Bioteh_Klonesana un in vivo inhenierija_2015
... a | Nuclease-induced double-strand breaks (DSBs) can lead to sequence insertion, nucleotide correction or change (red box) through homology-directed repair (HDR) in the presence of a donor DNA or a single-strand oligodeoxynucleotide (ssODN), both of which contain homology arms. DSBs can also be repa ...
... a | Nuclease-induced double-strand breaks (DSBs) can lead to sequence insertion, nucleotide correction or change (red box) through homology-directed repair (HDR) in the presence of a donor DNA or a single-strand oligodeoxynucleotide (ssODN), both of which contain homology arms. DSBs can also be repa ...
From DNA to proteins
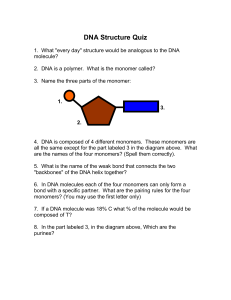
... ____________________________9. change in the DNA sequence ____________________________10. monomer that forms DNA and has a phosphate group, a sugar, and a nitrogencontaining base. ____________________________11. types of nucleotides that have a double ring structure ____________________________12. t ...
... ____________________________9. change in the DNA sequence ____________________________10. monomer that forms DNA and has a phosphate group, a sugar, and a nitrogencontaining base. ____________________________11. types of nucleotides that have a double ring structure ____________________________12. t ...
What is DNA?
... An organism that is genetically identical to the organism from which it is produced. What is a clone? ...
... An organism that is genetically identical to the organism from which it is produced. What is a clone? ...
分子生物學小考(一) 範圍ch3~ch7
... (C) Mitochondrial DNA encodes rRNAs and tRNAs. (D) The human mitochondrial genome is smaller than the yeast mitochondrial genome. ...
... (C) Mitochondrial DNA encodes rRNAs and tRNAs. (D) The human mitochondrial genome is smaller than the yeast mitochondrial genome. ...
Chapter 12
... 1. How many chromosomes are in a normal human cell? _______ In a normal human gamete? ________ 2. What is the product of meiosis? ...
... 1. How many chromosomes are in a normal human cell? _______ In a normal human gamete? ________ 2. What is the product of meiosis? ...
Text S1.
... whether in rice a fusion protein was created with both coding sequences or whether in maize a coding sequence was split to generate two individual proteins with separate functions. Ultimately, genetic studies will be necessary to reveal the functions of the element-encoded proteins and their require ...
... whether in rice a fusion protein was created with both coding sequences or whether in maize a coding sequence was split to generate two individual proteins with separate functions. Ultimately, genetic studies will be necessary to reveal the functions of the element-encoded proteins and their require ...
File - Ricci Math and Science
... 1.Which type of RNA is a copy from DNA? _________________ 2.How many main types of RNA are there? _________ 3.Unlike DNA, RNA contains _________________ 4.Which parts of the nucleotide are found in both DNA and RNA? ___________________________________ ________________________________________________ ...
... 1.Which type of RNA is a copy from DNA? _________________ 2.How many main types of RNA are there? _________ 3.Unlike DNA, RNA contains _________________ 4.Which parts of the nucleotide are found in both DNA and RNA? ___________________________________ ________________________________________________ ...
assignment DNA - UniMAP Portal
... 4. Why are mutation and recombination important in the process of natural selection and the evolution of organisms? ...
... 4. Why are mutation and recombination important in the process of natural selection and the evolution of organisms? ...
DNA - eduBuzz.org
... genetic instructions that the cells uses to make proteins. Proteins are made from amino acids joined together into chains. There are 20 different types of amino acids and the differences between proteins are due to the amino acids they contain. DNA is a sequence of bases and each set of three bases ...
... genetic instructions that the cells uses to make proteins. Proteins are made from amino acids joined together into chains. There are 20 different types of amino acids and the differences between proteins are due to the amino acids they contain. DNA is a sequence of bases and each set of three bases ...
this certificate as PDF
... This certificate is issued based on tests performed on DNA samples to PiGen by accredited veterinarians and/or FCI officials appointed by the persons that confirmed, on the date of DNA sampling, to be the respective owners of the pigeons with the ringnumbers mentioned in this certificate. ...
