Chapter 13-15 Essential Knowledge
... c. Excision of introns (why doesn’t this happen in prokaryotes?) 8. Describe a genetic mutation and explain when it is beneficial and when it is harmful. 9. How do external factors (radiation, reactive chemicals) cause DNA mutations? 10. Describe the role of promoter, terminators and enhancers in ge ...
... c. Excision of introns (why doesn’t this happen in prokaryotes?) 8. Describe a genetic mutation and explain when it is beneficial and when it is harmful. 9. How do external factors (radiation, reactive chemicals) cause DNA mutations? 10. Describe the role of promoter, terminators and enhancers in ge ...
Chapter 21: Genomes & Their Evolution 1. Sequencing & Analyzing Genomes
... Mobile DNA elements that can be copied & inserted Elsewhere in the genome. • the transposon encodes the enzyme transposase which can copy transposon sequence and randomly insert elsewhere ...
... Mobile DNA elements that can be copied & inserted Elsewhere in the genome. • the transposon encodes the enzyme transposase which can copy transposon sequence and randomly insert elsewhere ...
Is an inducible operon normally off or on?
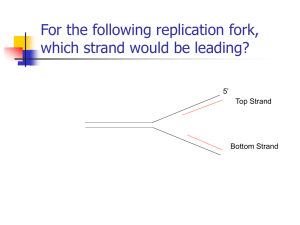
... Put the following enzymes in order for DNA replication ...
... Put the following enzymes in order for DNA replication ...
My Dinosaur
... • This uses the genes nucleotide sequence for the genetic structure needed • The DNA sequence allows scientist to have defined fragments of DNA, which is greatly needed in the cloning process ...
... • This uses the genes nucleotide sequence for the genetic structure needed • The DNA sequence allows scientist to have defined fragments of DNA, which is greatly needed in the cloning process ...
DNA
... Importance of Base Sequences • Sequence = order of bases • Sequence of bases determines the proteins made by the cell • We can also use sequence to determine: – How closely 2 organisms are related – If 2 people are related (paternity) – If crime scene DNA matches suspect’s DNA ...
... Importance of Base Sequences • Sequence = order of bases • Sequence of bases determines the proteins made by the cell • We can also use sequence to determine: – How closely 2 organisms are related – If 2 people are related (paternity) – If crime scene DNA matches suspect’s DNA ...
Applying Our Knowledge of Genetics
... • Gene therapy involves the insertion of a properly working gene into a patient that has a faulty gene in hopes that the new, healthy gene could be used to cure the disorder. • A vector, or DNA delivery system, would need to be used to insert the “foreign” DNA into the patient’s cells. • Some vector ...
... • Gene therapy involves the insertion of a properly working gene into a patient that has a faulty gene in hopes that the new, healthy gene could be used to cure the disorder. • A vector, or DNA delivery system, would need to be used to insert the “foreign” DNA into the patient’s cells. • Some vector ...
Slide 1 - Brookwood High School
... DNA extraction – opening cell to separate DNA from rest of cell parts Restriction enzymes – used to cut DNA at specific points to make small fragments Gel electrophoresis – used to separate DNA fragments on the basis of their length ...
... DNA extraction – opening cell to separate DNA from rest of cell parts Restriction enzymes – used to cut DNA at specific points to make small fragments Gel electrophoresis – used to separate DNA fragments on the basis of their length ...
Leukaemia Section t(1;12)(p36;p13) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Myeloid disorders: one chronic myelogenous leukemia with t(9;22) and one refractory anemiia with excee of blasts in transformation. ...
... Myeloid disorders: one chronic myelogenous leukemia with t(9;22) and one refractory anemiia with excee of blasts in transformation. ...
2 - Blue Valley Schools
... the experiments they conducted in order to make their specific conclusions. 5. You should be able to name those scientists who contributed to our knowledge of DNA’s structure, as well as describe the general methods they used in order to make their specific conclusions. 6. You should know the monome ...
... the experiments they conducted in order to make their specific conclusions. 5. You should be able to name those scientists who contributed to our knowledge of DNA’s structure, as well as describe the general methods they used in order to make their specific conclusions. 6. You should know the monome ...
Unit I: Genes, Nucleic A...d Chromosomes - BioWiki
... Chapter 2 covers the structures of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and methods for analyzing them biochemically. Methods for isolating genes, such as recombinant DNA technology and the polymerase chain reaction, are discussed in Chapter 3. In addition, this chapter explores some of the insights into gen ...
... Chapter 2 covers the structures of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and methods for analyzing them biochemically. Methods for isolating genes, such as recombinant DNA technology and the polymerase chain reaction, are discussed in Chapter 3. In addition, this chapter explores some of the insights into gen ...
Chapter 2
... 9. Explain why Okazaki fragments must be synthesized along the lagging strand of DNA during replication. 10. There are 4 fundamental types of biomolecules found in cells: nucleic acids, lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins. Briefly describe some functions of proteins in the living cell. 11. Genes ar ...
