Genes and Evolution - Mad River Local Schools
... ◦ Those that fit best are more likely to reproduce and survive (natural selection) ...
... ◦ Those that fit best are more likely to reproduce and survive (natural selection) ...
Transposition - Pennsylvania State University
... • Transposase nicks at ends of transposon (note cleavage is at the same sequence, since the ends are inverted repeats). • Transposase also cuts the target to generate 5’ overhangs • The 3’ end of each strand of the transposon is ligated to the 5’ overhang of the target site, forming a crossover stru ...
... • Transposase nicks at ends of transposon (note cleavage is at the same sequence, since the ends are inverted repeats). • Transposase also cuts the target to generate 5’ overhangs • The 3’ end of each strand of the transposon is ligated to the 5’ overhang of the target site, forming a crossover stru ...
Name - Canvas by Instructure
... 4. Which of the following occurs first during the process of transcription? a. Introns are removed and exons are joined together. b. Two DNA strands start to separate. c. DNA polymerases join together complementary base pairs. d. tRNA translates codons. 5. Stretches of noncoding nucleotides found in ...
... 4. Which of the following occurs first during the process of transcription? a. Introns are removed and exons are joined together. b. Two DNA strands start to separate. c. DNA polymerases join together complementary base pairs. d. tRNA translates codons. 5. Stretches of noncoding nucleotides found in ...
Chapter 11 review - Canvas by Instructure
... 4. Which of the following occurs first during the process of transcription? a. Introns are removed and exons are joined together. b. Two DNA strands start to separate. c. DNA polymerases join together complementary base pairs. d. tRNA translates codons. 5. Stretches of noncoding nucleotides found in ...
... 4. Which of the following occurs first during the process of transcription? a. Introns are removed and exons are joined together. b. Two DNA strands start to separate. c. DNA polymerases join together complementary base pairs. d. tRNA translates codons. 5. Stretches of noncoding nucleotides found in ...
PAG XXIV San Diego 2016 Duckweeds, the smallest flowering
... • Duckweeds belong to the Lemnoideae and are the fastest growing plants on earth used in bioremediation and industrial applications. ...
... • Duckweeds belong to the Lemnoideae and are the fastest growing plants on earth used in bioremediation and industrial applications. ...
Honors Biology Test 1 - BellevilleBiology.com
... Elements Compound Activation Energy Cation Anion Review Questions 1. How many kinds of atoms, what kinds of atoms and what proportion of atoms are given in the formula for Carbon Dioxide? 2. What are the 6 elements that make up all living matter: 3. Where are protons, neutrons and electrons position ...
... Elements Compound Activation Energy Cation Anion Review Questions 1. How many kinds of atoms, what kinds of atoms and what proportion of atoms are given in the formula for Carbon Dioxide? 2. What are the 6 elements that make up all living matter: 3. Where are protons, neutrons and electrons position ...
1. The products of mitosis are .
... B. four genetically identical nuclei C. four nuclei containing half as much DNA as the parent nucleus D. two genetically identical nuclei E. two genetically identical cells 2. Genetically diverse offspring result from __________. A. binary fission B. mitosis C. sexual reproduction D. cytokinesis E. ...
... B. four genetically identical nuclei C. four nuclei containing half as much DNA as the parent nucleus D. two genetically identical nuclei E. two genetically identical cells 2. Genetically diverse offspring result from __________. A. binary fission B. mitosis C. sexual reproduction D. cytokinesis E. ...
Name period ______ Date
... Polymerase – Attaches new nucleotides to _____________ new strands 14) DNA Checkpoints - DNA must be replicated perfectly so the new cells that form are identical. The Cell cycle use proofreader enzymes to ensure there are no ____________ in the DNA Mutation – when an ____________ sequence gets copi ...
... Polymerase – Attaches new nucleotides to _____________ new strands 14) DNA Checkpoints - DNA must be replicated perfectly so the new cells that form are identical. The Cell cycle use proofreader enzymes to ensure there are no ____________ in the DNA Mutation – when an ____________ sequence gets copi ...
polymer of nucleotides = nitrogen base, pentose sugar, a phosphate
... with 360A or ~ 10 base pairs per turn -the 2 strands are held by hydrogen bonds between the paired bases and Van der Waals interactions between the stacked bases Watson-Crick Model of the DNA Structure ...
... with 360A or ~ 10 base pairs per turn -the 2 strands are held by hydrogen bonds between the paired bases and Van der Waals interactions between the stacked bases Watson-Crick Model of the DNA Structure ...
Practice Question for Replication, Genetics and Biotechnology
... 10. Enzymes that join two fragments of DNA together are called? ...
... 10. Enzymes that join two fragments of DNA together are called? ...
a copy of the Candy DNA Replication
... Prelab questions: 1. What is the end product of the DNA replication? ______________________________ 2. Why is it important that DNA replicates? ______________________________________ 3. Why is it necessary for DNA to replicate accurately in a cell in order for an organism to survive? _______________ ...
... Prelab questions: 1. What is the end product of the DNA replication? ______________________________ 2. Why is it important that DNA replicates? ______________________________________ 3. Why is it necessary for DNA to replicate accurately in a cell in order for an organism to survive? _______________ ...
Nucleotide Sequence Manipulation - ILRI Research Computing
... ~85% of its genome is in coding regions 3. Calling genes involves using programs that carry out 6 frame translation and identify all the ORFs longer than a given threshold. ...
