Supercourse - Scientific Basis for Genetics Part II
... appropriate amino acid to the protein – Link between mRNA and protein – Part of the ribosomes – Involved with translation by helping to align the mRNAs and tRNAs ...
... appropriate amino acid to the protein – Link between mRNA and protein – Part of the ribosomes – Involved with translation by helping to align the mRNAs and tRNAs ...
GOALS OF THE HUMAN GENOME PROJECT
... appropriate amino acid to the protein – Link between mRNA and protein – Part of the ribosomes – Involved with translation by helping to align the mRNAs and tRNAs ...
... appropriate amino acid to the protein – Link between mRNA and protein – Part of the ribosomes – Involved with translation by helping to align the mRNAs and tRNAs ...
Document
... 5) cDNA is made from mRNA by the enzyme______________________ 6a) Double stranded cDNA for a protein coding gene usually has what three identifiable regions: ___________ ___________ _____________ 6b) Must these three regions equate to three exons? (yes, no –circle one) 7) The triplet code for transl ...
... 5) cDNA is made from mRNA by the enzyme______________________ 6a) Double stranded cDNA for a protein coding gene usually has what three identifiable regions: ___________ ___________ _____________ 6b) Must these three regions equate to three exons? (yes, no –circle one) 7) The triplet code for transl ...
Review–Protein Synthesis 15
... 10. Given the mRNA sequence, A C G C C G U A A U C A , determine how many amino acids long the protein will be. 11. What 2 types of RNA are involved in Protein Synthesis and describe their function. a. b. 12. What would the anti-codon of tRNA look like if the mRNA is CCG? ...
... 10. Given the mRNA sequence, A C G C C G U A A U C A , determine how many amino acids long the protein will be. 11. What 2 types of RNA are involved in Protein Synthesis and describe their function. a. b. 12. What would the anti-codon of tRNA look like if the mRNA is CCG? ...
Exam 4
... To keep the two chains of a DNA molecule parallel, one large ____________________ base must be paired with one small ____________________ base across the middle. This large base/small base pairing occurs normally in DNA, but also occurs with a point mutation type known as a(n) ______________________ ...
... To keep the two chains of a DNA molecule parallel, one large ____________________ base must be paired with one small ____________________ base across the middle. This large base/small base pairing occurs normally in DNA, but also occurs with a point mutation type known as a(n) ______________________ ...
Gene!
... and&metabolism)&generally&proportional& to&genome&size& • DNA&is&“coding&gene&dense”& • Circular&DNA,&doesn't&need&telomeres& ...
... and&metabolism)&generally&proportional& to&genome&size& • DNA&is&“coding&gene&dense”& • Circular&DNA,&doesn't&need&telomeres& ...
Restriction Enzymes by Dr. Ty C.M. Hoffman
... The table shows just a sample of the many restriction endonucleases that have been discovered (and the bacterial species in which they were discovered). While restriction endonucleases are naturally used by ...
... The table shows just a sample of the many restriction endonucleases that have been discovered (and the bacterial species in which they were discovered). While restriction endonucleases are naturally used by ...
Chapter 20: DNA Technology and Genomics
... 20.6 The public consortium followed a hierarchy of three stages: (1) genetic (linkage) mapping that established about 200 markers/chromosome; (2) physical mapping that clones and ordered smaller and smaller overlapping fragments (using YAC or BAC vectors for cloning the large fragments); and (3) DNA ...
... 20.6 The public consortium followed a hierarchy of three stages: (1) genetic (linkage) mapping that established about 200 markers/chromosome; (2) physical mapping that clones and ordered smaller and smaller overlapping fragments (using YAC or BAC vectors for cloning the large fragments); and (3) DNA ...
Created with Sketch. Student activity
... 1. Decide in your group which lollies will be the bases (remember there are four sorts of these), the phosphate groups and the sugar. 2. Use the toothpicks and florist wire as bonds to hold parts together, just like in the real DNA molecule. A DNA molecule has two strands – how will you join the str ...
... 1. Decide in your group which lollies will be the bases (remember there are four sorts of these), the phosphate groups and the sugar. 2. Use the toothpicks and florist wire as bonds to hold parts together, just like in the real DNA molecule. A DNA molecule has two strands – how will you join the str ...
biomolecule computer activity - Coach Blair`s Biology Website
... The _____ structure of a protein refers to the folding caused by hydrogen bonding between amino and carboxyl groups within the same molecule, and usually leads to the formation of beta-pleated-sheets and alpha-helices. The _____ structure of a protein refers to the complex folding caused by interact ...
... The _____ structure of a protein refers to the folding caused by hydrogen bonding between amino and carboxyl groups within the same molecule, and usually leads to the formation of beta-pleated-sheets and alpha-helices. The _____ structure of a protein refers to the complex folding caused by interact ...
General
... At a low cutoff value there are substantial amount of low scoring sequences thus DLGM is low. At a high cutoff even the high scoring sequences are not being used thus ...
... At a low cutoff value there are substantial amount of low scoring sequences thus DLGM is low. At a high cutoff even the high scoring sequences are not being used thus ...
DNA Replication: The Details
... 1. What role does the enzyme helicase play in DNA replication? 2. What does the enzyme DNA polymerase III do? 3. What is the difference between the leading strand and the lagging strand? Which strand is made in pieces? 4. What is the name of these pieces? What is the name of the enzyme that attaches ...
