Transposable elements
... Transposable elements cause genetics changes and make important contributions to the evolution of genomes: •Insert into genes. •Insert into regulatory sequences; modify gene expression. •Produce chromosomal mutations. ...
... Transposable elements cause genetics changes and make important contributions to the evolution of genomes: •Insert into genes. •Insert into regulatory sequences; modify gene expression. •Produce chromosomal mutations. ...
Lecture
... note: two genes are homologs or they or not no such thing as %homology or “more homologous” ...
... note: two genes are homologs or they or not no such thing as %homology or “more homologous” ...
Review sheet
... 20. Use the genetic code chart from your packet to translate the sequence of mRNA below into its corresponding amino acids. List the amino acids in order on your answer sheet. Be sure to write the entire name of each amino acid; do not abbreviate them. mRNA: CCU CUC GAG AAU ...
... 20. Use the genetic code chart from your packet to translate the sequence of mRNA below into its corresponding amino acids. List the amino acids in order on your answer sheet. Be sure to write the entire name of each amino acid; do not abbreviate them. mRNA: CCU CUC GAG AAU ...
Chapter 19 - Biology Junction
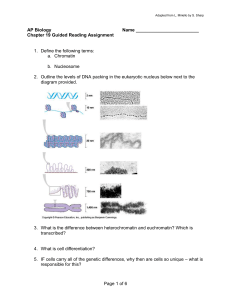
... 6. In the diagram below – highlight all of the potential locations for gene expression regulation in eukaryotic cells. How does this compare with prokaryotic cells? ...
... 6. In the diagram below – highlight all of the potential locations for gene expression regulation in eukaryotic cells. How does this compare with prokaryotic cells? ...
Making A DNA Model
... In the 1950’s James Watson and Francis Crick discovered the structure of the DNA molecule. They developed a model shaped like a double helix. This model helped introduce a whole new field of biology, often called molecular genetics, which in turn has led to areas as significant as genetic engineerin ...
... In the 1950’s James Watson and Francis Crick discovered the structure of the DNA molecule. They developed a model shaped like a double helix. This model helped introduce a whole new field of biology, often called molecular genetics, which in turn has led to areas as significant as genetic engineerin ...
8 th Grade Genes and Survival Test – Study Guide
... There is test on ________________________ that covers all of the concepts on this study guide. This completed guide is due on the day of the test or you receive a zero on it! Please use your notes and textbook to locate definitions and answers for all of the following vocabulary definitions. Read pa ...
... There is test on ________________________ that covers all of the concepts on this study guide. This completed guide is due on the day of the test or you receive a zero on it! Please use your notes and textbook to locate definitions and answers for all of the following vocabulary definitions. Read pa ...
Science - edl.io
... c) 3rd sentence = Explain HOW your evidence works d) 4th sentence = Summarize answer -OR- Second piece of evidence A) When cells make proteins, why do they make a copy of mRNA to send out of the nucleus to the ribosome? Why don’t they just send a piece of the original DNA, to make sure there can’t b ...
... c) 3rd sentence = Explain HOW your evidence works d) 4th sentence = Summarize answer -OR- Second piece of evidence A) When cells make proteins, why do they make a copy of mRNA to send out of the nucleus to the ribosome? Why don’t they just send a piece of the original DNA, to make sure there can’t b ...
Word Picture Definition Gene mRNA Base Uracil Ribosome tRNA
... c) 3rd sentence = Explain HOW your evidence works d) 4th sentence = Summarize answer -OR- Second piece of evidence A) When cells make proteins, why do they make a copy of mRNA to send out of the nucleus to the ribosome? Why don’t they just send a piece of the original DNA, to make sure there can’t b ...
... c) 3rd sentence = Explain HOW your evidence works d) 4th sentence = Summarize answer -OR- Second piece of evidence A) When cells make proteins, why do they make a copy of mRNA to send out of the nucleus to the ribosome? Why don’t they just send a piece of the original DNA, to make sure there can’t b ...
Chapter 10 Structure and Function of DNA
... How is DNA replication related to S- Phase? Primase Okazaki Fragments What is significant about the 3’-OH Why do chromosomes get shorter and shorter every round of replication? What are telomeres? What is telomerase? What happens if there is a mistake? What is the role of single-stranded binding pro ...
... How is DNA replication related to S- Phase? Primase Okazaki Fragments What is significant about the 3’-OH Why do chromosomes get shorter and shorter every round of replication? What are telomeres? What is telomerase? What happens if there is a mistake? What is the role of single-stranded binding pro ...
DNA
... change a codon to one that encodes a different amino acid and cause a small change in the protein produced. For example, sickle cell anemia is caused by a substitution which alters one amino acid in the protein responsible for ...