... ~85% of its genome is in coding regions 3. Calling genes involves using programs that carry out 6 frame translation and identify all the ORFs longer than a given threshold. ...
Chapter 8—Microbial Genetics Study Guide NOTE: I will not test you
... f. Why is DNA replication said to be semi-conservative? 4. Describe transcription and translation. a. What is the function of RNA Polymerase? b. In prokaryotic cells, where does transcription occur? In eukaryotic cells, where does transcription occur? c. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA. d. What are ...
... f. Why is DNA replication said to be semi-conservative? 4. Describe transcription and translation. a. What is the function of RNA Polymerase? b. In prokaryotic cells, where does transcription occur? In eukaryotic cells, where does transcription occur? c. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA. d. What are ...
Lecture 2 PSY391S John Yeomans
... • Blotting to find specific chains: SouthernDNA, Northern-RNA, Western-proteins. • In situ hybridization: Find RNA in brain. • Immunocytochemistry: Find proteins in ...
... • Blotting to find specific chains: SouthernDNA, Northern-RNA, Western-proteins. • In situ hybridization: Find RNA in brain. • Immunocytochemistry: Find proteins in ...
Chapter 16 and 17 Test Review
... 13. What happens to DNA when mutations occur? Name each type of mutation and describe their effects on the mRNA and proteins? Chapter 15- Genes and How They Work 1. Differences between DNA and RNA. 2. How did the study of metabolic disease help lead to Beadle and Tatum’s hypothesis-“One gene equals ...
... 13. What happens to DNA when mutations occur? Name each type of mutation and describe their effects on the mRNA and proteins? Chapter 15- Genes and How They Work 1. Differences between DNA and RNA. 2. How did the study of metabolic disease help lead to Beadle and Tatum’s hypothesis-“One gene equals ...
AP Biology - TeacherWeb
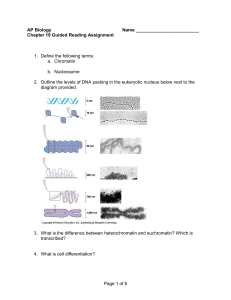
... 2. Outline the levels of DNA packing in the eukaryotic nucleus below next to the diagram provided. ...
... 2. Outline the levels of DNA packing in the eukaryotic nucleus below next to the diagram provided. ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS QUESTIONS
... acid chart and pay attention to 5’ and 3’ ends). Predict how well the protein synthesized from the nontemplate strand would function if at all. 4. What makes RNA polymerase start transcribing a gene at the right place on the DNA in a bacterial cell? In a eukaryotic cell? 5. Suppose X-rays caused a s ...
... acid chart and pay attention to 5’ and 3’ ends). Predict how well the protein synthesized from the nontemplate strand would function if at all. 4. What makes RNA polymerase start transcribing a gene at the right place on the DNA in a bacterial cell? In a eukaryotic cell? 5. Suppose X-rays caused a s ...
You should be able to find the information necessary to answer
... 19. Distinguish between the 2 types of point mutations in DNA. Describe how a frameshift mutation occurs and how it differs from a point mutation, and compare the possible severity of each type of mutation on an organisms phenotype. ...
... 19. Distinguish between the 2 types of point mutations in DNA. Describe how a frameshift mutation occurs and how it differs from a point mutation, and compare the possible severity of each type of mutation on an organisms phenotype. ...
Lecture 20 DNA Repair and Genetic Recombination
... recombination: – Homologous recombination – also known as generalized; occurs at meiosis (as we have just discussed) or not…. – Site specific (specialized) recombination – typically in bacteria and viruses; enzymes involved act only on a particular pair of target sequences in an intermolecular react ...
... recombination: – Homologous recombination – also known as generalized; occurs at meiosis (as we have just discussed) or not…. – Site specific (specialized) recombination – typically in bacteria and viruses; enzymes involved act only on a particular pair of target sequences in an intermolecular react ...
Learning Goals Chapter 13
... 2. To compare and contrast the human and chimpanzee gene sequence for the beta subunit of the hemoglobin gene. 3. To generate the amino acid sequence of one exon of the HBB gene. 4. To identify exons and introns in the sequence. 5. To analyze the differences between the sequences and conclude why th ...
... 2. To compare and contrast the human and chimpanzee gene sequence for the beta subunit of the hemoglobin gene. 3. To generate the amino acid sequence of one exon of the HBB gene. 4. To identify exons and introns in the sequence. 5. To analyze the differences between the sequences and conclude why th ...
Molecular Genetics
... - DNA mutations can be positive, negative, or neutral based on the effect or lack of effect they have on the resulting protein and the phenotypes that are conferred by the protein. - Changes in genotype may affect phenotype which, in turn, may affect natural selection and evolution. - Viral reproduc ...
... - DNA mutations can be positive, negative, or neutral based on the effect or lack of effect they have on the resulting protein and the phenotypes that are conferred by the protein. - Changes in genotype may affect phenotype which, in turn, may affect natural selection and evolution. - Viral reproduc ...
6.3 Advances in Genetics
... one organism are put into the DNA of another • Genetic engineering can produce and improve medicines and foods. • Genes have been inserted into animals (example- creating blood clotting protein to help people with hemophilia • Genes have been inserted into plants (example- creating crops that are re ...
... one organism are put into the DNA of another • Genetic engineering can produce and improve medicines and foods. • Genes have been inserted into animals (example- creating blood clotting protein to help people with hemophilia • Genes have been inserted into plants (example- creating crops that are re ...