Lecture 8
... 1. Simple Ds elements are deletion derivatives of Ac, which have lost internal sequence for trans-acting factor. 2. Composite Ds elements internally contain rearranged Ac and unrelated sequences. Transposition 1. Insertion results in short target site duplication (“footprint”). This suggests that th ...
... 1. Simple Ds elements are deletion derivatives of Ac, which have lost internal sequence for trans-acting factor. 2. Composite Ds elements internally contain rearranged Ac and unrelated sequences. Transposition 1. Insertion results in short target site duplication (“footprint”). This suggests that th ...
DIY DNA.Study Plan-Obj
... reproduction ("non-sexual" reproduction). 12. Recognize the most important result of sexual reproduction, and how this relates to natural selection. 13. Recognize the kinds of organisms in which sexual reproduction has been shown to occur. 14. Recognize the way in which gene mutations are related to ...
... reproduction ("non-sexual" reproduction). 12. Recognize the most important result of sexual reproduction, and how this relates to natural selection. 13. Recognize the kinds of organisms in which sexual reproduction has been shown to occur. 14. Recognize the way in which gene mutations are related to ...
ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
... 1. Give a ewe hormones to make her superovulate. Apply ram sperm to ewe’s reproductive tract. Flush out fertilized ova, and inject them with human AAT gene linked to sheep gene promoter that will control its expression. Place GM fertilized ova into sheep surrogate mothers. Select heterozygous offspr ...
... 1. Give a ewe hormones to make her superovulate. Apply ram sperm to ewe’s reproductive tract. Flush out fertilized ova, and inject them with human AAT gene linked to sheep gene promoter that will control its expression. Place GM fertilized ova into sheep surrogate mothers. Select heterozygous offspr ...
7.1 - DNA Structure
... proteins and held together by another histone protein. The DNA double helix has major and minor groves on the outer diameter, exposing chemical groups that can form hydrogen bonds. These groups are bonded to positively-charged proteins called histones, forming two loops around them. DNA is wound aro ...
... proteins and held together by another histone protein. The DNA double helix has major and minor groves on the outer diameter, exposing chemical groups that can form hydrogen bonds. These groups are bonded to positively-charged proteins called histones, forming two loops around them. DNA is wound aro ...
4.4 Genetic engineering and biotechnology - McLain
... 6. plasmid removed from bacteria; plasmid cleaved/cut open by restriction enzymes; desired gene/DNA extracted from donor; DNA from donor cleaved using same restriction enzyme; results in sticky ends; with complementary base sequences; pieces of DNA from two organisms mixed; ligase used to splice pie ...
... 6. plasmid removed from bacteria; plasmid cleaved/cut open by restriction enzymes; desired gene/DNA extracted from donor; DNA from donor cleaved using same restriction enzyme; results in sticky ends; with complementary base sequences; pieces of DNA from two organisms mixed; ligase used to splice pie ...
Honors Biology
... cell). 5. Describe the process of protein synthesis (both transcription and translation). 6. Explain the steps of mRNA processing and how it can result in different proteins. 7. Describe the relationship between control of gene expression and cell differentiation or specialization. 8. Describe the w ...
... cell). 5. Describe the process of protein synthesis (both transcription and translation). 6. Explain the steps of mRNA processing and how it can result in different proteins. 7. Describe the relationship between control of gene expression and cell differentiation or specialization. 8. Describe the w ...
Molecular Genetics Review
... Leading strand vs. lagging strand Okazaki fragments Pro vs. Eukaryotic replication ...
... Leading strand vs. lagging strand Okazaki fragments Pro vs. Eukaryotic replication ...
Principles of Biology Lake Tahoe Community College
... D. Eukaryotic RNA may be spliced in more than one way E. Translation and later stages of gene expression are also subject to regulation 1. Breakdown of mRNA 2. Initiation of translation 3. protein activation 4. protein breakdown F. Multiple mechanisms regulate gene expression 1. flow of genetic info ...
... D. Eukaryotic RNA may be spliced in more than one way E. Translation and later stages of gene expression are also subject to regulation 1. Breakdown of mRNA 2. Initiation of translation 3. protein activation 4. protein breakdown F. Multiple mechanisms regulate gene expression 1. flow of genetic info ...