... 1. What role does the enzyme helicase play in DNA replication? 2. What does the enzyme DNA polymerase III do? 3. What is the difference between the leading strand and the lagging strand? Which strand is made in pieces? 4. What is the name of these pieces? What is the name of the enzyme that attaches ...
No Slide Title
... to the high gene copy number, up to 100 000 compared with single-copy nuclear genes. And there does not seem to be gene-silencing and other instability that plague nuclear transformation. The gene product is retained inside the chloroplasts or can in principle be targeted to a specific compartment i ...
... to the high gene copy number, up to 100 000 compared with single-copy nuclear genes. And there does not seem to be gene-silencing and other instability that plague nuclear transformation. The gene product is retained inside the chloroplasts or can in principle be targeted to a specific compartment i ...
rna (ribonucleic acid) - Social Circle City Schools
... • All traits you have due to proteins of amino acids • Genes contain “blueprints” to make protein • Ribosomes are site of protein synthesis • RNA reads blueprints & makes protein ...
... • All traits you have due to proteins of amino acids • Genes contain “blueprints” to make protein • Ribosomes are site of protein synthesis • RNA reads blueprints & makes protein ...
Chapter 28
... Centromeres in higher eukaryotic chromosomes contain large amounts of repetitive DNA. The function of the repetitive DNA is not known. ...
... Centromeres in higher eukaryotic chromosomes contain large amounts of repetitive DNA. The function of the repetitive DNA is not known. ...
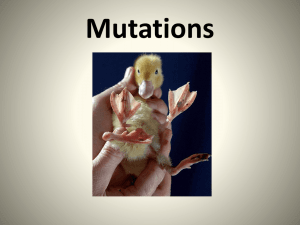
Mutations
... 1. Chromosomal mutations: -entire chromosomes is affected therefore many genes are involved resulting in the most severe forms of mutations. A baby can be born with an extra chromosome or missing one chromosome. -Example: Down Syndrome Turner Syndrome ...
... 1. Chromosomal mutations: -entire chromosomes is affected therefore many genes are involved resulting in the most severe forms of mutations. A baby can be born with an extra chromosome or missing one chromosome. -Example: Down Syndrome Turner Syndrome ...
Bis2A 8.2 The Flow of Genetic Information
... Energy Story is simply a rubric for describing a process) and its role in the expression of genetic information. We focus on problems and questions associated with transcription and describe how the process is used by Nature to create a variety of functional RNA molecules (that may have various stru ...
... Energy Story is simply a rubric for describing a process) and its role in the expression of genetic information. We focus on problems and questions associated with transcription and describe how the process is used by Nature to create a variety of functional RNA molecules (that may have various stru ...
DNA Fingerprinting of Bacterial Communities
... • Targets gene for ribosomal RNA (16S rDNA) • Make many DNA copies of the gene for the entire community DNA using modified PCR • Cut amplified DNA with restriction enzyme • Slight variations in 16S rDNA sequence among the different organisms results in different ...
... • Targets gene for ribosomal RNA (16S rDNA) • Make many DNA copies of the gene for the entire community DNA using modified PCR • Cut amplified DNA with restriction enzyme • Slight variations in 16S rDNA sequence among the different organisms results in different ...
Ch 17 From Gene to Protei
... c. the 5' caps are removed from the mRNA. d. the DNA introns are removed from the template. e. DNA nucleases have isolated the transcription unit. 2. All of the following are true of a codon except? a. It consists of three nucleotides. b. It may code for the same amino acid as another codon. c. It n ...
... c. the 5' caps are removed from the mRNA. d. the DNA introns are removed from the template. e. DNA nucleases have isolated the transcription unit. 2. All of the following are true of a codon except? a. It consists of three nucleotides. b. It may code for the same amino acid as another codon. c. It n ...
No Slide Title
... orders on the basis of their mechanistic features, sequence organization, and reverse transcriptase phylogeny: LTR retrotransposons, DIRS-like elements, Penelope-like elements, LINEs, and SINEs. ...
... orders on the basis of their mechanistic features, sequence organization, and reverse transcriptase phylogeny: LTR retrotransposons, DIRS-like elements, Penelope-like elements, LINEs, and SINEs. ...
PCR questions
... 3. What is the purpose of heating the DNA sample to 94-96 C? 4. What is the process of adding primers called? What kind of bond forms between the primers and the DNA? ...
... 3. What is the purpose of heating the DNA sample to 94-96 C? 4. What is the process of adding primers called? What kind of bond forms between the primers and the DNA? ...
Sc9 - a 3.1(teacher notes)
... Both genes in a pair carry DNA instructions for the same thing Specific characteristic genes occupy matching locations on the two chromosomes DNA code may not be exactly the same in both locations ...
... Both genes in a pair carry DNA instructions for the same thing Specific characteristic genes occupy matching locations on the two chromosomes DNA code may not be exactly the same in both locations ...
Chapter 16
... Evolution of the toe • Toes are short, which make humans great long distance runners • Short toes are great for push off during running (toes are for balance too) • The pinky toes – are not used for running…so it may be possible that people may start being born without them… ...
... Evolution of the toe • Toes are short, which make humans great long distance runners • Short toes are great for push off during running (toes are for balance too) • The pinky toes – are not used for running…so it may be possible that people may start being born without them… ...