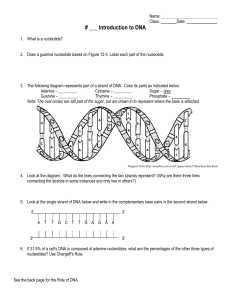
DNA Paper Model Activity Try to attach and mode the Gene Reading
... 1. Try to attach and mode the Gene Reading Machinery cut-out to any length of the inaccessible DNA ribbon that is not spooled around a histone or covered by a methyl. Can the machinery read any significant stretch of DNA? No, it cannot. 2. Refer to question 1, would this be an active or inactive gen ...
... 1. Try to attach and mode the Gene Reading Machinery cut-out to any length of the inaccessible DNA ribbon that is not spooled around a histone or covered by a methyl. Can the machinery read any significant stretch of DNA? No, it cannot. 2. Refer to question 1, would this be an active or inactive gen ...
18 Things You Should Know About Genetics
... (7)The particular ORDER of the bases determines the species of the organism as well as its characteristics. (8)The SIDES of the DNA ladder are composed of alternating sugar and phosphate groups. (9)The HUMAN genome is made up of 3.2 billion base pairs. (10)The human genome would take 9.5 YEARS to re ...
... (7)The particular ORDER of the bases determines the species of the organism as well as its characteristics. (8)The SIDES of the DNA ladder are composed of alternating sugar and phosphate groups. (9)The HUMAN genome is made up of 3.2 billion base pairs. (10)The human genome would take 9.5 YEARS to re ...
GENETICS – BIO 300
... 2 types (at least) of transposition mechanisms 1. replicative: copy remains in original site recombination event ...
... 2 types (at least) of transposition mechanisms 1. replicative: copy remains in original site recombination event ...
WEEK 1 PROBLEMS Problems From Chapter 1
... cultures lacking Z, they cannot grow. If Z is added to the medium, they grow. Experiments are carried out to determine whether any of the intermediates can substitute for Z in supporting growth. It is found that mutant cells can grow in the presence of Y but not in the presence of W or X. Deduce fro ...
... cultures lacking Z, they cannot grow. If Z is added to the medium, they grow. Experiments are carried out to determine whether any of the intermediates can substitute for Z in supporting growth. It is found that mutant cells can grow in the presence of Y but not in the presence of W or X. Deduce fro ...
DNA and RNA
... Griffith hypothesized… • when the live, harmless bacteria and the heat-killed bacteria were mixed, some factor was transferred from the heat-killed cells into the live cells • The ability to cause disease was inherited by the transformed bacteria’s offspring, the transforming factor might be a gene ...
... Griffith hypothesized… • when the live, harmless bacteria and the heat-killed bacteria were mixed, some factor was transferred from the heat-killed cells into the live cells • The ability to cause disease was inherited by the transformed bacteria’s offspring, the transforming factor might be a gene ...
Cytosine – ______ Sugar
... Note: The oval circles are still part of the sugar, but are drawn in to represent where the base is attached. ...
... Note: The oval circles are still part of the sugar, but are drawn in to represent where the base is attached. ...
1 Genetics (BIL-250) Review Questions #1 (2
... (3-1) Draw a DNA replication fork and identify and label the locations of the following major components: (1) 5’ and 3’ ends of each strand, (2) leading strand, (3) lagging strand, (4) single-stranded binding proteins, (5) DNA polymerase, (6)Okazaki fragments, (7) RNA primer, (8) DNA helicase, (9) D ...
... (3-1) Draw a DNA replication fork and identify and label the locations of the following major components: (1) 5’ and 3’ ends of each strand, (2) leading strand, (3) lagging strand, (4) single-stranded binding proteins, (5) DNA polymerase, (6)Okazaki fragments, (7) RNA primer, (8) DNA helicase, (9) D ...
Plant Molecular Biology
... 5. What is meant by lateral or horizontal DNA transfer? How do organelle introns fit into this topic? Why might they be particularly likely to undergo lateral transfer? What plant genome(s) seem to be particularly prone to receiving DNA laterally? ...
... 5. What is meant by lateral or horizontal DNA transfer? How do organelle introns fit into this topic? Why might they be particularly likely to undergo lateral transfer? What plant genome(s) seem to be particularly prone to receiving DNA laterally? ...
The exchange of Genetic Material between bacteria or How
... The exchange of Genetic Material between bacteria ...
... The exchange of Genetic Material between bacteria ...
13.3- The Human Genome
... make up the human genome.They were able to learn that all genes do not have one specific role, as was previously believed, but can actually make up to three proteins” (Discovery Channel). ...
... make up the human genome.They were able to learn that all genes do not have one specific role, as was previously believed, but can actually make up to three proteins” (Discovery Channel). ...
Nucleotide - Jackson County School District
... changed by a gene or genes from another strain of bacteria ...