... This certificate is issued based on tests performed on DNA samples to PiGen by accredited veterinarians and/or FCI officials appointed by the persons that confirmed, on the date of DNA sampling, to be the respective owners of the pigeons with the ringnumbers mentioned in this certificate. ...
WS 12 Notes - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... from here to Eugene. Get it? Eu-Gene? ...
... from here to Eugene. Get it? Eu-Gene? ...
DNA STANDARDS FLIP BOOK
... FUNCTION of DNA. Be sure to label all of its parts. (Section 8.2 in your book – Fig. 8.7 & more labels) STANDARD: Students know the general structure and functions of DNA, RNA, and protein. PAGE 2: REPLICATION: Draw (Fig. 8.8) and define replication. Explain why replication is important. Explain wha ...
... FUNCTION of DNA. Be sure to label all of its parts. (Section 8.2 in your book – Fig. 8.7 & more labels) STANDARD: Students know the general structure and functions of DNA, RNA, and protein. PAGE 2: REPLICATION: Draw (Fig. 8.8) and define replication. Explain why replication is important. Explain wha ...
2.5 Genetics - Elaine Galvin
... To establish presence or absence of gene(s) The process of producing mRNA using DNA as a template. The process of making a protein using the mRNA code a template ...
... To establish presence or absence of gene(s) The process of producing mRNA using DNA as a template. The process of making a protein using the mRNA code a template ...
Document
... Average gene length: ~ 8,000 bp Average of 5-6 exons/gene Average exon length: ~200 bp Average intron length: ~2,000 bp ~8% genes have a single exon ...
... Average gene length: ~ 8,000 bp Average of 5-6 exons/gene Average exon length: ~200 bp Average intron length: ~2,000 bp ~8% genes have a single exon ...
Slide 1
... The exam was written based on 100 points. Dr. Cline will weight its contribution to your final grade based on the fact that the exam covers material presented in 6 classes. Important – please keep your answers short; confine your answers to the space provided; do not write on the back of any pages ! ...
... The exam was written based on 100 points. Dr. Cline will weight its contribution to your final grade based on the fact that the exam covers material presented in 6 classes. Important – please keep your answers short; confine your answers to the space provided; do not write on the back of any pages ! ...
BSC 219
... The study of evolution through the analysis of development Some genes in distantly related organisms can shape similar developmental pathways, but they may exert quite different effects. Many major evolutionary adaptations are through changes in the expression of genes that encode proteins that regu ...
... The study of evolution through the analysis of development Some genes in distantly related organisms can shape similar developmental pathways, but they may exert quite different effects. Many major evolutionary adaptations are through changes in the expression of genes that encode proteins that regu ...
Genetic code, transcription and translation
... of the coding region (i.e., at 5' end on sense strand) that tells the RNA polymerase both where to start and on which strand to continue synthesis. E.g. TATA box. • Terminator. Regulatory DNA region signaling end of transcription, at 3' end . • Transcription factor. A protein needed to initiate the ...
... of the coding region (i.e., at 5' end on sense strand) that tells the RNA polymerase both where to start and on which strand to continue synthesis. E.g. TATA box. • Terminator. Regulatory DNA region signaling end of transcription, at 3' end . • Transcription factor. A protein needed to initiate the ...
SI Worksheet 12
... 1. Your muscle and bone cells are different because a. they contain different sets of genes b. they are differentiated c. they contain different operons d. different genes are switched on and off in each e. they contain different histones 2. DNA packing - the way DNA is folded into chromosomes- affe ...
... 1. Your muscle and bone cells are different because a. they contain different sets of genes b. they are differentiated c. they contain different operons d. different genes are switched on and off in each e. they contain different histones 2. DNA packing - the way DNA is folded into chromosomes- affe ...