Molecular Genetics
... We have studied “classical” or “Mendelian” genetics up to this point. - It leaves a lot of questions unanswered. i. . What really is a gene? ii. ...
... We have studied “classical” or “Mendelian” genetics up to this point. - It leaves a lot of questions unanswered. i. . What really is a gene? ii. ...
Gene Therapy - MsSunderlandsBiologyClasses
... • Adenoviruses - A class of viruses with doublestranded DNA genomes that cause respiratory, intestinal, and eye infections in humans. • Adeno-associated viruses - A class of small, single-stranded DNA viruses that can insert their genetic material at a specific site on chromosome ...
... • Adenoviruses - A class of viruses with doublestranded DNA genomes that cause respiratory, intestinal, and eye infections in humans. • Adeno-associated viruses - A class of small, single-stranded DNA viruses that can insert their genetic material at a specific site on chromosome ...
File
... a) some may carry oncogenes- genes to send cell cycle out of control b) some viruses may turn on protooncogenes at inappropriate times ...
... a) some may carry oncogenes- genes to send cell cycle out of control b) some viruses may turn on protooncogenes at inappropriate times ...
1 - BEHS Science
... 15.complementary: the sequence of bases on one strand determines the sequence of bases on the other strand 16.replication: the process of synthesizing a new strand of DNA 17.helicase: enzymes that catalyze the unwinding and separation of double-stranded DNA or RNA during its replication 18.replicati ...
... 15.complementary: the sequence of bases on one strand determines the sequence of bases on the other strand 16.replication: the process of synthesizing a new strand of DNA 17.helicase: enzymes that catalyze the unwinding and separation of double-stranded DNA or RNA during its replication 18.replicati ...
Ch 16 homework
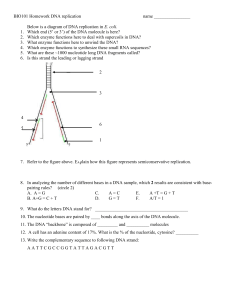
... Which enzyme functions to synthesize these small RNA sequences? What are these ~1000 nucleotide long DNA fragments called? Is this strand the leading or lagging strand ...
... Which enzyme functions to synthesize these small RNA sequences? What are these ~1000 nucleotide long DNA fragments called? Is this strand the leading or lagging strand ...
Know your molecules organizer
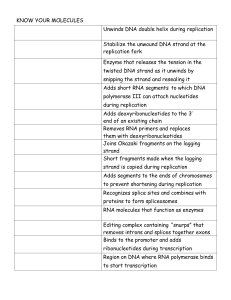
... Unwinds DNA double helix during replication Stabilize the unwound DNA strand at the replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during repl ...
... Unwinds DNA double helix during replication Stabilize the unwound DNA strand at the replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during repl ...
Study Guide Unit 4 - Mrs. Wolodkowicz`s Biological Realm
... the components of DNA the nitrogen bases & their complementary base pairs in DNA & RNA functions of tRNA & mRNA the laws of segregation & independent assortment the terms: dominant, recessive, genotype, phenotype, homozygous, heterozygous, heredity, genetics, purebred, hybrid, codominant, ...
... the components of DNA the nitrogen bases & their complementary base pairs in DNA & RNA functions of tRNA & mRNA the laws of segregation & independent assortment the terms: dominant, recessive, genotype, phenotype, homozygous, heterozygous, heredity, genetics, purebred, hybrid, codominant, ...
Name_____________________ Date__________ Class
... substituted with (or exchanged for) a different nucleotide that may result in an altered sequence of amino acid during translation. occurs when a DNA gene is damaged or changed in such a way as to alter the genetic message carried by that gene. is a type of mutation involving the loss of genetic mat ...
... substituted with (or exchanged for) a different nucleotide that may result in an altered sequence of amino acid during translation. occurs when a DNA gene is damaged or changed in such a way as to alter the genetic message carried by that gene. is a type of mutation involving the loss of genetic mat ...
STUDY GUIDE for MICROBIAL GENETICS 1. Define the following
... What is the Rolling Circle Model of bacterial DNA replication? In other words, describe the bidirectionality of bacterial DNA replication. Describe transcription and translation. a. What is the function of RNA Polymerase? b. In prokaryotic cells, where does transcription occur? In eukaryotic cells, ...
... What is the Rolling Circle Model of bacterial DNA replication? In other words, describe the bidirectionality of bacterial DNA replication. Describe transcription and translation. a. What is the function of RNA Polymerase? b. In prokaryotic cells, where does transcription occur? In eukaryotic cells, ...
DNA Sequencing Sequence(s) carr(y) the information a cell needs
... Genetic markers can help link an inherited disease with the responsible gene. DNA segments close to each other on a chromosome tend to be inherited together. (They) are used to track the inheritance of a nearby gene that has not yet been identified, but whos approximate location is known. ...
... Genetic markers can help link an inherited disease with the responsible gene. DNA segments close to each other on a chromosome tend to be inherited together. (They) are used to track the inheritance of a nearby gene that has not yet been identified, but whos approximate location is known. ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis Worksheet
... Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of cells and are made up of long molecules of tightly coiled …………………. These molecules carry coded information that controls ………………… and the characteristics of the organism. A ………………… is a small section of a DNA molecule. DNA has a ………………… structure that is formed ...
... Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of cells and are made up of long molecules of tightly coiled …………………. These molecules carry coded information that controls ………………… and the characteristics of the organism. A ………………… is a small section of a DNA molecule. DNA has a ………………… structure that is formed ...
Microbiology Unit 3 Study Guide
... 5. Which enzyme makes RNA by reading a strand of DNA? 6. Which enzymes cut DNA in specific locations? 7. What occurs during transcription? 8. What are the steps to obtaining DNA fragments for gel electrophoresis? 9. Which enzyme reads DNA to make a new copy of DNA? 10. How has Escherichia coli been ...
... 5. Which enzyme makes RNA by reading a strand of DNA? 6. Which enzymes cut DNA in specific locations? 7. What occurs during transcription? 8. What are the steps to obtaining DNA fragments for gel electrophoresis? 9. Which enzyme reads DNA to make a new copy of DNA? 10. How has Escherichia coli been ...
to view and/or print October 2016 eDay assignment.
... Go to this website: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu Click: BASIC GENETICS (under GENETICS on left of screen) Under TOUR OF BASIC GENETICS, click on the three questions listed below. QUESTION 1 - WHAT ARE TRAITS? Play the video and answer the following questions: 1. Name two traits that are inhe ...
... Go to this website: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu Click: BASIC GENETICS (under GENETICS on left of screen) Under TOUR OF BASIC GENETICS, click on the three questions listed below. QUESTION 1 - WHAT ARE TRAITS? Play the video and answer the following questions: 1. Name two traits that are inhe ...
Name - EdWeb
... 1. What is DNA? __________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. What does DNA stand for? ________________________________________________________ 3. Why is DNA called a blueprint? ___________________ ...
... 1. What is DNA? __________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. What does DNA stand for? ________________________________________________________ 3. Why is DNA called a blueprint? ___________________ ...
No Slide Title
... 1. Introduction of foreign genetic material into a host organism. 2. Ability of the new genetic material to be transmitted to offspring of the host. 3. Potential of the new genetic material to be expressed in the host. ...
... 1. Introduction of foreign genetic material into a host organism. 2. Ability of the new genetic material to be transmitted to offspring of the host. 3. Potential of the new genetic material to be expressed in the host. ...
Genetic Engineering II
... particular piece of DNA in the test tube (rather than in living cells like E. coli). • Very useful if only have small quantities such as blood or semen. • Use temperature changes to separate the DNA strand, add primers, polymerase and ta-dah... new strand is made. ...
... particular piece of DNA in the test tube (rather than in living cells like E. coli). • Very useful if only have small quantities such as blood or semen. • Use temperature changes to separate the DNA strand, add primers, polymerase and ta-dah... new strand is made. ...
TRANSPOSABLE ELEMENTS IN BACTERIA Transposable
... IS elements consist of a relatively short (700-1500 bp) DNA segment flanked by a 10-40 bp inverted terminal repeat (ITR) sequence. A complete IS element codes for the protein (transposase) that catalyses the transposition event. Thus, transposition requires that the IS element carry a promoter recog ...
... IS elements consist of a relatively short (700-1500 bp) DNA segment flanked by a 10-40 bp inverted terminal repeat (ITR) sequence. A complete IS element codes for the protein (transposase) that catalyses the transposition event. Thus, transposition requires that the IS element carry a promoter recog ...
Transposons
... Mu integrates by transposition replicates when E. coli replicates During the lysogenic cycle, Mu remains integrated in E. coli chromosome ...
... Mu integrates by transposition replicates when E. coli replicates During the lysogenic cycle, Mu remains integrated in E. coli chromosome ...
View a technical slide presentation
... • The ZFP design platform is robust and highly specific. ZFPs can be designed and validated to bind to almost any sequence. • Because plant genomes are complex and highly redundant, a priori knowledge of target gene sequence and genome representation is critical. • Expression of ZFNs is necessary an ...
... • The ZFP design platform is robust and highly specific. ZFPs can be designed and validated to bind to almost any sequence. • Because plant genomes are complex and highly redundant, a priori knowledge of target gene sequence and genome representation is critical. • Expression of ZFNs is necessary an ...
Guided Notes-Genetic Code
... What is a gene? How does a gene specify the production of a protein? How many bases are needed to specify an amino acid What is the three base code known as? How many codons are there? How many code for amino acids? There are 61 codons that code for amino acids but only 20 amino acids. Explain Give ...
... What is a gene? How does a gene specify the production of a protein? How many bases are needed to specify an amino acid What is the three base code known as? How many codons are there? How many code for amino acids? There are 61 codons that code for amino acids but only 20 amino acids. Explain Give ...
Document
... • Extra credit: How many 3 letter words can you make from the letters A,T,G and C? • Answer: 64 ...
... • Extra credit: How many 3 letter words can you make from the letters A,T,G and C? • Answer: 64 ...
Research Questions
... methionine (Met), and tryptophan (Trp).Hydrophobic amino have side-chains that do not like to reside in an aqueous environment. For this reason, one generally finds these amino acids buried within the hydrophobic core of the protein, or within the lipid portion of the membrane. Hydrophilic amino aci ...
... methionine (Met), and tryptophan (Trp).Hydrophobic amino have side-chains that do not like to reside in an aqueous environment. For this reason, one generally finds these amino acids buried within the hydrophobic core of the protein, or within the lipid portion of the membrane. Hydrophilic amino aci ...