... change a codon to one that encodes a different amino acid and cause a small change in the protein produced. For example, sickle cell anemia is caused by a substitution which alters one amino acid in the protein responsible for ...
Answers11.february
... Physical mapping Requires large numbers of organisms Is always based on optical methods Can use DNA fragment libraries Uses polymorphic restriction sites Can use sequence tagged sites (STSs) ...
... Physical mapping Requires large numbers of organisms Is always based on optical methods Can use DNA fragment libraries Uses polymorphic restriction sites Can use sequence tagged sites (STSs) ...
DNA Replication Worksheet
... 1. Draw a wound (spiral) molecule of DNA. Use multiple colors for nitrogen bases, sugars and phosphates. Give your double helix the following sequence: ACCGTATTGATC ...
... 1. Draw a wound (spiral) molecule of DNA. Use multiple colors for nitrogen bases, sugars and phosphates. Give your double helix the following sequence: ACCGTATTGATC ...
MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS
... cells are removed; but ! Mutations in germ cells and embryos can cause developmental defects; mutations in adult cells can cause cancer ! The genetic code has apparently evolved to minimize the effects of mutation ...
... cells are removed; but ! Mutations in germ cells and embryos can cause developmental defects; mutations in adult cells can cause cancer ! The genetic code has apparently evolved to minimize the effects of mutation ...
GENE SEQUENCING - Amirkabir University of Technology
... • The fragments in a set are separated by gel electrophoresis (separation step). • New fluorescent dyes allow separation of all four fragments in a single lane on the gel. • The final base at the end of each fragment is identified (base-calling step). This process recreates the original sequence of ...
... • The fragments in a set are separated by gel electrophoresis (separation step). • New fluorescent dyes allow separation of all four fragments in a single lane on the gel. • The final base at the end of each fragment is identified (base-calling step). This process recreates the original sequence of ...
Questions11.february
... Physical mapping Requires large numbers of organisms Is always based on optical methods Can use DNA fragment libraries Uses polymorphic restriction sites Can use sequence tagged sites (STSs) ...
... Physical mapping Requires large numbers of organisms Is always based on optical methods Can use DNA fragment libraries Uses polymorphic restriction sites Can use sequence tagged sites (STSs) ...
What Is Gene cloning and How Is It Used? 1. Explain what is meant
... Define the term "restriction enzymes" and explain how they are used to insert genes into a vector. ...
... Define the term "restriction enzymes" and explain how they are used to insert genes into a vector. ...
DNA and Individuality
... • mRNA = AGUAAA codes for Serine +Lysine • If the T is deleted in the DNA, now is GUAAA • Ribosome will read GUA first which is for Valine ...
... • mRNA = AGUAAA codes for Serine +Lysine • If the T is deleted in the DNA, now is GUAAA • Ribosome will read GUA first which is for Valine ...
Name Date Class ______ DNA Replication Worksheet Use the
... 23. Copying part of a nucleotide sequence of DNA into a complementary sequence in RNA is called _________________________________. 24. An enzyme that binds to DNA during transcription is RNA _____________________________. 25. During the process of __________________________, the information carried ...
... 23. Copying part of a nucleotide sequence of DNA into a complementary sequence in RNA is called _________________________________. 24. An enzyme that binds to DNA during transcription is RNA _____________________________. 25. During the process of __________________________, the information carried ...
MITOCHONDRIA BIOLOGY - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... CRTA sequence (R = purine) within 20 bp of transcription start site. 2. Phage-like RNA polymerase – Single, large catalytic subunit – Small specificity factor protein ...
... CRTA sequence (R = purine) within 20 bp of transcription start site. 2. Phage-like RNA polymerase – Single, large catalytic subunit – Small specificity factor protein ...
Use the diagram to answer the questions to the right
... 23. Copying part of a nucleotide sequence of DNA into a complementary sequence in RNA is called _________________________________. 24. An enzyme that binds to DNA during transcription is RNA _____________________________. 25. During the process of __________________________, the information carried ...
... 23. Copying part of a nucleotide sequence of DNA into a complementary sequence in RNA is called _________________________________. 24. An enzyme that binds to DNA during transcription is RNA _____________________________. 25. During the process of __________________________, the information carried ...
... a. base. b. protein. c. gene. d. ribosome. _____ 3. Who discovered that the amount of adenine in DNA always equals the amount of thymine? a. Rosalind Franklin b. James Watson c. Erwin Chargaff d. Francis Crick _____ 4. What scientist made images of DNA by using X-ray diffraction? a. Rosalind Frankli ...