... 9. Explain why Okazaki fragments must be synthesized along the lagging strand of DNA during replication. 10. There are 4 fundamental types of biomolecules found in cells: nucleic acids, lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins. Briefly describe some functions of proteins in the living cell. 11. Genes ar ...
Study Guide 2016-17 DNA
... Draw a single RNA subunit. Make sure to label the following: one nucleotide, nitrogenous base, sugar, phosphate group, covalent bonds, and hydrogen bonds. ...
... Draw a single RNA subunit. Make sure to label the following: one nucleotide, nitrogenous base, sugar, phosphate group, covalent bonds, and hydrogen bonds. ...
Bononformatics
... The difficult part was in figuring out which parts of the DNA strand were genes that had a specified outcome in the final human created by the genetic program. Much of the DNA strand is made up of junk material that serves no actual purpose, which makes figuring it out all the more difficult. Comput ...
... The difficult part was in figuring out which parts of the DNA strand were genes that had a specified outcome in the final human created by the genetic program. Much of the DNA strand is made up of junk material that serves no actual purpose, which makes figuring it out all the more difficult. Comput ...
DNA structure and replication Three key features needed for any
... the pairs of bases holding the chains together. The vertical line marks the fibre axis. …………….It ...
... the pairs of bases holding the chains together. The vertical line marks the fibre axis. …………….It ...
Microbial Genetics
... recombination In the same way that mutations can be beneficial, neutral or harmful, so is the recombination of incoming DNA New gene combinations are maintained if they provide the organism with a selective ...
... recombination In the same way that mutations can be beneficial, neutral or harmful, so is the recombination of incoming DNA New gene combinations are maintained if they provide the organism with a selective ...
EMS Lesson 4: Ladders of Life
... (Pre-Exhibit Visit) By constructing a paper model of a strand of DNA, students will show the importance of the sequencing of four nitrogen bases in the genetic code. ...
... (Pre-Exhibit Visit) By constructing a paper model of a strand of DNA, students will show the importance of the sequencing of four nitrogen bases in the genetic code. ...
Genome_Layout_Jodi (Page 3) - Genome: The Secret of How Life
... Objective: By constructing a paper model of a strand of DNA, students will show the importance of the sequencing of four nitrogen bases in the genetic code. ...
... Objective: By constructing a paper model of a strand of DNA, students will show the importance of the sequencing of four nitrogen bases in the genetic code. ...
nucleic acids definitions
... TRANSCRIPTION: First phase of protein synthesis when a segment of DNA codes for an mRNA. ...
... TRANSCRIPTION: First phase of protein synthesis when a segment of DNA codes for an mRNA. ...
Goal 3.05 Examine the Theory of Evolution by Natural
... 10.Stem cells are UNSPECIALIZED cells (have no assigned TISSUE) that can be used to repair damaged NERVE, MUSCLE, & LIVER cells. There is significant controversy over stem cells because scientists can get them from EMBRYOS. 11.An advantage of cloning is that it produces IDENTICAL organisms/ tissues ...
... 10.Stem cells are UNSPECIALIZED cells (have no assigned TISSUE) that can be used to repair damaged NERVE, MUSCLE, & LIVER cells. There is significant controversy over stem cells because scientists can get them from EMBRYOS. 11.An advantage of cloning is that it produces IDENTICAL organisms/ tissues ...
1. Adenine The Nitrogen Base in DNA that always pairs with
... 6. Cytosine The Nitrogen Base in DNA that always pairs with Guanine 7. Deoxyribose The sugar found in DNA 8. DNA A double-stranded nucleic acid that contains the genetic information for cell growth, division, and function 9. Double Helix The shape of DNA’s structure 10. Electrophoresis The method of ...
... 6. Cytosine The Nitrogen Base in DNA that always pairs with Guanine 7. Deoxyribose The sugar found in DNA 8. DNA A double-stranded nucleic acid that contains the genetic information for cell growth, division, and function 9. Double Helix The shape of DNA’s structure 10. Electrophoresis The method of ...
DNA Structure
... A always pairs with T, and G always pairs with C. The bases that pair with each other are called complementary bases. ...
... A always pairs with T, and G always pairs with C. The bases that pair with each other are called complementary bases. ...
day2
... • Eukaryotic cells- Intronless genes are rare (avg. # of introns in HG is 3-7, highest # is 234); dystrophin gene is > 2.4 Mb. ...
... • Eukaryotic cells- Intronless genes are rare (avg. # of introns in HG is 3-7, highest # is 234); dystrophin gene is > 2.4 Mb. ...
Viscous Drag in DNA Replication
... One of the original concerns about Watson and Crick’s proposal that DNA replication occurs by unzipping the double helix was that the energy required to overcome viscous effects in order to twist a very long cylinder in water would be far too large. In this problem, you will show that viscous effect ...
... One of the original concerns about Watson and Crick’s proposal that DNA replication occurs by unzipping the double helix was that the energy required to overcome viscous effects in order to twist a very long cylinder in water would be far too large. In this problem, you will show that viscous effect ...