Daniela Barillà Borrowing building blocks from bacteria and eukarya
... machine in archaea The precise distribution of newly replicated genomes to progeny cells is vital for stable maintenance of genetic information. In contrast to eukarya and bacteria, the fundamental biological question of DNA segregation remains virtually unexplored in archaea. We have investigated t ...
... machine in archaea The precise distribution of newly replicated genomes to progeny cells is vital for stable maintenance of genetic information. In contrast to eukarya and bacteria, the fundamental biological question of DNA segregation remains virtually unexplored in archaea. We have investigated t ...
Name Bozeman – What is DNA? http://backpack.tv/video/biology
... 4. To what end of DNA do new nucleotides get added? 5. DNA can be described as a ladder. What makes up the backbone? What makes up the rungs of the ladder? 6. Which nitrogenous bases pair together? What kind of bonds hold them together? 7. How many nitrogenous bases code for an amino acid? 8. Where ...
... 4. To what end of DNA do new nucleotides get added? 5. DNA can be described as a ladder. What makes up the backbone? What makes up the rungs of the ladder? 6. Which nitrogenous bases pair together? What kind of bonds hold them together? 7. How many nitrogenous bases code for an amino acid? 8. Where ...
Human Genome Project, Gene Therapy, and Cloning
... 1. Isolate the normal sequence for a gene and package it into a virus (vector). 2. Infect a target cell, usually the one with the illness, such as a liver or lung cell. 3. The cell uses the normal sequence to produce the missing protein and is thus repaired. ...
... 1. Isolate the normal sequence for a gene and package it into a virus (vector). 2. Infect a target cell, usually the one with the illness, such as a liver or lung cell. 3. The cell uses the normal sequence to produce the missing protein and is thus repaired. ...
Slide 1 - Piscataway High School
... Each strand acts as a template to make a new one. Both strands are copied at the same time, but in the opposite direction. ...
... Each strand acts as a template to make a new one. Both strands are copied at the same time, but in the opposite direction. ...
Genetics Vocabulary Allele: One of the variant forms of a gene at a
... Allele: One of the variant forms of a gene at a particular locus, or location, on a chromosome. Different alleles produce variation in inherited characteristics such as hair color or blood type. In an individual, one form of the allele (the dominant one) may be expressed more than another form (the ...
... Allele: One of the variant forms of a gene at a particular locus, or location, on a chromosome. Different alleles produce variation in inherited characteristics such as hair color or blood type. In an individual, one form of the allele (the dominant one) may be expressed more than another form (the ...
IS91 transposase is related to the rolling-circle
... transposases of IS91/IS801 suggests that transposition of these elements also involves single-strand nicking by the transposases, followed by single-stranded rolling-circle replication of the transposon. This will be in contrast to any of the mechanisms of transposition that have been shown or sugge ...
... transposases of IS91/IS801 suggests that transposition of these elements also involves single-strand nicking by the transposases, followed by single-stranded rolling-circle replication of the transposon. This will be in contrast to any of the mechanisms of transposition that have been shown or sugge ...
Slide 1
... Took all the information that the other scientists gathered and put together the first complete model of DNA Won the Nobel Prize for this ...
... Took all the information that the other scientists gathered and put together the first complete model of DNA Won the Nobel Prize for this ...
Biology Chapter 12 Review 5-6
... 6. Nitrogenous bases can be sorted into two groups. Name the groups and explain how they are classified. 7. What units make up the backbone of DNA? 8. Explain how the information Watson and Crick acquired from Rosalind Franklin and Chargaff was used to determine the structure of DNA. 9. Explain comp ...
... 6. Nitrogenous bases can be sorted into two groups. Name the groups and explain how they are classified. 7. What units make up the backbone of DNA? 8. Explain how the information Watson and Crick acquired from Rosalind Franklin and Chargaff was used to determine the structure of DNA. 9. Explain comp ...
The Genome of Theobroma Cacao
... The genome, consisting of long strings of chemicals called DNA sequence, includes all the genes of a given organism, but also DNA that is not part of a gene, or noncoding DNA sequence. Each gene contains instructions for assembly of proteins, which consist of strands of amino acids that fold into an ...
... The genome, consisting of long strings of chemicals called DNA sequence, includes all the genes of a given organism, but also DNA that is not part of a gene, or noncoding DNA sequence. Each gene contains instructions for assembly of proteins, which consist of strands of amino acids that fold into an ...
Webquest
... happening. You will have to answer some questions based on what you see. 1. First go to the page: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/tour/ . Use the tabs at the top of the page and answer the following questions: a. What is DNA? b. What does “DNA” stand for? ...
... happening. You will have to answer some questions based on what you see. 1. First go to the page: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/tour/ . Use the tabs at the top of the page and answer the following questions: a. What is DNA? b. What does “DNA” stand for? ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis Organizer
... Flow of genetic information DNA to RNA to protein Proteins carry out specific functions in body, form enzymes, responsible for physical differences (phenotypes) Gene holds the information for making a specific protein ...
... Flow of genetic information DNA to RNA to protein Proteins carry out specific functions in body, form enzymes, responsible for physical differences (phenotypes) Gene holds the information for making a specific protein ...
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 16 OUTLINE
... AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 16 OUTLINE THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE I. DNA AS THE GENETIC MATERIAL A. The search for the genetic material led to DNA: science as a process Proteins were thought to be the genetic material because: ...
... AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 16 OUTLINE THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE I. DNA AS THE GENETIC MATERIAL A. The search for the genetic material led to DNA: science as a process Proteins were thought to be the genetic material because: ...
DNA Notes
... Structure of DNA • Looks like a twisted ladder • Two sides of the ladder: – Made up of alternating molecules of deoxyribose and phosphates • Each rung is made up of a pair of molecules called nitrogen bases. ...
... Structure of DNA • Looks like a twisted ladder • Two sides of the ladder: – Made up of alternating molecules of deoxyribose and phosphates • Each rung is made up of a pair of molecules called nitrogen bases. ...
Gene Technology
... Recombinant DNA • Donor gene - a specific gene isolated from an organism – Ex. Insulin gene needed to produce insulin for diabetes patients • Recombinant DNA - the combination of DNA from two or more organisms. • The donor gene can be placed into an organism to give it a new characteristic. • Organ ...
... Recombinant DNA • Donor gene - a specific gene isolated from an organism – Ex. Insulin gene needed to produce insulin for diabetes patients • Recombinant DNA - the combination of DNA from two or more organisms. • The donor gene can be placed into an organism to give it a new characteristic. • Organ ...
A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism
... 1. A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism carries in its DNA. 2. A karyotype shows the complete diploid set of chromosomes grouped together in pairs, arranged in order of decreasing size. 3. Two of the 46 chromosomes in the human genome are known as sex chromosomes, because ...
... 1. A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism carries in its DNA. 2. A karyotype shows the complete diploid set of chromosomes grouped together in pairs, arranged in order of decreasing size. 3. Two of the 46 chromosomes in the human genome are known as sex chromosomes, because ...
DNA - World of Teaching
... DNA Structure DNA consists of two molecules that are arranged into a ladder-like structure called a Double Helix. A molecule of DNA is made up of millions of ...
... DNA Structure DNA consists of two molecules that are arranged into a ladder-like structure called a Double Helix. A molecule of DNA is made up of millions of ...
DNA - Franklin County Public Schools
... DNA Structure DNA consists of two molecules that are arranged into a ladder-like structure called a Double Helix. A molecule of DNA is made up of millions of ...
... DNA Structure DNA consists of two molecules that are arranged into a ladder-like structure called a Double Helix. A molecule of DNA is made up of millions of ...
REPLICATION, TRANSCRIPTION, TRANSLATION TAKS
... 14 Part of a DNA strand is represented in the diagram above. In order for DNA to replicate, the strand must separate at which of the following locations? F Between every phosphate-sugar pair G Between the eight sugar-base pairs H* Between the four nitrogenous base pairs J Between any two chemical bo ...
... 14 Part of a DNA strand is represented in the diagram above. In order for DNA to replicate, the strand must separate at which of the following locations? F Between every phosphate-sugar pair G Between the eight sugar-base pairs H* Between the four nitrogenous base pairs J Between any two chemical bo ...
2016 N2 Week 4
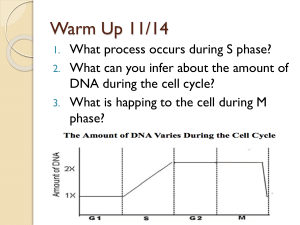
... What biomolecule is DNA? What is the function of DNA? Where is DNA found in eukaryotic organisms? What does DNA stand for? Why does DNA double during S phase? What are the X-shaped structures DNA is coiled into? ...
... What biomolecule is DNA? What is the function of DNA? Where is DNA found in eukaryotic organisms? What does DNA stand for? Why does DNA double during S phase? What are the X-shaped structures DNA is coiled into? ...
Assignment of the TIMP gene to the murine X
... It inhibits to a lesser extent the PMN leucocyte metalloproteinases (1). The gene far human TTMP has been cloned (2), and it was shown to be identical to a cDNA previously identified as erythroid potentiating activity. This human gene has been mapped to the X-chromosome (3,4). We have isolated the m ...
... It inhibits to a lesser extent the PMN leucocyte metalloproteinases (1). The gene far human TTMP has been cloned (2), and it was shown to be identical to a cDNA previously identified as erythroid potentiating activity. This human gene has been mapped to the X-chromosome (3,4). We have isolated the m ...
BIO 220 Chapter 8 lecture outline Vocabulary Central dogma of
... 2. What is the central dogma of biology? Who proposed this theory? 3. What is the difference between the terms genotype and phenotype? Are bacteria typically diploid or haploid? What do diploid and haploid mean? 4. How many chromosomes does the typical bacterial cell have? In what form do these chro ...
... 2. What is the central dogma of biology? Who proposed this theory? 3. What is the difference between the terms genotype and phenotype? Are bacteria typically diploid or haploid? What do diploid and haploid mean? 4. How many chromosomes does the typical bacterial cell have? In what form do these chro ...
Practice Multiple Choice- Set 1 - mvhs
... c) The amount of energy indicates what is passed out as feces d) It indicates the diversity of an environment f) Animals can only be at the top level ...
... c) The amount of energy indicates what is passed out as feces d) It indicates the diversity of an environment f) Animals can only be at the top level ...
Jeffreys - OldForensics 2012-2013
... first developed DNA fingerprinting techniques those of which are commonly used today for police and detective work, paternity tests, and immigration issues ...
... first developed DNA fingerprinting techniques those of which are commonly used today for police and detective work, paternity tests, and immigration issues ...