Nelson Bio 12 Ch. 4 – DNA : The Molecular Basis of Life
... nucleic acid contained deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group and 4 nitrogenous bases He didn’t know the molecular arrangement but he did know that the one sugar, one phosphate and one base linked together He called this unit a nucleotide. ...
... nucleic acid contained deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group and 4 nitrogenous bases He didn’t know the molecular arrangement but he did know that the one sugar, one phosphate and one base linked together He called this unit a nucleotide. ...
DNA DNA Structure ~ The Specifics
... instructions for the cell. The sequence of chemicals is unique for every individual. ...
... instructions for the cell. The sequence of chemicals is unique for every individual. ...
6.4 Manipulating the Genome - Hutchison
... mammals, but plasmid vectors are not. • A cold virus is a good choice to target lung cells but not bone cells. ...
... mammals, but plasmid vectors are not. • A cold virus is a good choice to target lung cells but not bone cells. ...
20.1 Structural Genomics Determines the DNA Sequences of Entire
... a. Orthologs are homologous sequences; paralogs are analogous sequences. b. Orthologs are more similar than paralogs. c. Orthologs are in the same organism; paralogs are in different organisms. d. Orthologs are in different organisms; paralogs are in the same organism. ...
... a. Orthologs are homologous sequences; paralogs are analogous sequences. b. Orthologs are more similar than paralogs. c. Orthologs are in the same organism; paralogs are in different organisms. d. Orthologs are in different organisms; paralogs are in the same organism. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 4. Which gene is associated with obesity? a) FTO b) HNF ...
... 4. Which gene is associated with obesity? a) FTO b) HNF ...
DNA
... 3 scientists who won the Nobel Prize by understanding the 3-deminsional structure of DNA ...
... 3 scientists who won the Nobel Prize by understanding the 3-deminsional structure of DNA ...
Recombinant DNA and Cloning The Impact of Biotechnology
... GloFish, marketed as the world’s first GM-pet ...
... GloFish, marketed as the world’s first GM-pet ...
DNA Nucleotide Chargaff`s Rule Double
... before the final mRNA strand is made. These parts are spliced together to create the final mRNA strand. The synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template. A long chain of amino acids that makes proteins. A collection of codons of mRNA, each of which directs the incorporation of a particular amino ...
... before the final mRNA strand is made. These parts are spliced together to create the final mRNA strand. The synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template. A long chain of amino acids that makes proteins. A collection of codons of mRNA, each of which directs the incorporation of a particular amino ...
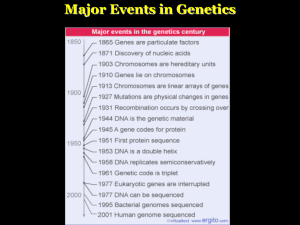
Major Events in Genetics
... Properties of the genetic material: -Potentially it contains a huge amount of information -The information can be translated in a phenotype. -The information can be copied in a faithfull manner ...
... Properties of the genetic material: -Potentially it contains a huge amount of information -The information can be translated in a phenotype. -The information can be copied in a faithfull manner ...
Adapted
... 1. Plant wound phenolics sense by VirA signal passed to VirG T-DNA excise 2. Phenolics plant wound sense by VirA signal passed to VirG T-DNA excise 3. Plant wound phenolics sense by VirG signal passed to VirA T-DNA excise 4. Plant wound Signal passed to VirG phenolics sense ...
... 1. Plant wound phenolics sense by VirA signal passed to VirG T-DNA excise 2. Phenolics plant wound sense by VirA signal passed to VirG T-DNA excise 3. Plant wound phenolics sense by VirG signal passed to VirA T-DNA excise 4. Plant wound Signal passed to VirG phenolics sense ...
May 4, 2004 B4730/5730 Plant Physiological Ecology
... expression • Gene expression can be modified at any point between DNA and final protein • Control of gene expression allows development and response to environment ...
... expression • Gene expression can be modified at any point between DNA and final protein • Control of gene expression allows development and response to environment ...
DNA
... Genes are like the chapters in the books (Humans have Between 25,000 and 80,000 genes – research is still ongoing!) ...
... Genes are like the chapters in the books (Humans have Between 25,000 and 80,000 genes – research is still ongoing!) ...