Ch. 16 Molecular Basis of Genetics
... the replication forks) liga - = bound or tied (DNA ligase: a linking enzyme for DNA replication) -phage = to eat (bacteriophages: viruses that infect bacteria) semi - = half (semiconservative model: type of DNA replication in which the replicated double helix consists of one old strand, derived from ...
... the replication forks) liga - = bound or tied (DNA ligase: a linking enzyme for DNA replication) -phage = to eat (bacteriophages: viruses that infect bacteria) semi - = half (semiconservative model: type of DNA replication in which the replicated double helix consists of one old strand, derived from ...
Tour of the Basics Web Quest
... 17. Does the second baby in the What is Heredity? animation inherit the exact same chromosomes as the first? Do both babies have a complete set? ...
... 17. Does the second baby in the What is Heredity? animation inherit the exact same chromosomes as the first? Do both babies have a complete set? ...
Document
... and a clone derived from that library hybridized to the 2 kb, 6 kb, and 9 kb restriction fragments only. When sequenced, this cDNA clone was 720 nucleotides in length and therefore incomplete. The amino terminal sequence of the protein encoding this gene was known, however, and a synthetic oligonucl ...
... and a clone derived from that library hybridized to the 2 kb, 6 kb, and 9 kb restriction fragments only. When sequenced, this cDNA clone was 720 nucleotides in length and therefore incomplete. The amino terminal sequence of the protein encoding this gene was known, however, and a synthetic oligonucl ...
DNA and RNA
... Griffith hypothesized… • when live, harmless bacteria and heat-killed bacteria were mixed, some factor was transferred from the heat-killed cells into the live cells • The ability to cause disease was inherited by the transformed bacteria’s offspring, • Transforming factor might be a gene ...
... Griffith hypothesized… • when live, harmless bacteria and heat-killed bacteria were mixed, some factor was transferred from the heat-killed cells into the live cells • The ability to cause disease was inherited by the transformed bacteria’s offspring, • Transforming factor might be a gene ...
Genetic Test Study Guide
... 14. Next label the placement of the 1 , 2 , and 3 generations on the pedigree. 15. Using the pedigree, how many individuals in the 2nd generation are carriers? 3 16. How many individuals in the 3rd generation on pedigree are affected by the trait? 1 17. A carrier is a person who has what? One recess ...
... 14. Next label the placement of the 1 , 2 , and 3 generations on the pedigree. 15. Using the pedigree, how many individuals in the 2nd generation are carriers? 3 16. How many individuals in the 3rd generation on pedigree are affected by the trait? 1 17. A carrier is a person who has what? One recess ...
Smurfs, Trolls & Elves
... • The inherited blue began to disappear as the recessive gene spread to families where it is unlikely to be paired to a similar gene ...
... • The inherited blue began to disappear as the recessive gene spread to families where it is unlikely to be paired to a similar gene ...
DNA notes File
... A nucleotide is when one phosphate group, one nitrogen base and one _______________ are ...
... A nucleotide is when one phosphate group, one nitrogen base and one _______________ are ...
BIO_Protein_Synthesis_Outline - Cole Camp R-1
... ▸Describe the DNA molecule as being Spiral in Shape with the BASES on the inside and the Sugar- Phosphate Groups on the outside. ...
... ▸Describe the DNA molecule as being Spiral in Shape with the BASES on the inside and the Sugar- Phosphate Groups on the outside. ...
DNA Review Cards
... Explain why all mutations do not necessarily have a negative impact on the protein or on the organism as a whole. ...
... Explain why all mutations do not necessarily have a negative impact on the protein or on the organism as a whole. ...
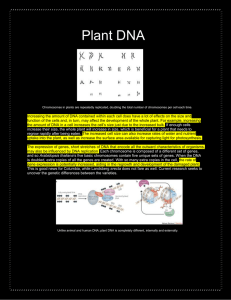
Plant DNA - The uniqueness of DNA
... The expression of genes, short stretches of DNA that encode all the outward characteristics of organisms, may also be influenced by DNA replication. Each chromosome is composed of a different set of genes, and so Arabidopsis thaliana’s five basic chromosomes contain five unique sets of genes. When t ...
... The expression of genes, short stretches of DNA that encode all the outward characteristics of organisms, may also be influenced by DNA replication. Each chromosome is composed of a different set of genes, and so Arabidopsis thaliana’s five basic chromosomes contain five unique sets of genes. When t ...