20% of histone proteins' amino acids. Given the structure of DNA, why is this expected? Hint: see the amino acid chart in Chapter 5 -- figure 5.16. ...
... Lysine and arginine make up more than 20% of histone proteins' amino acids. Given the structure of DNA, why is this expected? Hint: see the amino acid chart in Chapter 5 -- figure 5.16. ...
Intro to Genetics Webquest
... What is a Trait? 22) Give an example of a physical trait: 23) A dog fetching a bone is an example of what kind of trait. 24) Scientists describe the set of information for each form of a trait as an ...
... What is a Trait? 22) Give an example of a physical trait: 23) A dog fetching a bone is an example of what kind of trait. 24) Scientists describe the set of information for each form of a trait as an ...
Genomics Glossary
... different pathogenic mutations in the same gene, typically one from each unaffected parent; this differs from homozygous mutations in which the child receives two copies of an identical pathogenic mutation, one from each parent. Epigenome* Set of chemical compounds that modify, or mark, the genome i ...
... different pathogenic mutations in the same gene, typically one from each unaffected parent; this differs from homozygous mutations in which the child receives two copies of an identical pathogenic mutation, one from each parent. Epigenome* Set of chemical compounds that modify, or mark, the genome i ...
DNA in classifying species
... The DNA used to identify differences and similarities between organisms must be ...
... The DNA used to identify differences and similarities between organisms must be ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 6. Gene silencing can be used for turning off a gene 7. Meristem culture is used to eliminate virus in tissue culture 8. Barbara McClintok discovered jumping genes 9. Particle gun bombardment technique cannot be used for gene transfer in plants 10. Haploid set of chromosome (n) of an organism is ter ...
... 6. Gene silencing can be used for turning off a gene 7. Meristem culture is used to eliminate virus in tissue culture 8. Barbara McClintok discovered jumping genes 9. Particle gun bombardment technique cannot be used for gene transfer in plants 10. Haploid set of chromosome (n) of an organism is ter ...
1 BIOL 213 Fifth Exam All atoms, chemical bonding and structures
... CAAT and TATA promoter boxes of the gene and transcription start is indicated by AAA. The open reading frame is designated to start at +1, ATG=Met and the ORF stops at the amino acid Tyr = TAT. The last amino acid codon in the ORF is followed by the stop codon ...
... CAAT and TATA promoter boxes of the gene and transcription start is indicated by AAA. The open reading frame is designated to start at +1, ATG=Met and the ORF stops at the amino acid Tyr = TAT. The last amino acid codon in the ORF is followed by the stop codon ...
Exam II Study Guide
... go to help sessions, and look at relevant course web site information and videos. Exam II will consist of three parts [i.e., I. General genetics knowledge (~20 points), II. Multiple choice (~40 points), and III. Short answer (~40 points)]. You should know the following information for the second exa ...
... go to help sessions, and look at relevant course web site information and videos. Exam II will consist of three parts [i.e., I. General genetics knowledge (~20 points), II. Multiple choice (~40 points), and III. Short answer (~40 points)]. You should know the following information for the second exa ...
Chapter 12 SWBAT`s and Standards
... Students know how to apply the genetic coding rules to predict the sequence of amino acids from a sequence of codons in RNA. ...
... Students know how to apply the genetic coding rules to predict the sequence of amino acids from a sequence of codons in RNA. ...
Bill Nye - Genetics (worksheet)
... Greatest Discoveries with Bill Nye: Genetics 1) In Mendel’s experiments, what percentage of plants showed the “hidden” characteristic in the second generation? ...
... Greatest Discoveries with Bill Nye: Genetics 1) In Mendel’s experiments, what percentage of plants showed the “hidden” characteristic in the second generation? ...
Genetic Exchange - Pennsylvania State University
... • During phage replication and assembly, capsids may package chromosomal or plasmid DNA by mistake. • When transferred to a new host it may recombine. ...
... • During phage replication and assembly, capsids may package chromosomal or plasmid DNA by mistake. • When transferred to a new host it may recombine. ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... • The term “selfish DNA” implies that insertion sequences and other transposons replicate at the expense of their hosts, providing no value in return • Some transposons do carry genes that are valuable to their hosts, antibiotic resistance is among most familiar ...
... • The term “selfish DNA” implies that insertion sequences and other transposons replicate at the expense of their hosts, providing no value in return • Some transposons do carry genes that are valuable to their hosts, antibiotic resistance is among most familiar ...
Chapter 23 Lecture PowerPoint
... Phage coat is made of protein Always has the same volume DNA is much denser than protein More DNA in phage, denser phage Extra DNAs that can inactivate a gene by inserting into the gene were the first transposons discovered in bacteria • These transposons are called insertion sequences (ISs) ...
... Phage coat is made of protein Always has the same volume DNA is much denser than protein More DNA in phage, denser phage Extra DNAs that can inactivate a gene by inserting into the gene were the first transposons discovered in bacteria • These transposons are called insertion sequences (ISs) ...
Human Genome - BEHS Science
... cells of the immune system are separated from blood samples and the functional gene is added to when the drawback with most current forms of gene therapy is that the gene does not always stay active for a long time, or long life spans, and treatment must be repeated often. ...
... cells of the immune system are separated from blood samples and the functional gene is added to when the drawback with most current forms of gene therapy is that the gene does not always stay active for a long time, or long life spans, and treatment must be repeated often. ...
Genetics - Bill Nye ANSWERS
... DNA is composed of 4 bases. What are they? Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine DNA is a double helix. DNA bases are held together by hydrogen bonds. DNA is responsible for making proteins. RNA is similar to DNA, but its different. What’s different? RNA only has one strand. There are 20 amino acids t ...
... DNA is composed of 4 bases. What are they? Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine DNA is a double helix. DNA bases are held together by hydrogen bonds. DNA is responsible for making proteins. RNA is similar to DNA, but its different. What’s different? RNA only has one strand. There are 20 amino acids t ...
Microorganisms in Biotechnology
... • Viral vectors are viruses to carry altered DNA into cells and are created by removing genes in a virus and replacing them with the gene to be transferred • The vector is then mixed with growing cells and enter the cell, depositing the new gene in the chromosome of that cell • The gene is then pass ...
... • Viral vectors are viruses to carry altered DNA into cells and are created by removing genes in a virus and replacing them with the gene to be transferred • The vector is then mixed with growing cells and enter the cell, depositing the new gene in the chromosome of that cell • The gene is then pass ...