... changed by a gene or genes from another strain of bacteria ...
Glossary (34,35)
... Study that evaluates the association of specific genetic variants with an outcome of interest, the variants chosen based on their postulated association with the outcome or disease ...
... Study that evaluates the association of specific genetic variants with an outcome of interest, the variants chosen based on their postulated association with the outcome or disease ...
Greatest Discoveries with Bill Nye: Genetics
... ______________________________. 21. With restriction enzymes, scientists had a pair of molecular ______________ to ________ DNA molecules. #10- RNA Alternative Splicing ...
... ______________________________. 21. With restriction enzymes, scientists had a pair of molecular ______________ to ________ DNA molecules. #10- RNA Alternative Splicing ...
Biological ideas relating to genetic modification
... One of four chemicals which make up the ‘rungs’ of DNA. A,T,C and G ...
... One of four chemicals which make up the ‘rungs’ of DNA. A,T,C and G ...
Greatest Discoveries with Bill Nye: Genetics
... 3. Dropsphila melanogaster is known as the common _____________ _____________. 4. Human females have 2 _____ chromosomes, while human males have 1 _____ and 1 _____ chromosome. 5. Morgan was awarded the Nobel Prize for Medicine in the year _________. #3- Genes Control Biochemical Events ...
... 3. Dropsphila melanogaster is known as the common _____________ _____________. 4. Human females have 2 _____ chromosomes, while human males have 1 _____ and 1 _____ chromosome. 5. Morgan was awarded the Nobel Prize for Medicine in the year _________. #3- Genes Control Biochemical Events ...
DNA Jeopardy Review
... Prokaryotes have slightly different translation mechanisms name one difference? ...
... Prokaryotes have slightly different translation mechanisms name one difference? ...
3-10
... Subject: The structure and replication of DNA. Reading in ‘An introduction to genetic analysis’ (Griffiths et al., 7th edition) Chapter 8: The structure and replication of DNA. ________________________________________________________________________ Key concepts and keywords: DNA: the genetic materi ...
... Subject: The structure and replication of DNA. Reading in ‘An introduction to genetic analysis’ (Griffiths et al., 7th edition) Chapter 8: The structure and replication of DNA. ________________________________________________________________________ Key concepts and keywords: DNA: the genetic materi ...
DNA RNA Test Review Guide
... Name the process during which copies of DNA are made. Name the process during which a complementary RNA strand is made from DNA. Name the process during which amino acids are assembled into polypeptides according to DNA instructions. Give another name for a large polypeptide Name the monomer and mon ...
... Name the process during which copies of DNA are made. Name the process during which a complementary RNA strand is made from DNA. Name the process during which amino acids are assembled into polypeptides according to DNA instructions. Give another name for a large polypeptide Name the monomer and mon ...
Study Guide for LS
... Ultraviolet radiation from the sun is known to cause mutations in skin cells that can lead to cancer, which is why you should wear sunscreen in the summertime. A disease that occurs when a child inherits a mutated gene from parents who do not have the disease is a recessive disorder. ...
... Ultraviolet radiation from the sun is known to cause mutations in skin cells that can lead to cancer, which is why you should wear sunscreen in the summertime. A disease that occurs when a child inherits a mutated gene from parents who do not have the disease is a recessive disorder. ...
Molecular Genetics Outcome Checklist
... _____ I can explain how, in general, restriction enzymes cut DNA molecules into smaller fragments based on a specific nucleotide sequence, leaving “sticky ends”. _____ I understand the purpose and function of ligases. _____ I can explain how restriction enzymes, ligases, and other DNA technology ca ...
... _____ I can explain how, in general, restriction enzymes cut DNA molecules into smaller fragments based on a specific nucleotide sequence, leaving “sticky ends”. _____ I understand the purpose and function of ligases. _____ I can explain how restriction enzymes, ligases, and other DNA technology ca ...
Exam 1 Study Guide – General Concepts
... Eukaryotic (has 3 different RNA polymerases for transcription) - Still have promoters and regulatory elements (but promoters are less conserved and are shorter and regulatory elements are classified as enhancers & silencers) - RNA processing of heterogeneous RNA (primary transcript into mRNA) Intron ...
... Eukaryotic (has 3 different RNA polymerases for transcription) - Still have promoters and regulatory elements (but promoters are less conserved and are shorter and regulatory elements are classified as enhancers & silencers) - RNA processing of heterogeneous RNA (primary transcript into mRNA) Intron ...
Transposons
... transcriptase into cDNA the cDNA integrates into the genome Retroelements are found in all eukaryotes such as Tos in rice, copia in animals Ty1 in yeast ...
... transcriptase into cDNA the cDNA integrates into the genome Retroelements are found in all eukaryotes such as Tos in rice, copia in animals Ty1 in yeast ...