Glossary of Terms – DNA and the production of proteins
... Structures found in nucleus which carry genetic information Molecule, found in the nucleus which carries the genetic code Strand of DNA which codes for a protein Subunit of DNA molecule which consists of a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar and a base Parts of the DNA structure which pair up with on ...
... Structures found in nucleus which carry genetic information Molecule, found in the nucleus which carries the genetic code Strand of DNA which codes for a protein Subunit of DNA molecule which consists of a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar and a base Parts of the DNA structure which pair up with on ...
Type of sugar
... a cell. It is made up of millions of tiny subunits called ____________________. In each nucleotide, there is a ______________, a phosphate, and a ____________________ base (_______________, guanine, ______________, cytosine). When connected, these nucleotides form the shape of DNA, a _______________ ...
... a cell. It is made up of millions of tiny subunits called ____________________. In each nucleotide, there is a ______________, a phosphate, and a ____________________ base (_______________, guanine, ______________, cytosine). When connected, these nucleotides form the shape of DNA, a _______________ ...
Genetic Engineering
... The simple addition, deletion, or manipulation of a single trait in an organism to create a desired change. ...
... The simple addition, deletion, or manipulation of a single trait in an organism to create a desired change. ...
Learning Guide:
... 5. Explain what would happen to the process of gene expression if the gene for RNA polymerase was mutated. 6. Each amino acid has a tRNA synthetase enzyme that is responsible for attaching it to a tRNA molecule. Explain what would happen if there was a mutation in the gene encoding one of these enzy ...
... 5. Explain what would happen to the process of gene expression if the gene for RNA polymerase was mutated. 6. Each amino acid has a tRNA synthetase enzyme that is responsible for attaching it to a tRNA molecule. Explain what would happen if there was a mutation in the gene encoding one of these enzy ...
Chromosomes Key - Iowa State University
... 7. The DNA sequence at the end of chromosomes that consists of -CCC(A/T)- repeats is called what? Why are these important? Telomere – stabilize chromosome; play role in aging ...
... 7. The DNA sequence at the end of chromosomes that consists of -CCC(A/T)- repeats is called what? Why are these important? Telomere – stabilize chromosome; play role in aging ...
Name Date
... Part 3: Using the putting it together section, click on the base pairing interactive section and follow the instruction on the screen to determine the structure of DNA. Provide a diagram of DNA, which shows the general shape of the DNA molecule with the nitrogen bases (A, T, C and G), sugar and phos ...
... Part 3: Using the putting it together section, click on the base pairing interactive section and follow the instruction on the screen to determine the structure of DNA. Provide a diagram of DNA, which shows the general shape of the DNA molecule with the nitrogen bases (A, T, C and G), sugar and phos ...
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) - UMB Biology-Resources
... DNA Live replication takes much longer Only requires a small amount of DNA (ng) Many types of PCR ...
... DNA Live replication takes much longer Only requires a small amount of DNA (ng) Many types of PCR ...
What is a protein?
... Transcription. (The DNA code is transcribed or copied into RNA.) •In RNA, _______ and ________ are paired together and __________ and __________ are paired together. •Many copies of the ___________________ are made and leave the ______________________. •The ______________________ binds with a riboso ...
... Transcription. (The DNA code is transcribed or copied into RNA.) •In RNA, _______ and ________ are paired together and __________ and __________ are paired together. •Many copies of the ___________________ are made and leave the ______________________. •The ______________________ binds with a riboso ...
Chromosomes, genes, alleles, and mutation
... • Humans have 23 pairs • Prokaryotes only have one chromosome and DNA is not associated with proteins ...
... • Humans have 23 pairs • Prokaryotes only have one chromosome and DNA is not associated with proteins ...
Assignment 3 - OpenWetWare
... the 17th nucleotide of the gene for the -chain of hemoglobin changes the codon GAG (for glutamic acid) to GTG (which encodes valine), leading to the 6th amino acid in the protein being converted to valine instead of glutamic acid. Please introduce single base-pair mutations (i.e. replacement of A ...
... the 17th nucleotide of the gene for the -chain of hemoglobin changes the codon GAG (for glutamic acid) to GTG (which encodes valine), leading to the 6th amino acid in the protein being converted to valine instead of glutamic acid. Please introduce single base-pair mutations (i.e. replacement of A ...